Load FindZebra Summary
Disclaimer:
FindZebra Search conducts a search using our specialized medical search engine.
FindZebra Summary uses the text completions API
(subject to OpenAI’s API data usage policies)
to summarize and reason about the search results.
The search is conducted in publicly available information on the Internet that we present “as is”.
You should be aware that FindZebra is not supplying any of the content in the search results.
FindZebra Summary is loading...
-
Botellón
Wikipedia
Also, loud music contributes to the amount of noise, which is one reason why participants have begun moving to less populated areas in cities. [8] Vandalism : The intoxicated participants of a botellón may potentially leave trash or vandalize a public area and because botellón occurs in public spaces, the city's cleaning crews have to clean it up, which can cause frustration and anxiety with non-participants. ... Instead, they buy alcohol at lower prices from a store and participate in a botellón. [9] Countermeasures [ edit ] Sign prohibiting botellón in Cordoba, Spain. ... May, 2004. ^ A.Baigorri, M.Chaves: "Más que ruido, alcohol y drogas (la Sociología en su papel)". http://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/fichero_articulo?codigo=2519999 ^ http://www.unex.es/eweb/sociolog/botellon%201.pdf ^ Articulo de la consejería de cultura y patrimonio ^ "Archived copy" (PDF) . ... CS1 maint: archived copy as title ( link ) ^ "Media España se cita en la Red para celebrar un macrobotellón el 17 de marzo" . 2006-03-07. ^ http://www.20minutos.es/noticia/97295/0/macrobotellones/ciudades/espana/ | Literally translated from Spanish ^ "El Ayuntamiento "no consentirá" el macrobotellón que se prepara en Moncloa" . 2006-03-07.
-
Angularis Nigra
Wikipedia
Papillae dimension can be changed due to any of the following reasons: 1. Inter-proximal space between teeth; diverging roots can result in the presence of an interproximal space when the contact point between the two clinical crowns is situated too incisally, diverging roots may also be a result of orthodontic treatment. [8] 2. ... Publisher: Munksgaard International Publishers Ltd., Price: D.kr. 460.00". The European Journal of Orthodontics . 6 (3): 234. doi : 10.1093/ejo/6.3.234 . ... PMID 20523177 . External links [ edit ] https://web.archive.org/web/20101219042017/http://www.1stcosmeticdentist.com/restorative-dentistry-article33.html https://web.archive.org/web/20110505195404/http://www.thordarson.ca/black-triangles-between-tooth
-
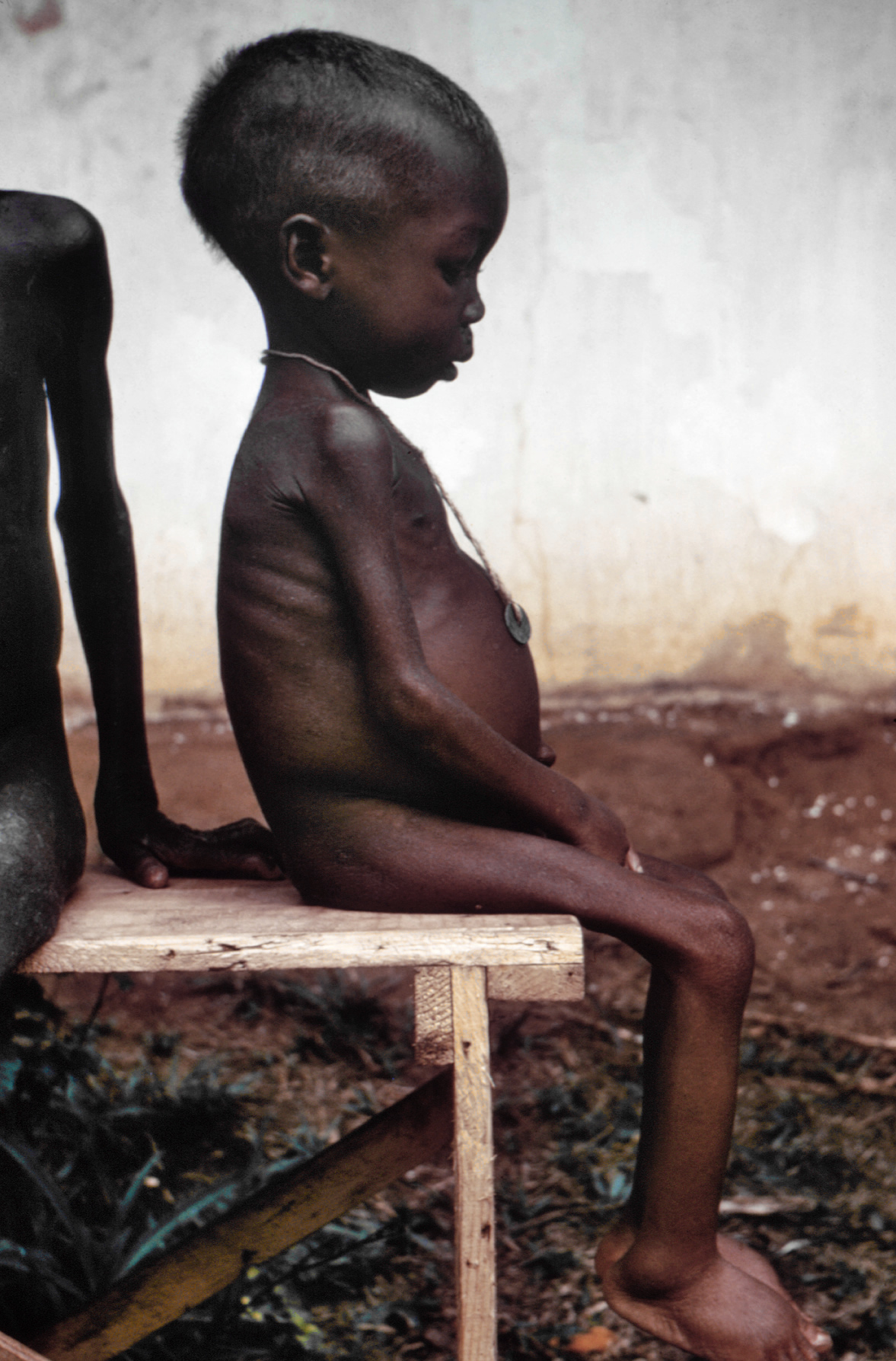
Starvation
Wikipedia
