Load FindZebra Summary
Disclaimer:
FindZebra Search conducts a search using our specialized medical search engine.
FindZebra Summary uses the text completions API
(subject to OpenAI’s API data usage policies)
to summarize and reason about the search results.
The search is conducted in publicly available information on the Internet that we present “as is”.
You should be aware that FindZebra is not supplying any of the content in the search results.
FindZebra Summary is loading...
-
Leukemia, Acute Myeloid
OMIM
Fong et al. (2015) used primary mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells immortalized with the fusion protein MLL-AF9 (see 159555) to generate several single-cell clones that demonstrated resistance, in vitro and in vivo, to the prototypical bromodomain and extra terminal protein (BET) inhibitor I-BET. Resistance to I-BET conferred cross-resistance to chemically distinct BET inhibitors such as JQ1, as well as resistance to genetic knockdown of BET proteins. ... Fong et al. (2015) demonstrated that resistance to BET inhibitors, in human and mouse leukemia cells, is in part a consequence of increased Wnt/beta-catenin (see 116806) signaling, and negative regulation of this pathway results in restoration of sensitivity to I-BET in vitro and in vivo. ... Rathert et al. (2015) performed a chromatin-focused RNAi screen in a sensitive MLL-AF9;Nras(G12D)-driven AML mouse model to identify factors involved in primary and acquired BET resistance in leukemia. The screen showed that suppression of the Polycomb repressive complex-2 (PRC2; see 606245), contrary to effects in other contexts, promotes BET inhibitor resistance in AML. ... This process involved the activation and recruitment of WNT (see 606359) signaling components, which compensated for the loss of BRD4 and drove resistance in various cancer models. Additional studies revealed that BET-resistant states are characterized by remodeled regulatory landscapes, involving the activation of a focal MYC enhancer that recruits WNT machinery in response to BET inhibition. Rathert et al. (2015) concluded that their results identified and validated WNT signaling as a driver and candidate biomarker of primary and acquired BET resistance in leukemia, and implicated the rewiring of transcriptional programs as an important mechanism promoting resistance to BET inhibitors and, potentially, other chromatin-targeted therapies.
-
Nut Midline Carcinoma
Wikipedia
One of the most helpful and characteristic findings is the focal abrupt squamous differentiation, where stratification and gradual differentiation are absent, resembling a Hassall corpuscle of the thymus. [6] The defining feature of NMCs is rearrangement of the NUT gene. [4] Most common is a translocation involving the BRD4 gene and NUT gene (t(15;19)(q13;p13.1)). [5] [7] Treatment [ edit ] BET inhibitors are used for treatment [ citation needed ] Prognosis [ edit ] NUT midline carcinoma is very resistant to standard chemotherapy treatments. ... Specific molecular targeted therapies ( BET inhibitors and histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi)) may help to yield growth arrest of the neoplastic cells. [6] Overall, there is a mean survival of 6–9 months. [8] [9] See also [ edit ] BET inhibitor Mediastinum References [ edit ] ^ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS.
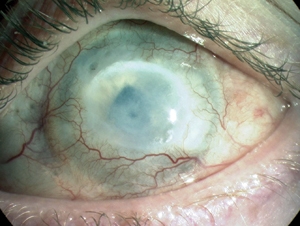
- Chemical Eye Injury Wikipedia
-
Compulsive Gambling
Mayo Clinic
If you have a problem with compulsive gambling, you may continually chase bets that lead to losses, use up savings and create debt. ... Tell yourself it's too risky to gamble at all. One bet typically leads to another and another. ... Recognize and then avoid situations that trigger your urge to bet. Family members of people with a compulsive gambling problem may benefit from counseling, even if the gambler is unwilling to participate in therapy.
