Load FindZebra Summary
Disclaimer:
FindZebra Search conducts a search using our specialized medical search engine.
FindZebra Summary uses the text completions API
(subject to OpenAI’s API data usage policies)
to summarize and reason about the search results.
The search is conducted in publicly available information on the Internet that we present “as is”.
You should be aware that FindZebra is not supplying any of the content in the search results.
FindZebra Summary is loading...
-
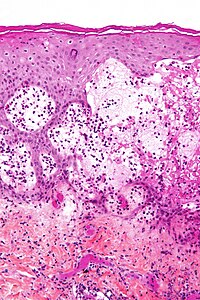
Pemphigoid Gestationis
Orphanet
Clinical description Pemphigoid gestationis (PG) Pemphoid gestationis (PG) typically presents during the second or third trimesters, although onset during the first trimester and postpartum is possible. ... Recurrence in subsequent pregnancies is common (35-50%), and is typically more severe with earlier onset. PG is associated with the autoimmune Graves' disease in the mother. ... PG is strongly associated with maternal MHC class II antigens haplotypes HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR4. Diagnostic methods Clinical and histological features are not specific to PG; therefore, additional tests are required for diagnosis. ... The disease can persist and converts to bullous pemphigoid (in less than 5% of patients). * European Reference Network
-
Skin Cancer In Horses
Wikipedia
XIV Congress. ^ a b c d e Valentine, Neoplasia , pg. 147. ^ a b Knottenbelt and McGarry, Sarcoids. , pg. 400. ^ a b c Valentine, "Neoplasia" pg. 149. ^ a b c d Torrontegui, B.O.; S. ... Retrieved August 11, 2011 . ^ Pascoe and Knottenbelt, Equine sarcoids. , pg. 247 ^ Pascoe and Knottenbelt. Equine sarcoids. , pg. 249. ^ a b c Pascoe and Knottenbelt. Equine sarcoids. pg. 251. ^ a b Knottenbelt, Derek C.; Donald F. ... Squamous cell carcinoma. , pg. 433. ^ Knight, C.G.; J. S. Munday; J. ... Pg. 148 ^ Rooney and Robertson. [1] , pg. 305 ^ Fleury, Catherine; Frederic Bérard; Agnés Leblond; Christine Faure; Nathalie Ganem; Luc Thomas (February 2000).
-
Purple Glove Syndrome
Wikipedia
Purple glove syndrome Specialty Dermatology Purple glove syndrome (PGS) is a poorly understood skin disease in which the extremities become swollen , discoloured and painful. [1] PGS is potentially serious, and may require amputation . PGS is most common among elderly patients and those receiving multiple large intravenous doses of the epilepsy drug phenytoin . [2] Compartment syndrome is a complication of PGS. Contents 1 Cause 2 Diagnosis 3 Treatment 4 References 5 External links Cause [ edit ] Purple glove syndrome is caused by the intravenous anticonvulsant phenytoin.