This imbalance can arise from one or more medical conditions or circumstantial situations, which can include: Medical reasons Anorexia nervosa Bulimia nervosa Eating disorder, not otherwise specified Celiac disease Coma Major depressive disorder Diabetes mellitus Digestive disease Constant vomiting Circumstantial causes Child, elder or dependant abuse Famine – for any reason, such as political strife and war [7] [8] Hunger striking Excessive fasting Poverty Biochemistry [ edit ] With a typical high-carbohydrate diet, the human body relies on free blood glucose as its primary energy source. ... "The State of Food Insecurity in the World, 2008 : High food prices and food security - threats and opportunities" . ... "FAO’s most recent estimates put the number of hungry people at 923 million in 2007, an increase of more than 80 million since the 1990–92 base period.". ^ https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/15-07-2019-world-hunger-is-still-not-going-down-after-three-years-and-obesity-is-still-growing-un-report ^ Fogel, RW (2004). ... "The State of Food Insecurity in the World, 2008 : High food prices and food security - threats and opportunities" . ... The estimates show that rising food prices have thrown that progress into reverse, with the proportion of undernourished people worldwide moving back towards 17 percent.". ^ Donald, Leland (1997).
-
Hiv/aids In Europe
Wikipedia
Transmission among people who inject drugs has stabilized but prevalence rates are very high. [13] So far injecting drug use remains the most important transmission route and the HIV epidemic continues to affect vulnerable populations more, particularly injecting drug users (IDUs) and their sexual partners. [14] In 2018, 190 new cases of HIV and 25 cases of AIDS were diagnosed in Estonia. ... Germany [ edit ] HIV has a typical prevalance to western Europe. Gay and drug users are high risk populations. ... -case-study-2011 ^ https://news.err.ee/897589/190-new-cases-of-hiv-diagnosed-in-estonia-in-2018 ^ https://www.aidshealth.org/global/estonia/ ^ https://news.postimees.ee/3967981/estonia-has-fewer-hiv-positive-people-than-thought ^ The directorate of health in Iceland. 2015 [cited 2015 Sep 2]. ... Infection Ecology & Epidemiology . 7 (1): 1328964. doi : 10.1080/20008686.2017.1328964 . PMC 5475329 . PMID 28649306 . ^ http://aidsinfo.unaids.org/ ^ https://www.tvnet.lv/6466173/kapec-visaugstakais-hiv-inficesanas-limenis-es-ir-latvija ^ https://www.spkc.gov.lv/lv/statistika-un-petijumi/infekcijas-slimibas/datu-vizualizacija/hivaids ^ McDermott, Doireann (4 May 2017). ... -duomenys ^ https://www.dsptimis.ro/promovare/zml_hiv_19_analiza.pdf ^ https://360medical.ro/stiri/raport-incidenta-hiv-din-romania-este-in-scadere-dar-ramane-printre-cele-mai-mari-din-regiune/2019/11/28/ ^ https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/russianfederation ^ a b "HIV AND AIDS IN W & C EUROPE & N AMERICA REGIONAL OVERVIEW" .