-
Numerophobia
Wikipedia
ISBN 978-1-4381-2098-0 . v t e Superstition Main topics Amulet Evil eye Luck Omen Talismans Myth and ritual Lists List of superstitions List of lucky symbols List of bad luck signs Sailors' superstitions Theatrical superstitions Africa Buda Gris-gris Sampy Sleeping child Americas Ascalapha odorata Carranca Cooties Curupira Djucu Fortune cookie Groundhog Day I'noGo tied Oscar love curse Susto White lighter myth Witch window Asia Superstition in India Superstition in Pakistan Japanese superstitions Bhoot (ghost) Chhaupadi Churel Ghosts in Bengali culture Jackal's horn Kuai Kuai culture Muhurta Navaratna Nazar battu Pichal Peri Puppy pregnancy syndrome Akabeko Kanai Anzen Maneki-neko Okiagari-koboshi Omamori Fan death Agimat Arbularyo Barang Kulam Lihi Pagtatawas Pasma Usog Kuman Thong Palad khik Takrut Nang Kwak White elephant Curse of 39 Jin Chan Numbers in Chinese culture Superstitions of Malaysian Chinese Europe August curse Barbary macaques in Gibraltar Bayern-luck Blarney Stone Cimaruta Cornicello The Goodman's Croft Himmelsbrief Icelandic magical staves In bocca al lupo Kitchen witch Klabautermann Mooncalf Nazar Need-fire Painted pebbles Powder of sympathy Rabbit rabbit rabbit Ravens of the Tower of London Russian traditions and superstitions Spilling water for luck The Scottish Play Troll cross Tycho Brahe days Witch post Wolfssegen General 11:11 4 ( Four-leaf clover , Tetraphobia ) 7 ( Seventh son of a seventh son ) 8 9 13 ( Friday the 13th , The Thirteen Club , Thirteenth floor , Triskaidekaphobia ) 108 111 666 ( Number of the Beast ) Ace of spades Auspicious wedding dates Baseball superstition Beginner's luck Black cat Bread and butter Break a leg Chain letter Cramp-ring Curse Davy Jones' Locker Dead man's hand End-of-the-day betting effect Fear of frogs Fear of ghosts First-foot Flying Dutchman Four Eleven Forty Four Gambler's conceit Good luck charm Human sacrifice Jinx Knocking on wood Law of contagion Literomancy Lock of hair Maternal impression Miasma theory Nelson Numismatic charm Penny Rabbit's foot Rainmaking Ship sponsor Shoes on a table Sign of the horns Something old Spilling salt Statue rubbing Three on a match Threshold Toi toi toi 27 Club Wishing well Witch ball Witching hour Related Apotropaic magic Astrology and science Coincidence Debunker Divination Folk religion Fortune-telling Magic and religion Magical thinking Numerology Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena Post hoc ergo propter hoc Traditional medicine Urban legend Jew Muslim This article about a mental disorder is a stub .
-
Costochondritis
Wikipedia
"Towards evidence based emergency medicine: best BETs from the Manchester Royal Infirmary. BET 3: The use of corticosteroids in the management of costochondritis".
-
Puppy Pregnancy Syndrome
Wikipedia
PMID 12793514 . v t e Superstition Main topics Amulet Evil eye Luck Omen Talismans Myth and ritual Lists List of superstitions List of lucky symbols List of bad luck signs Sailors' superstitions Theatrical superstitions Africa Buda Gris-gris Sampy Sleeping child Americas Ascalapha odorata Carranca Cooties Curupira Djucu Fortune cookie Groundhog Day I'noGo tied Oscar love curse Susto White lighter myth Witch window Asia Superstition in India Superstition in Pakistan Japanese superstitions Bhoot (ghost) Chhaupadi Churel Ghosts in Bengali culture Jackal's horn Kuai Kuai culture Muhurta Navaratna Nazar battu Pichal Peri Puppy pregnancy syndrome Akabeko Kanai Anzen Maneki-neko Okiagari-koboshi Omamori Fan death Agimat Arbularyo Barang Kulam Lihi Pagtatawas Pasma Usog Kuman Thong Palad khik Takrut Nang Kwak White elephant Curse of 39 Jin Chan Numbers in Chinese culture Superstitions of Malaysian Chinese Europe August curse Barbary macaques in Gibraltar Bayern-luck Blarney Stone Cimaruta Cornicello The Goodman's Croft Himmelsbrief Icelandic magical staves In bocca al lupo Kitchen witch Klabautermann Mooncalf Nazar Need-fire Painted pebbles Powder of sympathy Rabbit rabbit rabbit Ravens of the Tower of London Russian traditions and superstitions Spilling water for luck The Scottish Play Troll cross Tycho Brahe days Witch post Wolfssegen General 11:11 4 ( Four-leaf clover , Tetraphobia ) 7 ( Seventh son of a seventh son ) 8 9 13 ( Friday the 13th , The Thirteen Club , Thirteenth floor , Triskaidekaphobia ) 108 111 666 ( Number of the Beast ) Ace of spades Auspicious wedding