-
Pyoderma Gangrenosum
Orphanet
Pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) is a primarily sterile inflammatory neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by recurrent cutaneous ulcerations with a mucopurulent or hemorrhagic exudate. Epidemiology The exact prevalence of PG is unknown. The incidence has been estimated to range between 1 and 3.3 in 330,000. ... Management and treatment The treatment of PG is a challenge. Randomized, double-blind prospective multicenter trials for PG are not available. ... The combinations of steroids with sulfa drugs or immunosuppressants are used as steroid sparing modalities. Rapid improvement of PG has been obtained by anti-tumor necrosis alpha therapy used in Crohn's disease. ... Prognosis Despite recent advances in therapy, the prognosis of PG remains unpredictable.PSTPIP1, MEFV, NOD2, NLRP3, TCIRG1, SYN3, ELANE, GFI1, SRP54, GLI3, TNF, PAPPA, MTHFR, MAP6, JAK2, RAG1, MPO, JAK1, INSRR, DERL1, IL25, CD40, NELFCD, IL37, ACAD8, TRAF3IP2, CD40LG, USP15, CCR3, COL17A1, TYK2, GYPA, TIMP3, TG, IL5, SOAT1, CXCL8, PTPN6, CXCR1, NM, CXCR2, PRDM1, IL15, IL17A, LAD1, JAK3, ALB
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease 24
OMIM
The mean +/- standard error of the mean (SEM) serum DCR3 concentration increased from 84 +/- 37 pg/ml in healthy controls to 4,333 +/- 1,637 pg/ml in individuals with IBD carrying the major allelic variants, and 11,793 +/- 2,452 pg/ml in individuals with IBD carrying the minor allelic variants, (P less than 0.05 for IBD vs control, and within IBD for major vs minor allelic variants). The UK IBD Genetics Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (2009) performed a genomewide association scan in 2,361 ulcerative colitis (UC) cases and 5,417 controls followed by genotyping in an independent set of 2,321 UC cases and 4,818 controls, and found the strongest association (combined p = 8.5 x 10(-17)) at rs6017342, which maps within a recombination hotspot on 20q13 and is located 5 kb distal to the 3-prime UTR of the HNF4A gene (600281), within an expressed sequence tag (DB076868).
-
Fear Of Medical Procedures
Wikipedia
Formally, medical fear is defined as "any experience that involves medical personnel or procedures involved in the process of evaluating or modifying health status in traditional health care settings." [1] Contents 1 Classification 2 Fear of surgery 2.1 Children 2.2 Adults 3 Fear of dental work 3.1 Children 3.2 Adults 4 Fear of doctors and fear of needles 4.1 Fear of doctors 4.2 Fear of needles 5 Notes and references 5.1 Articles used 6 Further reading Classification [ edit ] Fear of medical procedures can be classified under a broader category of “blood, injection, and injury phobias”. This is one of five subtypes that classify specific phobias. [2] A specific phobia is defined as a “marked and persistent fear that is excessive or unreasonable, cued by the presence (or anticipation) of a specific object or situation.” [3] [4] Often these fears begin to appear in childhood, around the age of five to nine. [2] It is normal to become squeamish at the sight of blood, injury, or gross deformity, [5] but many overcome these fears by the time they reach adulthood. ... ISBN 0-8261-1427-X . ^ a b c d Specific Phobias: Clinical Applications of Evidence-Based Psychotherapy pg 5 ^ Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-IV; American Psychiatric Association, 1994) ^ Phobic Disorders and Panic in Adults: A guide to Assessment and Treatment pg 79 ^ Fears, Phobias, and Rituals: Panic, Anxiety and their Disorders pg 376 ^ Phobic Disorders and Panic in Adults: A guide to Assessment and Treatment pg 82 ^ a b Fears, Phobias, and Rituals: Panic, Anxiety and their Disorders pg 377 ^ Fears, Phobias, and Rituals: Panic, Anxiety and their Disorders pg 378 ^ Phobic Disorders and Panic in Adults: A guide to Assessment and Treatment pg 84 ^ Phobic Disorders and Panic in Adults: A guide to Assessment and Treatment pg 98-102 ^ Schmid, Markus; Wolf, Robert C; Freudenmann, Roland W; Schönfeldt-Lecuona, Carlos (2009-11-18). ... USA Today Magazine, 01617389, Feb96, Vol. 124, Issue 2609 ^ a b Fear of Cataract Operation in Aged Persons, Ritva Fagerstro:m Psychological Reports, 1993, 72, 1339-1346, pg.1339 ^ Fear of Cataract Operation in Aged Persons, Ritva Fagerstro:m Psychological Reports, 1993, 72, 1339-1346pg.1339 (Paddison, Strain, Strain & Strain, 1989) ^ Fear of Cataract Operation in Aged Persons, Ritva Fagerstro:m Psychological Reports, 1993, 72, 1339- 1346, pg. 1340 ^ Fear of Cataract Operation in Aged Persons, Ritva Fagerstro:m Psychological Reports, 1993, 72, 1339-1346, pg. 1342 ^ a b Fear of Cataract Operation in Aged Persons, Ritva Fagerstro:m Psychological Reports, 1993, 72, 1339-1349, pg. 1344 ^ Fear of Cataract Operation in Aged Persons, Ritva Fagerstro:m Psychological Reports, 1993, 72, 1339-1349, pg. 1345 ^ a b c Dental fear: Comparisons Between Younger and Older Adults, M. Michelle Rowe, PhD American Journal of Health Studies: 20(4) 2005 pg. 219-224 ^ a b c d Dental Fear in Children- a proposed model, H.R.