-
Alcoholism In Adolescence
Wikipedia
"These factors include normal maturational changes that all adolescents experience; genetic, psychological and social factors specific to each adolescent and the various social and cultural environments that surround adolescent, including their families , schools and communities ". [4] It is also shown that early onset of alcohol intake can lead to high levels of alcohol use in adulthood. [4] Alcoholism throughout adolescents is increasing yearly for a number of different reasons. These reasons include: Availability of alcohol Peer pressure Role model Television Anxiety or stress [7] Prevention [ edit ] There are a number of ways to preventing alcoholism throughout adolescents. ... Hoboken, NJ, USA: Jossey-Bass. Retrieved from http://www.ebrary.com.ipacez.nd.edu.au ^ "Consequences of Underage Drinking" . ... New York, NY, USA: Nova. Retrieved from http://www.ebrary.com.ipacez.nd.edu.auhttps://ipacez.nd.edu.au/login?url=http://site.ebrary.com/lib/notredameaustralia/reader.action? ... Sulfonic acids : Acamprosate Religion and alcohol Christian views on alcohol alcohol in the Bible Islam and alcohol History Bratt System Related Index of alcohol-related articles Austrian syndrome Ban on caffeinated alcoholic beverages Brief intervention Gateway drug effect Last call Mood disorder Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Self-medication Spins Sober companion Sober living houses Sobering center Town drunk Category
-
Burusera
Wikipedia
See also [ edit ] Clothing fetish Uniform fetishism Panty fetishism Shoe fetishism Child pornography laws in Japan Panchira Zettai ryōiki AV idol JK business Cosplay restaurant Host and hostess clubs Maid café Hentai Kogal Gyaru Upskirt References [ edit ] ^ "The economics of pricing used panties." http://aprilsbody.com/used-panties-prices-explained/ Archived 2014-02-22 at the Wayback Machine (Retrieved on Feb. 16, 2014). ^ Telegraph news report ^ Sydney Morning Herald news report ^ 警察白書 (Police White Paper), 1994.
-
Hiv/aids In Ukraine
Wikipedia
Prevalence in the southern and eastern oblasts ( Odessa , Mykolaiv , Dnipropetrovsk , and Donetsk ) is about three times higher than rates in the rest of the country. [16] A major reason for this is the fact that the urbanized and industrialized regions in the East and South of Ukraine suffered most from the economic crisis in the 90s, which in turn led to the spread of unemployment, alcoholism, and drug abuse, thus setting the conditions for wider spread of the epidemic. [17] From 1995 to 2007, the primary means of HIV transmission was through injection drug use, but by 2008, sexual contact outpaced injection drug use as the primary form of transmission. [16] By 2009, almost 44 percent of new infections occurred through sexual transmission, and 36 percent were through injecting drug use (according to USAID ; according to CSIS in 2009 the proportion of new cases of HIV/AIDS attributable to injecting drug use was 60%). [18] [16] In 2007 about 0.96 percent of Ukrainians , or about 440,000 citizens, were estimated to be living with HIV/AIDS, [19] down from 1.46 percent of the population in 2005, or 685,600 citizens, according to UNAIDS. [6] The number of HIV/AIDS cases in Ukraine reduced by 200 or 3.9% to 4,900 in the period of January–November 2008, compared with the corresponding period of last year. ... According to the obtained data around 15.5% of street minors in Ukraine used the injected drugs at least once, 9.8% of boys reported anal sex experience when only 36% of them acknowledged using condom during their most recent sexual encounter. [25] Preventive measures [ edit ] From 2001 till June 2015 HIV-positive Ukrainian citizens were barred from travelling abroad and HIV-positive foreigners were forbidden to enter Ukraine. [26] Harm reduction programs [ edit ] An ambulance in Kiev Since 2003, drug substitution programs have been introduced in Ukraine. ... Methadone, in contrast, is viewed as a drug subscribed at public expense. [28] In 2012 patients and advocacy groups complained of occasional supply shortages in Ukrainian AIDS clinics. [1] [29] In June 2012 advocacy groups accused Health Ministry officials of embezzling money that should be used to treat AIDS patients by buying AIDS drugs at hugely inflated prices and then receiving kickbacks. [29] In the War in Donbass the separatist authorities of the Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk People's Republic have banned methadone and substitution therapy and have taken a hard line on drug addiction and have banned most international medical organizations. [30] As a result people living with HIV/AIDS fled separatist-controlled areas. [30] National response [ edit ] The policy and legal environment in Ukraine is generally favorable for combating the spread of HIV/AIDS, but there is a gap between national-level policies and laws and local-level practices. ... This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain . ^ a b Vulnerability Assessment of People Living With HIV (PLHIV) in Ukraine United Nations Development Programme , page 24 - Retrieved on 8 December 2009. ^ Injecting Drug Use in Ukraine , Center for Strategic and International Studies (March 2012) ^ http://www.unaids.org/en/KnowledgeCentre/HIVData/mapping_progress.asp Archived August 31, 2009, at the Wayback Machine ^ World Youth Report 2007:Young People's Transition to Adulthood . ... Weber Assessment 2007 in Donetsk. http://www.aids-ukraine.org . ^ a b Ukraine:Corruption blamed for AIDS non-treatment , Associated Press (29 June 2012) ^ a b "HIV: East Ukraine's Silent Crisis" .
-
Female Foeticide In India
Wikipedia
They move from an already low number of females due to social reasons to even fewer daughters than before due to the added financial liability of daughters being more expensive. ... India's weak social security system [ edit ] Another reason for this male preference is based on the economic benefits of having a son and the costs of having a daughter. ... In the graph, the supply of brides outside each village, locality, or region is depicted as 'supply foreign'. This foreign supply values the price of getting a wife at much cheaper than the first domestic price P1 and the second domestic price P2. ... Women act like imports in an international trade market if the import price is lower than the high price of domestic dowries with a low supply of women. The foreign price is lower than the market price and this results in even fewer domestic brides than without importation (Q3 instead of Q2).