dates Baseball superstition Beginner's luck Black cat Bread and butter Break a leg Chain letter Cramp-ring Curse Davy Jones' Locker Dead man's hand End-of-the-day betting effect Fear of frogs Fear of ghosts First-foot Flying Dutchman Four Eleven Forty Four Gambler's conceit Good luck charm Human sacrifice Jinx Knocking on wood Law of contagion Literomancy Lock of hair Maternal impression Miasma theory Nelson Numismatic charm Penny Rabbit's foot Rainmaking Ship sponsor Shoes on a table Sign of the horns Something old Spilling salt Statue rubbing Three on a match Threshold Toi toi toi 27 Club Wishing well Witch ball Witching hour Related Apotropaic magic Astrology and science Coincidence Debunker Divination Folk religion Fortune-telling Magic and religion Magical thinking Numerology Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena Post hoc ergo propter hoc Traditional medicine Urban legend Jew Muslim
- Covering Sickness Wikipedia
-
Mooncalf
Wikipedia
Chapter X, p. 86, et infra . v t e Superstition Main topics Amulet Evil eye Luck Omen Talismans Myth and ritual Lists List of superstitions List of lucky symbols List of bad luck signs Sailors' superstitions Theatrical superstitions Africa Buda Gris-gris Sampy Sleeping child Americas Ascalapha odorata Carranca Cooties Curupira Djucu Fortune cookie Groundhog Day I'noGo tied Oscar love curse Susto White lighter myth Witch window Asia Superstition in India Superstition in Pakistan Japanese superstitions Bhoot (ghost) Chhaupadi Churel Ghosts in Bengali culture Jackal's horn Kuai Kuai culture Muhurta Navaratna Nazar battu Pichal Peri Puppy pregnancy syndrome Akabeko Kanai Anzen Maneki-neko Okiagari-koboshi Omamori Fan death Agimat Arbularyo Barang Kulam Lihi Pagtatawas Pasma Usog Kuman Thong Palad khik Takrut Nang Kwak White elephant Curse of 39 Jin Chan Numbers in Chinese culture Superstitions of Malaysian Chinese Europe August curse Barbary macaques in Gibraltar Bayern-luck Blarney Stone Cimaruta Cornicello The Goodman's Croft Himmelsbrief Icelandic magical staves In bocca al lupo Kitchen witch Klabautermann Mooncalf Nazar Need-fire Painted pebbles Powder of sympathy Rabbit rabbit rabbit Ravens of the Tower of London Russian traditions and superstitions Spilling water for luck The Scottish Play Troll cross Tycho Brahe days Witch post Wolfssegen General 11:11 4 ( Four-leaf clover , Tetraphobia ) 7 ( Seventh son of a seventh son ) 8 9 13 ( Friday the 13th , The Thirteen Club , Thirteenth floor , Triskaidekaphobia ) 108 111 666 ( Number of the Beast ) Ace of spades Auspicious wedding dates Baseball superstition Beginner's luck Black cat Bread and butter Break a leg Chain letter Cramp-ring Curse Davy Jones' Locker Dead man's hand End-of-the-day betting effect Fear of frogs Fear of ghosts First-foot Flying Dutchman Four Eleven Forty Four Gambler's conceit Good luck charm Human sacrifice Jinx Knocking on wood Law of contagion Literomancy Lock of hair Maternal impression Miasma theory Nelson Numismatic charm Penny Rabbit's foot Rainmaking Ship sponsor Shoes on a table Sign of the horns Something old Spilling salt Statue rubbing Three on a match Threshold Toi toi toi 27 Club Wishing well Witch ball Witching hour Related Apotropaic magic Astrology and science Coincidence Debunker Divination Folk religion Fortune-telling Magic and religion Magical thinking Numerology Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena Post hoc ergo propter hoc Traditional medicine Urban legend Jew Muslim
- Tricyclic Antidepressant Overdose Wikipedia
-
Fear Of Frogs
Wikipedia
Retrieved February 4, 2019 . v t e Superstition Main topics Amulet Evil eye Luck Omen Talismans Myth and ritual Lists List of superstitions List of lucky symbols List of bad luck signs Sailors' superstitions Theatrical superstitions Africa Buda Gris-gris Sampy Sleeping child Americas Ascalapha odorata Carranca Cooties Curupira Djucu Fortune cookie Groundhog Day I'noGo tied Oscar love curse Susto White lighter myth Witch window Asia Superstition in India Superstition in Pakistan Japanese superstitions Bhoot (ghost) Chhaupadi Churel Ghosts in Bengali culture Jackal's horn Kuai Kuai culture Muhurta Navaratna Nazar battu Pichal Peri Puppy pregnancy syndrome Akabeko Kanai Anzen Maneki-neko Okiagari-koboshi Omamori Fan death Agimat Arbularyo Barang Kulam Lihi Pagtatawas Pasma Usog Kuman Thong Palad khik Takrut Nang Kwak White elephant Curse