-
Duodenal Ulcer, Hyperpepsinogenemic I
OMIM
Human gastric mucosa contains 2 immunochemically distinct types of pepsinogens, I and II. Only pepsinogen I (PG I) is derived exclusively from the chief cells in the oxyntic glands of the gastric body and fundus. The level of PG I in the serum, as determined by radioimmunoassay, correlates with gastric secretory capacity, serves as a marker for the ulcer diathesis, and demonstrates heterogeneity, i.e., a bimodal distribution, in large groups of duodenal ulcer patients. Rotter et al. (1979) found autosomal dominant transmission of elevated serum PG I level in 2 large families with a prominent history of duodenal ulcer. An elevated PG I level identified genetically susceptible but clinically normal persons. About half of sibships with 2 or more cases of duodenal ulcer were found to segregate for high serum PG I. Rotter et al. (1982) did a variance component analysis of the distribution of serum pepsinogen I levels in normal individuals, using a maximum-likelihood method on entire pedigrees.
-
Abarognosis
Wikipedia
Abarognosis Other names Baragnosis, baroagnosis [1] Abarognosis () is type of cortical sensory defect [2] consisting of a loss of barognosis , the ability to detect the weight of an object held in the hand or to tell the difference in weight between two objects, [3] or more succinctly "Loss of the ability to sense weight". [4] This deficit may be caused by damage to the parietal lobe . [5] The term is from Greek "a" not, "baros" weight, "gnosis" knowledge. ... Notes [ edit ] ^ Dorland 2011, baragnosis ^ Black 1995, pg. 14 ^ abarognosis , Drugs.com , retrieved 2013-03-21 ^ "abarognosis" , The American Heritage® Stedman's Medical Dictionary , Houghton Mifflin , retrieved 2013-03-21 ^ Campbell 2012, pg. 554 Sources [ edit ] Black, Peter McLaren; Rossitch, Eugene (1995), "Neurological Diagnosis" , Neurosurgery: An Introductory Text (Google eBook), Oxford University Press , ISBN 9780195044492 , retrieved 2013-02-21 Buck, Carol J. (2013), "Section Index to Diseases and Injuries" , 2013 ICD-9-CM for Physicians (Google preview), Vol. 2 (Professional ed.), Elsevier Health Sciences , ISBN 9781455775033 , retrieved 2013-03-21 Campbell, William W. (2012), "36: Sensory Localization" , DeJong's The Neurologic Examination (Google eBook) (7th ed.), Lippincott Williams & Wilkins , ISBN 9781469817521 , retrieved 2013-03-21 Dorland (2011), Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (Google eBook) (32nd ed.), Elsevier Health Sciences, ISBN 9781455709854 , retrieved 2013-03-21 External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 9-CM : 781.99
-
Muscardine
Wikipedia
Principles And Techniques Of Silkworm Seed Production . Discovery Publishing House. 2004. pg. 277. ^ a b c d Lu, Y. Silkworm Diseases . FAO. 1991. pg. 37. ^ Mahr, S. Know Your Friends: The Entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana . ... Insect Pathology . Academic Press. 2012. pg. 433. ^ Chernin, L., et al. (1997). ... Canadian Journal of Microbiology 43(5) 440-46. ^ a b c White Muscardine Fungus. ... Effect of some natural pesticides on entomogenous muscardine fungi. Indian J Exp Biol. 30(5) 435-6. ^ Ravikumar, J., et al. Muscardine: a menace to silkworm in winter.