-
Autoimmune Gfap Astrocytopathy
Wikipedia
Causes [ edit ] The reason that anti-GFAP autoantibodies appear is currently unknown. ... Long et al., Autoimmune glial fibrillary acidic protein astrocytopathy in Chinese patients: a retrospective study, 29 November 2017, https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13531 ^ Patel N M, Bronder J, Motta M, Morris N. Mystery Case: A 23-year-old man with headaches, confusion, and lower extremity weakness. Neurology. 2018;92(18):863-867. https://n.neurology.org/content/92/18/863/tab-article-info ^ Iorio R, Damato V, Evoli A, et al, Clinical and immunological characteristics of the spectrum of GFAP autoimmunity: a case series of 22 patients, J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2018;89:138-146. ^ Shan F, Long Y, Qiu W. ... PMID 30568655 , PMCID PMC6290896, doi : 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02802 ^ Eoin Flanagan et al., Specificity of glial fibrillary acidic protein IgG autoantibody (GFAP-IgG) for Autoimmune Meningoencephalomyelitis Diagnosis, Neurology, April 18, 2017; 88 (16 Supplement) ^ Yang X. et al., Treatment of Autoimmune Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Astrocytopathy: Follow-Up in 7 Cases, Neuroimmunomodulation 2017;24:113-119, https://doi.org/10.1159/000479948 [1] ^ Patel N M, Bronder J, Motta M, Morris N. Mystery Case: A 23-year-old man with headaches, confusion, and lower extremity weakness. Neurology. 2018;92(18):863-867. https://n.neurology.org/content/92/18/863/tab-article-info
-
Abortion In Estonia
Wikipedia
Estonia fine-tuned their legislation after the restoration of independence. [1] Estonia allows abortion on-demand for any purpose, [1] before the end the 11th week of pregnancy . [2] Later abortions are permitted up to the 21st week (included) if the woman is younger than 15 years old or older than 45 years old, if the pregnancy endangers the woman's health, if the child may have a serious physical or mental defect , or if the woman's illness or other medical problem hinders the child's development. [2] Women who want to have an abortion for personal reasons not specified in the abortion legislation will be expected to pay a fee according to the abortion provider's price list. [1] Abortion performed for medical reasons is covered for insured persons by the Estonian Health Insurance Fund. [3] 38.7% of pregnancies ended in abortion in Estonia in 2006, a decline from 49.4% just six years before. [4] In 2010, there were 9087 abortions in Estonia, which meant 57.4 abortions for every hundred live births. [5] As of 2010 [update] , the abortion rate was 25.5 abortions per 1000 women aged 15–44 years. [6] Mifepristone (medical abortion) was registered in 2003. [7] References [ edit ] ^ a b c Estonia - ABORTION POLICY - United Nations ^ a b "Raseduse katkestamise ja steriliseerimise seadus" (in Estonian). ... CS1 maint: archived copy as title ( link ) v t e Abortion in Europe Sovereign states Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Kazakhstan Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Netherlands North Macedonia Norway Poland Portugal Romania Russia San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Turkey Ukraine United Kingdom England Northern Ireland Scotland Wales Vatican City States with limited recognition Abkhazia Artsakh Kosovo Northern Cyprus South Ossetia Transnistria v t e Abortion Main topics Definitions History Methods Abortion debate Philosophical aspects Abortion law Movements Abortion-rights movements Anti-abortion movements Issues Abortion and mental health Beginning of human personhood Beginning of pregnancy controversy Abortion-breast cancer hypothesis Anti-abortion violence Abortion under communism Birth control Crisis pregnancy center Ethical aspects of abortion Eugenics Fetal rights Forced abortion Genetics and abortion Late-term abortion Legalized abortion and crime effect Libertarian perspectives on abortion Limit of viability Malthusianism Men's rights Minors and abortion Natalism One-child policy Paternal rights and abortion Prenatal development Reproductive rights Self-induced abortion Sex-selective abortion Sidewalk counseling Societal attitudes towards abortion Socialism Toxic abortion Unsafe abortion Women's rights By country Africa Algeria Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Cameroon Cape Verde Central African Republic Chad Egypt Ghana Kenya Namibia Nigeria South Africa Uganda Zimbabwe Asia Afghanistan Armenia Azerbaijan Bahrain Bangladesh Bhutan Brunei Cambodia China Cyprus East Timor Georgia India Iran Israel Japan Kazakhstan South Korea Malaysia Nepal Northern Cyprus Philippines Qatar Saudi Arabia Singapore Turkey United Arab Emirates Vietnam Yemen Europe Albania Andorra Austria Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Kazakhstan Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Netherlands North Macedonia Norway Poland Portugal Romania Russia San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Ukraine United Kingdom North America Belize Canada Costa Rica Cuba Dominican Republic El Salvador Guatemala Mexico Nicaragua Panama Trinidad and Tobago United States Oceania Australia Micronesia Fiji Kiribati Marshall Islands New Zealand Papua New Guinea Samoa Solomon Islands Tonga Tuvalu Vanuatu South America Argentina Bolivia Brazil Chile Colombia Ecuador Guyana Paraguay Peru Suriname Uruguay Venezuela Law Case law Constitutional law History of abortion law Laws by country Buffer zones Conscientious objection Fetal protection Heartbeat bills Informed consent Late-term restrictions Parental involvement Spousal consent Methods Vacuum aspiration Dilation and evacuation Dilation and curettage Intact D&X Hysterotomy Instillation Menstrual extraction Abortifacient drugs Methotrexate Mifepristone Misoprostol Oxytocin Self-induced abortion Unsafe abortion Religion Buddhism Christianity Catholicism Hinduism Islam Judaism Scientology Category This abortion -related article is a stub .