of 39 Jin Chan Numbers in Chinese culture Superstitions of Malaysian Chinese Europe August curse Barbary macaques in Gibraltar Bayern-luck Blarney Stone Cimaruta Cornicello The Goodman's Croft Himmelsbrief Icelandic magical staves In bocca al lupo Kitchen witch Klabautermann Mooncalf Nazar Need-fire Painted pebbles Powder of sympathy Rabbit rabbit rabbit Ravens of the Tower of London Russian traditions and superstitions Spilling water for luck The Scottish Play Troll cross Tycho Brahe days Witch post Wolfssegen General 11:11 4 ( Four-leaf clover , Tetraphobia ) 7 ( Seventh son of a seventh son ) 8 9 13 ( Friday the 13th , The Thirteen Club , Thirteenth floor , Triskaidekaphobia ) 108 111 666 ( Number of the Beast ) Ace of spades Auspicious wedding dates Baseball superstition Beginner's luck Black cat Bread and butter Break a leg Chain letter Cramp-ring Curse Davy Jones' Locker Dead man's hand End-of-the-day betting effect Fear of frogs Fear of ghosts First-foot Flying Dutchman Four Eleven Forty Four Gambler's conceit Good luck charm Human sacrifice Jinx Knocking on wood Law of contagion Literomancy Lock of hair Maternal impression Miasma theory Nelson Numismatic charm Penny Rabbit's foot Rainmaking Ship sponsor Shoes on a table Sign of the horns Something old Spilling salt Statue rubbing Three on a match Threshold Toi toi toi 27 Club Wishing well Witch ball Witching hour Related Apotropaic magic Astrology and science Coincidence Debunker Divination Folk religion Fortune-telling Magic and religion Magical thinking Numerology Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena Post hoc ergo propter hoc Traditional medicine Urban legend Jew Muslim
-
Susto
Wikipedia
Retrieved 6 March 2013 . v t e Superstition Main topics Amulet Evil eye Luck Omen Talismans Myth and ritual Lists List of superstitions List of lucky symbols List of bad luck signs Sailors' superstitions Theatrical superstitions Africa Buda Gris-gris Sampy Sleeping child Americas Ascalapha odorata Carranca Cooties Curupira Djucu Fortune cookie Groundhog Day I'noGo tied Oscar love curse Susto White lighter myth Witch window Asia Superstition in India Superstition in Pakistan Japanese superstitions Bhoot (ghost) Chhaupadi Churel Ghosts in Bengali culture Jackal's horn Kuai Kuai culture Muhurta Navaratna Nazar battu Pichal Peri Puppy pregnancy syndrome Akabeko Kanai Anzen Maneki-neko Okiagari-koboshi Omamori Fan death Agimat Arbularyo Barang Kulam Lihi Pagtatawas Pasma Usog Kuman Thong Palad khik Takrut Nang Kwak White elephant Curse of 39 Jin Chan Numbers in Chinese culture Superstitions of Malaysian Chinese Europe August curse Barbary macaques in Gibraltar Bayern-luck Blarney Stone Cimaruta Cornicello The Goodman's Croft Himmelsbrief Icelandic magical staves In bocca al lupo Kitchen witch Klabautermann Mooncalf Nazar Need-fire Painted pebbles Powder of sympathy Rabbit rabbit rabbit Ravens of the Tower of London Russian traditions and superstitions Spilling water for luck The Scottish Play Troll cross Tycho Brahe days Witch post Wolfssegen General 11:11 4 ( Four-leaf clover , Tetraphobia ) 7 ( Seventh son of a seventh son ) 8 9 13 ( Friday the 13th , The Thirteen Club , Thirteenth floor , Triskaidekaphobia ) 108 111 666 ( Number of the Beast ) Ace of spades Auspicious wedding dates Baseball superstition Beginner's luck Black cat Bread and butter Break a leg Chain letter Cramp-ring Curse Davy Jones' Locker Dead man's hand End-of-the-day betting effect Fear of frogs Fear of ghosts First-foot Flying Dutchman Four Eleven Forty Four Gambler's conceit Good luck charm Human sacrifice Jinx Knocking on wood Law of contagion Literomancy Lock of hair Maternal impression Miasma theory Nelson Numismatic charm Penny Rabbit's foot Rainmaking Ship sponsor Shoes on a table Sign of the horns Something old Spilling salt Statue rubbing Three on a match Threshold Toi toi toi 27 Club Wishing well Witch ball Witching hour Related Apotropaic magic Astrology and science Coincidence Debunker Divination Folk religion Fortune-telling Magic and religion Magical thinking Numerology Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena Post hoc ergo propter hoc Traditional medicine Urban legend Jew Muslim
-
Morning Sickness
Wikipedia
"Towards evidence-based emergency medicine: Best BETs from the Manchester Royal Infirmary. BET 2: Steroid therapy in the treatment of intractable hyperemesis gravidarum".