-
Pygmy
OMIM
Clinical Features Efe Pygmies from the Ituri forest of northeast Zaire have the shortest mean adult stature of any population on earth, with a mean adult male height of 4 feet, 8 inches, and a mean adult female height of 4 feet, 5 inches (Diamond, 1991). Biochemical Features Rimoin et al. (1969) found that African Pygmies failed to respond to exogenous human growth hormone (GH; 139250) in the presence of normal serum levels of growth hormone and somatomedin, or insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1; 147440), suggesting a defect in end-organ responsiveness to one or both hormones. ... In a longitudinal growth study comparing Efe Pygmy children and children of non-Pygmy rural African farmers of known age from birth to age 5 years, Bailey (1991) found that suppression of Pygmy growth occurs from birth, not solely at puberty. Bailey (1991) emphasized that previous studies of Pygmy growth were of individuals of estimated, not known, age. In 5 of 7 Pygmies, Geffner et al. (1995) found a decrease in IGF1 levels compared to controls. ... Animal Model The mouse mutation called pygmy (pg), a recessive that maps to mouse chromosome 10, has only similarity of name to the human condition. In pg mice, Xiang et al. (1990) identified a mutation in the pg gene (HMGA2; 600698).
-
Whale Oil
Wikipedia
They yield plenty of high-quality oil and whalebone , [5] and as a result, they were hunted nearly to extinction. ... University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-03973-5 . ^ a b Robert Lloyd Webb (1988). ... A Practical Treatise on Friction, Lubrication, Fats and Oils . pg 23 ^ Frank Sims (1999). Engineering Formulas Interactive: Conversions, Definitions, and Tables . pg 132 ^ J. ... Goldsmith (1921). Table of Refractive Indices . pg 259 ^ Video on YouTube ^ Wilson Heflin (2004). Herman Melville's Whaling Years . pg 232 ^ "Thefreemanonline.org" . www.thefreemanonline.org . ^ "The "Whale Oil Myth " " .
-
Lymphoepithelial Lesion
Wikipedia
It may refer to a benign lymphoepithelial lesion of the parotid gland or benign lymphoepithelial lesion of the lacrimal gland , or may refer to the infiltration of malignant lymphoid cells into epithelium, in the context of primary gastrointestinal lymphoma. [1] In the context of GI tract lymphoma, it is most often associated with MALT lymphomas . [1] See also [ edit ] Gastric lymphoma MALT lymphoma References [ edit ] ^ a b Papadaki, L.; Wotherspoon, AC.; Isaacson, PG. (Nov 1992). "The lymphoepithelial lesion of gastric low-grade B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT): an ultrastructural study". Histopathology . 21 (5): 415–21. doi : 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb00425.x .
-
Ménétrier's Disease
Wikipedia
Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 2 Cause 3 Pathology 4 Diagnosis 5 Treatment 6 Epidemiology 7 References 8 External links Signs and symptoms [ edit ] Individuals with the disease present with upper abdominal pain (epigastric), at times accompanied by nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite , edema , weakness, and weight loss. A small amount of gastrointestinal bleeding may occur, which is typically due to superficial mucosal erosions; large volume bleeding is rare. [2] 20% to 100% of patients, depending on time of presentation, develop a protein-losing gastropathy accompanied by low blood albumin and edema . [2] [3] Symptoms and pathological features of Ménétrier disease in children are similar to those in adults, but disease in children is usually self-limited and often follows respiratory infection. [4] Cause [ edit ] The cause of Ménétrier disease is unknown, but it has been associated with HCMV infection in children and H. pylori infections in adults. [5] Additionally, increased TGF-α has been noted in the gastric mucosa of patients with the disease. [1] Pathology [ edit ] With Ménétrier disease, the stomach is characterized by large, tortuous gastric folds in the fundus and body, with the antrum generally spared, giving the mucosa a cobblestone or cerebriform (brain-like) appearance. [5] Histologically, the most characteristic feature is massive foveolar hyperplasia (hyperplasia of surface and glandular mucous cells). [3] The glands are elongated with a corkscrew-like appearance and cystic dilation is common. ... Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring reveals hypochlorhydria or achlorhydria, and a chromium-labelled albumin test reveals increased GI protein loss. [5] Serum gastrin levels will be within normal limits. ... Epidemiology [ edit ] The average age of onset is 40 to 60 years, and men are affected more often than women. [2] Risk of gastric adenocarcinoma is increased in adults with Ménétrier disease. [4] [5] References [ edit ] ^ a b Coffey RJ; et al. (2007). ... ISBN 978-0071802154 . ^ a b c d e Harrison's Principle of Internal Medicine, 18e, pg 2459 ^ a b c d Robbins and Cotran, Pathological Basis of Disease, 8e, pg 782 ^ a b c d Kumar et al., Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2e , pg 768 ^ Burdick JS, Chung E, Tanner G, et al.