-
Hiv/aids In Lesotho
Wikipedia
Drug treatments must also be stored properly. [9] Costs of medication and continual treatment are prohibitive for many Basotho. ... Consolidated Guidelines on the Use of Antiretroviral Drugs for Treating and Preventing Infection, 2004, pp. 1-156. ... World Bank. Accessed November 19, 2017. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SN.ITK.DEFC.ZS. ^ WHO, and United Nations. ... World Health Organization. Accessed November 19, 2017. https://www.who.int/gho/countries/lso.pdf. ^ Lai, YS; et al. (2015). ... XE Currency Converter. Accessed November 25, 2017. http://www.xe.com/currencyconverter/convert/?
-
Small-Cell Carcinoma
Wikipedia
PMID 21475596 . ^ National Organization for Rare Disorders -- Small Cell Lung Cancer | https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/small-cell-lung-cancer/ ^ SEER Cancer Stats (2016) | https://seer.cancer.gov/explorer/application.php? ... Cure Today . ^ FDA Approves Opdivo (Nivolumab) for Small Cell Lung Cancer | https://www.cancer.org/latest-news/fda-approves-opdivo-nivolumab-for-small-cell-lung-cancer.html ^ FDA approves atezolizumab for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer | https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm633814.htm ^ Concurrent Tecentriq Adds First Survival Benefit Seen in Small Cell Lung Cancer in 20 Years | https://www.curetoday.com/articles/concurrent-tecentriq-adds-first-survival-benefit-seen-in-small-cell-lung-cancer-in-20-years ^ Drugs.com - What is the cost of Tecentriq?| https://www.drugs.com/medical-answers/cost-tecentriq-3064818/ ^ Tecentriq: "Updated exploratory OS analysis" | https://www.tecentriq-hcp.com/sclc/clinical-data-efficacy/study-efficacy.html ^ Reuters, "Canadian regulator considers changes to new drug pricing plan", Feb 20, 2020. https://ca.reuters.com/article/domesticNews/idCAKBN20E2LI ^ Reuters, "NICE Cites Cost in Deciding Against Atezolizumab for Frontline Advanced Small Cell Lung Cancer", Jan 6, 2020 https://www.onclive.com/web-exclusives/nice-cites-cost-in-deciding-against-atezolizumab-for-frontline-advanced-small-cell-lung-cancer ^ https://www.cancer.org/latest-news/study-chest-radiation-helps-small-cell-lung-cancer-patients-live-longer.html ^ https://www.cancer.gov/types/lung/hp/small-cell-lung-treatment-pdq ^ [[Treatment for Small Cell Lung Cancer, Canadian Cancer Society| http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/lung/treatment/treatment-for-small-cell-lung-cancer/? ... sectionSEL=15&pageSEL=sect_15_table.13 ^ https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2015/browse_csr.php? ... PMID 18390646 . ^ a b [2016 Cancer Stats by SEER | https://seer.cancer.gov/explorer/application.php?SMARCA4, TP53, PYCARD, RB1, CYP2A6, UGT1A1, NPPA, MTOR, BIRC5, CDKN2A, KIT, PDGFRA, NKX2-1, EGFR, H3P10, TTF1, ERG, CHGA, GSTM1, SMARCA2, TMPRSS2, SYP, CD274, NCAM1, SMARCA1, AR, ASCL1, KRAS, SOX2, EZH2, NUTM1, ERBB2, ENO2, CCND1, BCL2, UVRAG, CKAP4, INSM1, STMN1, TP63, SCLC1, AXL, GRP, PAX5, KLK3, POMC, PTEN, ALK, AURKA, RPE65, FOXA2, CDX2, CD44, CHEK1, EWSR1, EML4, ING5, KRT20, BCOR, FBXW7, LOC110806263, RHBDF2, TLE1, LIN28A, THRA, THBD, TGM2, TGFBR2, SF3B6, TGFB1, TERT, DNER, H3P8, MUC16, SYK, SFXN1, CTAG1A, SNCA, SMARCC1, SMARCB1, H3P23, SCGB1A1, TICAM2, LAMTOR2, VIM, POU5F1P4, TMED7-TICAM2, DICER1, POU5F1P3, SATB2, CIC, RASSF1, RPP14, RIPK3, MIR148B, SUB1, YBX3P1, DCTN6, RPL17-C18orf32, IL23R, IGF2BP3, ZNRD2, CDK2AP2, RAD50, SPATA2, FEZ1, NAPSA, TMED7, ARID1A, C17orf97, SMUG1, ABL1, SLC22A3, IGF1R, CTNNB1, CYP1A1, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, DNMT3B, HBEGF, EGF, ETV4, FGFR1, FHIT, FSHR, SFN, MSH6, FOXA1, HRAS, CTAG1B, CREBBP, CLDN4, CALCA, AKT2, APC, STS, FOXL2, BRAF, BSG, CASP8, CPB2, CAV1, CBR1, CCK, CDK4, CDKN1B, CEACAM5, IFI27, IGFBP2, SKP2, IL6, PDCD1, PIGR, PIK3CA, ADA, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, POU5F1, PPARG, PSMD9, RAF1, RET, RNASE3, RPL17, S100A9, SET, PAX3, NOTCH2, NFATC2, MAP2, CXCL8, CXCR2, ISL1, KRT19, LGALS3, SMAD4, MET, MYCL, CD99, MLH1, MRC1, MSH2, MTHFR, MYB, PIK3CB
-
Ophidiophobia
Wikipedia