-
Myoclonus
Mayo Clinic
Treatment Treatment of myoclonus works bets if you can stop the problem that's causing it.MECP2, SGCE, PSEN1, CSTB, PRRT2, PRNP, KCNC1, POLG, SLC2A1, TAF1, KIF5A, ADCY5, APP, NOL3, SNCA, KCNQ2, NEU1, PRKCG, PSEN2, ANO3, ATXN2, SCN1A, SCN2A, SCN8A, FARS2, SLC1A2, NHLRC1, AFG3L2, NKX2-1, STXBP1, TBP, GOSR2, TH, NUP62, CASK, NFASC, PLCB1, DENND5A, CUX2, SZT2, ATP13A2, ABCA7, TRAK1, FRRS1L, CIZ1, SLC6A5, FBXO7, NDUFAF3, PARS2, NECAP1, CHMP2B, KIF1B, CNKSR2, ZNHIT3, TOMM40, GPHN, AP5Z1, MTHFS, STAMBP, DNAJC6, HIBCH, SYNJ1, ST3GAL5, CERS1, CPLX1, PIGQ, LIAS, PLPBP, PIGL, SYNGAP1, PNKP, CTSF, CNPY3, AARS1, BSCL2, TOE1, DHDDS, DNAJC5, CLPB, TRIM8, COG8, PIGO, LMNB2, ATAD1, PIGY, SLC25A46, RFT1, PGAP3, SLC52A3, EFHC1, SLC25A22, NUS1, GLYCTK, SIK1, ARX, C9orf72, PHACTR1, TSEN54, PIGW, SLC13A5, HCN1, SAMD12, SDHAF1, ST20-MTHFS, UBA5, KCTD17, CYFIP2, VPS13D, PGAP2, AP3B2, PSAT1, MECR, TRAPPC12, GLRX5, PIGP, ACTL6B, WWOX, TREM2, CLN6, MTPAP, PNPO, FOXRED1, CARS2, POMGNT1, PIGV, CCDC88A, NGLY1, TWNK, PRDM8, COQ8A, TBC1D24, GUF1, IRF2BPL, ARV1, SLC52A2, TMEM231, PLA2G6, YWHAG, MRE11, NUP214, GNAQ, GRIA3, GRIN1, GRIN2A, GRIN2B, GRIN2D, HTT, HLA-DQB1, HMGCL, CACNA1E, GNAO1, KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNB1, KCNC3, KCND3, KCNQ3, CACNA1B, CACNA1A, CLN3, SCARB2, GLRB, TRNF, CHD2, CLTC, CTNND2, TPP1, CYP27A1, DAB1, CLCN4, DDC, DNM1, ATN1, EEF1A2, GLRA1, CLN8, FGF12, GABRB2, GABRB3, GABRG2, GAMT, GBA, GCSH, GLDC, ATP6, CLN5, TRNI, QDPR, SCN3A, SDHA, SDHD, ST3GAL3, SLC6A1, SMS, SORL1, SPTAN1, CDKL5, CNTN2, ASAH1, TCF20, AMT, TSPYL1, TYROBP, ADSL, XPA, ADAR, USP7, EPM2A, ADRA2B, TRNK, SC5D, ATM, PPP3CA, TRNL1, TRNP, NAGA, NDUFV1, NEUROD2, NTRK2, SERPINI1, ATP6V1A, PODXL, PIGA, MAPK10, PURA, PPT1, PSAP, PTS, APOE, GCH1, TOR1A, CYP2D6, BRCA2, MFSD8, ZBTB38, PRICKLE1, COL6A4P1, CAMK2A, TMEM240, ATP1A3, AAAS, IL10, CYP2C19, PIK3C2A, PRKRA, UCN, TPO, TCN2, POLR1C, MARCHF6, RASA2, SLC27A4, SETX, CNTNAP2, DCX, MAPT, LY6E, LEP, REM1, ISYNA1, IL6, RMND1, SLC7A10, FLAD1, FAME3
- Croup Wikipedia
-
Aplastic Anemia
Wikipedia
Marie Curie , famous for her pioneering work in the field of radioactivity , died of aplastic anemia after working unprotected with radioactive materials for a long period of time; the damaging effects of ionizing radiation were not then known. [7] Aplastic anemia is present in up to 2% of patients with acute viral hepatitis . [8] One known cause is an autoimmune disorder in which white blood cells attack the bone marrow. [1] Acquired aplastic anemia is a T-cell mediated autoimmune disease, in which regulatory T cells are decreased in patients, and T-bet, a transcription factor and key regulator of Th1 development and function, is upregulated in affected T-cells. As a result of active transcription of the IFN-gamma gene by T-bet, IFN-gamma levels are increased, which reduces colony formation of hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro by inducing apoptosis of CD34+ cells of bone marrow. [9] Short-lived aplastic anemia can also be a result of parvovirus infection. [10] In humans, the P antigen (also known as globoside), one of the many cellular receptors that contribute to a person's blood type, is the cellular receptor for parvovirus B19 virus that causes erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) in