-
Mixed Transcortical Aphasia
Wikipedia
Retrieved March 22, 2015, from: https://books.google.com/books?id=wM9sBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA198 ^ Nussbaum, P. (1997). Handbook of neuropsychology and aging (p.305). ... Retrieved March 22, 2015 from https://books.google.com/books?id=QxR6EaATaUwC&pg=PA545 ^ LaPointe, L (2005). Aphasia and related neurogenic language disorders (3rd ed., p.117). ... Retrieved March 22, 2015, from https://books.google.com/books?id=PgRbFxayeQwC&pg=PA181 ^ a b LaPointe, L (2005). Aphasia and related neurogenic language disorders (3rd ed., p.117). ... Retrieved March 22, 2015, from https://books.google.com/books?id=PgRbFxayeQwC&pg=PA181 ^ a b c d e f g Farias, et al, (2006). ... Journal of Internal Medicine . 249 (5): 413–422. doi : 10.1046/j.1365-2796.2001.00812.x .
-
Blueberry Muffin Baby
Wikipedia
Contents 1 Causes 2 Diagnosis 3 See also 4 References 5 External links Causes [ edit ] The condition was originally considered characteristic of rubella , but is now considered to be potentially associated with many other conditions, [4] such as cytomegalovirus , [5] metastatic neuroblastoma , and Congenital Leukemia. ... PMID 18700111 . ^ Gaffin JM, Gallagher PG (November 2007). "Picture of the month.
-
Glucagonoma
Orphanet
Serum glucagon levels are markedly elevated (>500 pg/mL) and levels of more than 1000 pg/mL are considered diagnostic if the patient also displays features of glucagonoma syndrome.
-
Oslam Syndrome
Wikipedia
Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 2 Diagnosis 3 Treatment 4 See also 5 References 6 External links Signs and symptoms [ edit ] Bone cancer Curved fifth fingers (clinodactyly) with brachymesophalangy (shortened phalanges of the toes and/or fingers (digits)) Absence of one digital ray of the foot (a digit and corresponding metacarpal or metatarsal bone) Bilateral radioulnar synostosis Enlarged red blood cells Dental decay Short stature Diagnosis [ edit ] This section is empty. ... Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer , Springer, pg. 558. External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : C41.9 OMIM : 165660 MeSH : C537138 External resources Orphanet : 2760 This genetic disorder article is a stub .
-
Pyoderma Gangrenosum-Acne-Suppurative Hidradenitis Syndrome
Orphanet
A rare skin disease belonging to the spectrum of autoinflammatory syndromes characterized by the triad of pyoderma gangrenosum (PG), suppurative hidradenitis (SH) and acne.
-
Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia, Autosomal Dominant
OMIM
Metabolic studies revealed elevated PTH to 306.1 pg/ml (normal, 15-65 pg/ml) and serum alkaline phosphatase was 1491 IU/ L (normal, less than 455 IU/L). ... Parathyroid hormone was normal in the patient reported by Schaefer et al. (1986) and elevated in a 5-year-old boy reported by Brueton and Winter (1990).
-
Merciful Anosmia
Wikipedia
ISBN 9788131223642 . ^ "Atrophic rhinitis" . PG Blazer . Retrieved 14 March 2013 .