The word comes from the Greek words "ophis" ( ὄφις ), snake, and "phobia" ( φοβία ) meaning fear. [1] About a third of adult humans are ophidiophobic, making this the most common reported phobia. [2] In The Handbook of the Emotions (1993), psychologist Arne Öhman studied pairing an unconditioned stimulus with evolutionarily-relevant fear-response neutral stimuli ( snakes and spiders ) versus evolutionarily-irrelevant fear-response neutral stimuli ( mushrooms , flowers , and physical representation of polyhedra ) on human subjects and found that ophidiophobia and arachnophobia required only one pairing to develop a conditioned response while mycophobia, anthophobia, and phobias of physical representations of polyhedra required multiple pairings and went extinct without continued conditioning while the conditioned ophidiophobia and arachnophobia were permanent. [3] Psychologist Paul Ekman cites the following anecdote recounted by Charles Darwin in The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals (1872) in connection with Öhman's research: I put my face close to the thick glass-plate in front of a puff-adder in the Zoological Gardens , with the firm determination of not starting back if the snake struck at me; but, as soon as the blow was struck, my resolution went for nothing, and I jumped a yard or two backwards with astonishing rapidity. My will and reason were powerless against the imagination of a danger which had never been experienced. [4] Similarly, psychologists Susan Mineka, Richard Keir, and Veda Price found that laboratory-raised rhesus macaques did not display fear if required to reach across a toy snake to receive a banana unless the macaque was shown a video of another macaque withdrawing in fright from the toy (which produced a permanent fear-response), while being shown a similar video of another macaque displaying fear of a flower produced no similar response. [5] Psychiatrists Isaac Marks and Randolph M. ... ISBN 978-0805083392 . ^ Mineka, Susan; Keir, Richard; Price, Veda (1980). "Fear of snakes in wild- and laboratory-reared rhesus monkeys ( Macaca mulatta )" (PDF) . ... ISBN 978-0471264033 . ^ Nesse, Randolph (2019). Good Reasons for Bad Feelings: Insights from the Frontier of Evolutionary Psychiatry .
-
Early Childhood Caries
Wikipedia
With new products being put on supermarket shelves with irresistible prices, this can largely influence what people buy. ... Pediatr Dent [Internet]. 2016;38(6):52–54. Available from: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/aapd/pd/2016/00000038/00000006/art00024 ^ a b c d Fejerskov O, Edwina A, Kidd M. ... Early childhood caries: resource centre [Internet]. Elsevier; 2016. Available from: http://earlychildhoodcariesresourcecenter.elsevier.com/ ^ a b c Locker D. ... Colgate-Palmolive Company; 2017. Available from: http://www.colgate.com.au/en/au/oc/oral-health/basics/fluoride/article/what-is-fluoride ^ a b c d e f Kawashita Y, Kitamura M, Saito T. ... Retrieved 21 February 2020 . ^ U.S. Food &Drug Administration. "FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA review results in new warnings about using general anesthetics and sedation drugs in young children and pregnant women" .
-
Tuberculosis In India
Wikipedia
These patients were given all the first-line drugs and second-line drugs that usually are prescribed to treat TB, and as a result, were resistant to all. ... TB Facts. Retrieved April 3, 2013, from http://www.tbfacts.org/tb-statistics-india.html ^ WHO. ... C-Health. Retrieved April 3, 2103, from http://chealth.canoe.ca/channel_condition_info_details.asp? ... A; Ajbani, K. K; Rodrigues, C (2011). "Totally Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in India" . ... ] ^ Coghaln, Andy (12 January 2012). "Totally drug-resistant TB at large in India" .
-
Ras-Associated Autoimmune Leukoproliferative Disorder
Wikipedia
"Targeting RAS Signaling Pathways in Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia". Current Drug Targets . 8 (6): 715–725. doi : 10.2174/138945007780830773 . PMID 17584027 . ^ Calvo, K. R.; Price, S.; Braylan, R. C.; Oliveira, J. ... ISSN 0006-4971 . PMID 21063026 . ^ http://www.clinicaltrials.gov , study ID NCT00246857, NCT00001467, and others External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : D72.8 OMIM : 614470 External resources Orphanet : 268114
-
Hiv And Pregnancy
Wikipedia
Integrase inhibitors (IIs) are generally the third drug in the regimen when a PI cannot be used. ... Efavirenz ( brand name Sustiva, shortened as EFV, and a component of the combination drug Atripla ) is classified as a category D drug by the US Food and Drug Administration indicating there are risks associated with its use during pregnancy. ... Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, tuberculosis and injection drug use are some of the most common comorbidities associated with HIV. ... HIV Surveillance Report, 2018 (Updated); vol. 31. http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/hiv-surveillance.html. ... McGraw-Hill; Accessed 01/14/2021. https://accessmedicine-mhmedical-com.ezproxy.med.ucf.edu/content.aspx?