children.IFNG, TERT, NBN, SBDS, PRF1, CSF3, CSF2, KIT, PIGA, RASA3, TERC, SRP72, TINF2, HLA-DRB1, TNF, DNAJC21, EFL1, RPL5, HOXA11, NHP2, ACD, NOP10, ELANE, DIPK1A, TCIRG1, SRP54, GFI1, PALB2, THPO, GATA2, CD34, RBM45, TP53, FOXP3, CD59, IL6, CDR3, STAT3, RPS19, IL10, GSTT1, HLA-A, CD55, GSTM1, TBX21, CD247, TGFB1, HLA-B, PDCD1, CXCL8, GEM, SH2D1A, GATA3, ID4, MPL, HPGDS, GPI, HLA-DQA1, MSN, KIR3DL1, DKC1, NRAS, FCGR3B, FAS, FASLG, ITGA2B, MIR204, IL27, STAT4, CXCL10, ASXL1, CXCR4, IL17A, CD48, HAVCR2, TNFSF10, CEACAM8, CSF3R, PPARG, CTLA4, MYDGF, NLRP2, NQO1, VEGFA, IL17D, IL23A, FCGR3A, YWHAE, WT1, ALDH2, VDR, UROD, TRAF1, THBD, TGFBI, TFR2, TERF2, TERF1, TRB, TAL1, SPARC, SNCA, TFRC, BRD4, LOH19CR1, DGKZ, QRSL1, HAMP, IL21, BCORL1, NHEJ1, SLCO6A1, PPARGC1B, IL23R, HBFQTL4, APLF, FOLH1B, GSTK1, MIR126, MIR34A, CCR2, RPL17-C18orf32, KLRC4-KLRK1, TET2, SCLY, WT1-AS, CAP1, CD164, SPHK1, HACD1, MSC, SPATA2, GDF11, ECI2, SORBS1, SLC25A37, KLRK1, SF3B1, SELPLG, SH2B1, PTPN22, CD274, ANAPC2, SMARCA1, NFE2L2, SELP, F9, CSF1R, CTAA1, CYP1A1, CYP2B6, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, EGF, ETV6, EZH2, FANCA, GSTP1, FANCD2, FANCG, FGF1, FGF2, FLT1, FOLH1, GABPA, GATA1, CBLIF, CCR6, TPP1, CDKN2D, CDKN2A, AR, SERPINC1, B2M, BCL2, BGLAP, BMP4, BMP6, BRCA2, ZFP36L1, BTK, CA1, RUNX1, CBLB, CD3G, CD19, CD27, TNFRSF8, CD40LG, CD70, CXCR3, GYPA, CCL20, PMS1, SMAD4, MDM4, NCAM1, NFATC2, APC, NOS2, PAFAH1B1, SLC26A4, SERPINB6, PRTN3, GYPB, PTGDS, RAG2, REG1A, RMRP, RPL17, S100A8, S100A9, SCT, CCL2, LNPEP, LGALS9, LEPR, LEP, GYPE, HFE, HLA-DQB1, HOXB4, HP, HES1, ICAM1, IGH, IL1B, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL11, IL15, IL18, ITGB3, KIR3DL2, KRT7, KTN1, H3P13
-
Fear Of Ghosts
Wikipedia
Conklin ( 2001) ISBN 0-292-71236-7 , p. 161, "Ghost Fears and Dissociation" ^ "The Belief in Immortality and the Worship of the Dead", by James George Frazer (1913), [ p. 305] in Google Books v t e Ghosts and ghostlore List of ghosts Manifestations Ancestral spirits Haunted locations Haunted highways Haunted house Haunted trains Haunted ships Hungry ghost Phantom vehicle Poltergeist Residual haunting Vengeful ghost By continent and culture African South Africa Asian Burmese Chinese locations Ghost Festival Tibetan Filipino locations Indian locations Bengali Japanese Onryō Korean Malay Thai locations Vietnamese Europe France Slavic religion Romania United Kingdom Scotland North America Canada Caribbean Navajo Ghost sickness Mexican locations Day of the Dead United States District of Columbia South America Colombia Oceania Maori Polynesian History Mesopotamian Ancient Egyptian culture Classical Antiquity Ghosts in English-speaking cultures Ghosts in Spanish-speaking cultures Parapsychology Apparitional experience Electronic voice phenomenon kaidan Ghost hunting Séance Mediumship Spirit photography Popular culture Films about ghosts India Stories about ghosts Halloween Samhain Paranormal television Court cases Booty v Barnaby Related Fear of ghosts Spectrophilia Spiritualism Spiritism The Ghost Club Category v t e Superstition Main topics Amulet Evil eye Luck Omen Talismans Myth and ritual Lists List of superstitions List of lucky symbols List of bad luck signs Sailors' superstitions Theatrical superstitions Africa Buda Gris-gris Sampy Sleeping child Americas Ascalapha odorata Carranca Cooties Curupira Djucu Fortune cookie Groundhog Day I'noGo tied Oscar love curse Susto White lighter myth Witch window Asia Superstition in India Superstition in Pakistan Japanese superstitions Bhoot (ghost) Chhaupadi Churel Ghosts in Bengali culture Jackal's horn Kuai Kuai culture Muhurta Navaratna Nazar battu Pichal Peri Puppy pregnancy syndrome Akabeko Kanai Anzen Maneki-neko Okiagari-koboshi Omamori Fan death Agimat Arbularyo Barang Kulam Lihi Pagtatawas Pasma Usog Kuman Thong Palad khik Takrut Nang Kwak White elephant Curse of 39 Jin Chan Numbers in Chinese culture Superstitions of Malaysian Chinese Europe August curse Barbary macaques in Gibraltar Bayern-luck Blarney Stone Cimaruta Cornicello The Goodman's Croft Himmelsbrief Icelandic magical staves In bocca al lupo Kitchen witch Klabautermann Mooncalf Nazar Need-fire Painted pebbles Powder of sympathy Rabbit rabbit rabbit Ravens of the Tower of London Russian traditions and superstitions Spilling water for luck The Scottish Play Troll cross Tycho Brahe days Witch post Wolfssegen General 11:11 4 ( Four-leaf clover , Tetraphobia ) 7 ( Seventh son of a seventh son ) 8 9 13 ( Friday the 13th , The Thirteen Club , Thirteenth floor , Triskaidekaphobia ) 108 111 666 ( Number of the Beast ) Ace of spades Auspicious wedding dates Baseball superstition Beginner's luck Black cat Bread and butter Break a leg Chain letter Cramp-ring Curse Davy Jones' Locker Dead man's hand End-of-the-day betting effect Fear of frogs Fear of ghosts First-foot Flying Dutchman Four Eleven Forty Four Gambler's conceit Good luck charm Human sacrifice Jinx Knocking on wood Law of contagion Literomancy Lock of hair Maternal impression Miasma theory Nelson Numismatic charm Penny Rabbit's foot Rainmaking Ship sponsor Shoes on a table Sign of the horns Something old Spilling salt Statue rubbing Three on a match Threshold Toi toi toi 27 Club Wishing well Witch ball Witching hour Related Apotropaic magic Astrology and science Coincidence Debunker Divination Folk religion Fortune-telling Magic and religion Magical thinking Numerology Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena Post hoc ergo propter hoc Traditional medicine Urban legend Jew Muslim
-
Usog
Wikipedia
ScienceNOW . v t e Superstition Main topics Amulet Evil eye Luck Omen Talismans Myth and ritual Lists List of superstitions List of lucky symbols List of bad luck signs Sailors' superstitions Theatrical superstitions Africa Buda Gris-gris Sampy Sleeping child Americas Ascalapha odorata Carranca Cooties Curupira Djucu Fortune cookie Groundhog Day I'noGo tied Oscar love curse Susto White lighter myth Witch window Asia Superstition in India Superstition in Pakistan Japanese superstitions Bhoot (ghost) Chhaupadi Churel Ghosts in Bengali culture Jackal's horn Kuai Kuai culture Muhurta Navaratna Nazar battu Pichal Peri Puppy pregnancy syndrome Akabeko Kanai Anzen Maneki-neko Okiagari-koboshi Omamori Fan death Agimat Arbularyo Barang Kulam Lihi Pagtatawas Pasma Usog Kuman Thong Palad khik Takrut Nang Kwak White elephant Curse of 39 Jin Chan Numbers in Chinese culture Superstitions of Malaysian Chinese Europe August curse Barbary macaques in Gibraltar Bayern-luck Blarney Stone Cimaruta Cornicello The Goodman's Croft Himmelsbrief Icelandic magical staves In bocca al lupo Kitchen witch Klabautermann Mooncalf Nazar Need-fire Painted pebbles Powder of sympathy Rabbit rabbit rabbit Ravens of the Tower of London Russian traditions and superstitions Spilling water for luck The Scottish Play Troll cross Tycho Brahe days Witch post Wolfssegen General 11:11 4 ( Four-leaf clover , Tetraphobia ) 7 ( Seventh son of a seventh son ) 8 9 13 ( Friday the 13th , The Thirteen Club , Thirteenth floor , Triskaidekaphobia ) 108 111 666 ( Number of the Beast ) Ace of spades Auspicious wedding dates Baseball superstition Beginner's luck Black cat Bread and butter Break a leg Chain letter Cramp-ring Curse Davy Jones' Locker Dead man's hand End-of-the-day betting effect Fear of frogs Fear of ghosts First-foot Flying Dutchman Four Eleven Forty Four Gambler's conceit Good luck charm Human sacrifice Jinx Knocking on wood Law of contagion Literomancy Lock of hair Maternal impression Miasma theory Nelson Numismatic charm Penny Rabbit's foot Rainmaking Ship sponsor Shoes on a table Sign of the horns Something old Spilling salt Statue rubbing Three on a match Threshold Toi toi toi 27 Club Wishing well Witch ball Witching hour Related Apotropaic magic Astrology and science Coincidence Debunker Divination Folk religion Fortune-telling Magic and religion Magical thinking Numerology Perceptions of religious imagery in natural phenomena Post hoc ergo propter hoc Traditional medicine Urban legend Jew Muslim
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum Wikipedia
-
Dehydration
Mayo Clinic
If you work or exercise outdoors during hot or humid weather, cool water is your best bet. Sports drinks containing electrolytes and a carbohydrate solution also may be helpful.AVP, PDIA3, PCSK1N, DMD, NPY1R, NOS1, YWHAZ, OXT, PCSK1, P2RY2, SCNN1B, NR3C2, SLC26A3, SCNN1G, SCNN1A, CA12, KCNJ1, SPINK5, SLC12A1, LAMB3, LAMA3, IGHM, ALOXE3, PDX1, LAMC2, EGFR, HYMAI, LCT, LRRC8A, IGLL1, NLRC4, ABCA12, KCNJ11, PIK3R1, PLAGL1, ACAD8, HSD3B2, HMGCL, ITGB4, PKHD1, PLEC, VPS33B, IVD, BLNK, PCCB, ATP6V0A4, NEUROG3, PCCA, GCK, INS, ACAT1, CD79A, CYP4F22, EIF2AK3, ABCC8, CACNA1A, SULT2B1, MMAA, STX3, ACSF3, MMAB, AQP2, ZFP57, NIPAL4, ALOX12B, MMUT, AK2, NR0B1, LIPN, MYO5B, STAT3, DBH, SDR9C7, MCEE, CFTR, CYP24A1, CYP11B2, CYP11A1, CTNS, OCRL, NLRP3, CLCNKB, CD79B, TCF3, TGM1, REN, HPGDS, PTGDS, SLC5A2, LINC01672, AVPR2, CEBPZ, MYB, KCNN4, SRR, PAEP, HSPB3, NFAT5, PIEZO1, UGT1A1, FLG, PLA2G15, ACE, HCRT, ALB, AKR1B1, DECR1, SARDH, BPIFA1, ACCS, C1QTNF1, TBX1, CPA1, ACSS2, RENBP, TNF, NR1I2, TAC1, SMC3, ELOVL4, CLDN1, UBC, TRAF6, DLEU2, UVRAG, SOCS6, XK, AIMP2, GHS, NR4A3, TP63, ABCB11, HACD1, POLDIP2, KL, HSPA14, FXYD5, KLHL24, ZKSCAN7, TRPV4, AASDHPPT, SPX, KAT8, ZNF469, DGAT2, HSH2D, CREB3L1, RSAD2, DNER, NAXE, AASDH, SLC7A13, AWAT1, DNAJB1P1, MIR155, MUC5B, C20orf181, ABI3, ABHD5, GRAP2, F11R, BMS1, BCL2L11, UBA2, NUTF2, PRG4, MERTK, HMGN4, AHSA1, CKAP4, SDS, SLC27A4, NLRP1, ICE1, HEY1, RNF19A, TSKU, SRM, FGF21, SGSM3, CD274, DUOX2, ST14, ACACA, SORD, FBN1, DHFR, DPYD, DSC3, DSG3, EGF, ELAVL2, ENO1, EPHB2, EPO, F2, FASN, MTOR, CYBB, NR5A1, GCG, GLB1, GLUL, GPER1, GPT, HAS2, HBA1, HBA2, HBAP1, HIF1A, DCC, CST6, HSPA1B, TSPO, ACTB, ADH1B, ACAN, AGXT, APRT, AQP1, AQP3, AQP4, ATP6V1B1, ATR, BCS1L, CAD, CSF3, CAPN1, CASR, CAT, ENTPD1, CHRM3, CKB, COL4A2, COX8A, CLDN7, CRK, MAPK14, HSPA1A, HSPA4, SLC25A1, RBBP8, NFATC3, NTS, PAH, ABCB4, PHB, PLA2G4A, PPARG, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, MAPK1, RCD1, NEUROG1, RPE65, SRL, CCL21, SDHB, SFRP4, SGK1, SKI, SLC4A1, SLC5A3, SLC6A12, SLC12A4, NFATC1, NBN, HSPA8, KCNJ10, HSPB1, HSPB2, HSP90AA1, HSPD1, DNAJB1, IGF1, IL6, CXCL8, IRAK1, ITPK1, JUN, KCNMA1, MUC5AC, KHK, KIT, LEP, LEPR, LYZ, MEF2A, MEF2C, MFAP1, FOXO4, MMP2, MMP16, PGC