-
Abortion In Afghanistan
Wikipedia
This includes a pregnant mother being murdered, leading to the murderer being tried for both deaths; or if the father dies while the mother is pregnant, the estate will not be divided until the birth of the child, because the fetus has rights to the estate and the father's inheritances. [3] However, in cases of rape, abortion is not permitted because one crime cannot be solved with another crime, and having an abortion for reasons other than the health of the mother and the baby is considered a crime. ... Many women account that they are stuck deciding between whether to have an abortion or have a child outside of marriage, both of which cause them to be ostracized from society. [6] Some reasons that lead women to pursue abortions to avoid being ostracized include drug and/or alcohol addicted husbands, poverty, and being single. ... Since women are typically unemployed, rounding up the funds for an abortion can be difficult. The price of an abortion has decreased from 250,000 Afghanis (US$3,500) to 17,500 Afghanis (US$250). [6] This decrease has been seen because of the increasing need of abortions. But the price is still 15,000 Afghani (US$150) higher than the average price of an abortion in the United States , where abortions are legal and generally publicly accepted. [6] Safety of the procedure [ edit ] Afghanistan is in the top 16 countries worldwide for the highest mortality rate from abortion . [14] The healthcare system in Afghanistan is also not at a level to properly care for pregnant mothers. [4] Every 2 hours there is a pregnancy-related death in Afghanistan. [6] The high maternal mortality is due to lack of post procedure care. ... PMID 25645657 . v t e Abortion in Asia Sovereign states Afghanistan Armenia Azerbaijan Bahrain Bangladesh Bhutan Brunei Cambodia China Cyprus East Timor (Timor-Leste) Egypt Georgia India Indonesia Iran Iraq Israel Japan Jordan Kazakhstan North Korea South Korea Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Lebanon Malaysia Maldives Mongolia Myanmar Nepal Oman Pakistan Philippines Qatar Russia Saudi Arabia Singapore Sri Lanka Syria Tajikistan Thailand Turkey Turkmenistan United Arab Emirates Uzbekistan Vietnam Yemen States with limited recognition Abkhazia Artsakh Northern Cyprus Palestine South Ossetia Taiwan Dependencies and other territories British Indian Ocean Territory Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Hong Kong Macau Book Category Asia portal v t e Abortion Main topics Definitions History Methods Abortion debate Philosophical aspects Abortion law Movements Abortion-rights movements Anti-abortion movements Issues Abortion and mental health Beginning of human personhood Beginning of pregnancy controversy Abortion-breast cancer hypothesis Anti-abortion violence Abortion under communism Birth control Crisis pregnancy center Ethical aspects of abortion Eugenics Fetal rights Forced abortion Genetics and abortion Late-term abortion Legalized abortion and crime effect Libertarian perspectives on abortion Limit of viability Malthusianism Men's rights Minors and abortion Natalism One-child policy Paternal rights and abortion Prenatal development Reproductive rights Self-induced abortion Sex-selective abortion Sidewalk counseling Societal attitudes towards abortion Socialism Toxic abortion Unsafe abortion Women's rights By country Africa Algeria Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Cameroon Cape Verde Central African Republic Chad Egypt Ghana Kenya Namibia Nigeria South Africa Uganda Zimbabwe Asia Afghanistan Armenia Azerbaijan Bahrain Bangladesh Bhutan Brunei Cambodia China Cyprus East Timor Georgia India Iran Israel Japan Kazakhstan South Korea Malaysia Nepal Northern Cyprus Philippines Qatar Saudi Arabia Singapore Turkey United Arab Emirates Vietnam Yemen Europe Albania Andorra Austria Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Kazakhstan Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Netherlands North Macedonia Norway Poland Portugal Romania Russia San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Ukraine United Kingdom North America Belize Canada Costa Rica Cuba Dominican Republic El Salvador Guatemala Mexico Nicaragua Panama Trinidad and Tobago United States Oceania Australia Micronesia Fiji Kiribati Marshall Islands New Zealand Papua New Guinea Samoa Solomon Islands Tonga Tuvalu Vanuatu South America Argentina Bolivia Brazil Chile Colombia Ecuador Guyana Paraguay Peru Suriname Uruguay Venezuela Law Case law Constitutional law History of abortion law Laws by country Buffer zones Conscientious objection Fetal protection Heartbeat bills Informed consent Late-term restrictions Parental involvement Spousal consent Methods Vacuum aspiration Dilation and evacuation Dilation and curettage Intact D&X Hysterotomy Instillation Menstrual extraction Abortifacient drugs Methotrexate Mifepristone Misoprostol Oxytocin Self-induced abortion Unsafe abortion Religion Buddhism Christianity Catholicism Hinduism Islam Judaism Scientology Category
-
Abortion In Finland
Wikipedia
Otherwise two doctors' signatures are required. Reasons for approval are the potential physical or mental distress if the pregnancy runs to term; or if the pregnancy arises from a serious crime (e.g. rape or incest) or if an illness of either parent would make it difficult to provide a normal upbringing for the child. ... Above 20 weeks, a threat to the physical life of the mother is the only valid reason for terminating a pregnancy. [2] [3] [4] History [ edit ] In Finland , abortion was illegal until 1950, when the Parliament of Finland legalized abortions to preserve the physical or mental health of the woman, if the woman was under 16, if the fetus might be deformed, or the woman had been raped . [5] Under pressure from the women's liberation movement and supportive editorials from most national newspapers, Finnish law was further liberalized in 1970. [6] The 1970 law allowed abortion up to 16 weeks of pregnancy for broad socio-economic reasons, if the woman was younger than 17, if the woman was older than 40, if the woman had already had four children, or if at least one parent would be unable to raise the child owing to disease or mental disturbance. [7] This time limit was lowered from 16 to 12 weeks in 1979. [8] The 1970 law also allowed abortion up to 20 weeks of pregnancy in the event of fetal deformity or physical threat to the woman's health. ... See also [ edit ] Abortion by country Abortion debate Abortion law Religion and abortion References [ edit ] ^ [1] (in Finnish) ^ http://www.valvira.fi/terveydenhuolto/toimintaluvat/raskauden_keskeyttaminen/lupa_raskauden_keskeyttamiseen ^ http://www.valvira.fi/terveydenhuolto/toimintaluvat/raskauden_keskeyttaminen ^ http://www.infopankki.fi/en/living-in-finland/health/abortion ^ Pirkko Niemelä. 1988. ... Retrieved June 14, 2007. v t e Abortion in Europe Sovereign states Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Kazakhstan Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Netherlands North Macedonia Norway Poland Portugal Romania Russia San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Turkey Ukraine United Kingdom England Northern Ireland Scotland Wales Vatican City States with limited recognition Abkhazia Artsakh Kosovo Northern Cyprus South Ossetia Transnistria v t e Abortion Main topics Definitions History Methods Abortion debate Philosophical aspects Abortion law Movements Abortion-rights movements Anti-abortion movements Issues Abortion and mental health Beginning of human personhood Beginning of pregnancy controversy Abortion-breast cancer hypothesis Anti-abortion violence Abortion under communism Birth control Crisis pregnancy center Ethical aspects of abortion Eugenics Fetal rights Forced abortion Genetics and abortion Late-term abortion Legalized abortion and crime effect Libertarian perspectives on abortion Limit of viability Malthusianism Men's rights Minors and abortion Natalism One-child policy Paternal rights and abortion Prenatal development Reproductive rights Self-induced abortion Sex-selective abortion Sidewalk counseling Societal attitudes towards abortion Socialism Toxic abortion Unsafe abortion Women's rights By country Africa Algeria Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Cameroon Cape Verde Central African Republic Chad Egypt Ghana Kenya Namibia Nigeria South Africa Uganda Zimbabwe Asia Afghanistan Armenia Azerbaijan Bahrain Bangladesh Bhutan Brunei Cambodia China Cyprus East Timor Georgia India Iran Israel Japan Kazakhstan South Korea Malaysia Nepal Northern Cyprus Philippines Qatar Saudi Arabia Singapore Turkey United Arab Emirates Vietnam Yemen Europe Albania Andorra Austria Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Kazakhstan Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Netherlands North Macedonia Norway Poland Portugal Romania Russia San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Ukraine United Kingdom North America Belize Canada Costa Rica Cuba Dominican Republic El Salvador Guatemala Mexico Nicaragua Panama Trinidad and Tobago United States Oceania Australia Micronesia Fiji Kiribati Marshall Islands New Zealand Papua New Guinea Samoa Solomon Islands Tonga Tuvalu Vanuatu South America Argentina Bolivia Brazil Chile Colombia Ecuador Guyana Paraguay Peru Suriname Uruguay Venezuela Law Case law Constitutional law History of abortion law Laws by country Buffer zones Conscientious objection Fetal protection Heartbeat bills Informed consent Late-term restrictions Parental involvement Spousal consent Methods Vacuum aspiration Dilation and evacuation Dilation and curettage Intact D&X Hysterotomy Instillation Menstrual extraction Abortifacient drugs Methotrexate Mifepristone Misoprostol Oxytocin Self-induced abortion Unsafe abortion Religion Buddhism Christianity Catholicism Hinduism Islam Judaism Scientology Category
-
Delusional Disorder
Wikipedia
The patient may believe that he/she has been drugged, spied upon, harmed, harassed and so on and may seek "justice" by making reports, taking action or even acting violently. ... The delusions do not interfere with general logical reasoning (although within the delusional system the logic is perverted) and there is usually no general disturbance of behavior. ... Cleveland Clinic. 22 January 2018 . Retrieved 12 May 2020 . ^ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539855/#:~:text=Age%20mean%20age%20of%20onset,is%20more%20common%20in%20females . ^ https://www.webmd.com/schizophrenia/qa/how-can-you-recover-from-delusional-disorder ^ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9599-delusional-disorder#:~:text=Environmental%2Fpsychological.,vulnerable%20to%20developing%20delusional%20disorder . ^ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9599-delusional-disorder#:~:text=Environmental%2Fpsychological. ... Cite journal requires |journal= ( help ) ^ http://www.health.am/psy/delusional-disorder Delusional Disorder.