Load FindZebra Summary
Disclaimer:
FindZebra Search conducts a search using our specialized medical search engine.
FindZebra Summary uses the text completions API
(subject to OpenAI’s API data usage policies)
to summarize and reason about the search results.
The search is conducted in publicly available information on the Internet that we present “as is”.
You should be aware that FindZebra is not supplying any of the content in the search results.
FindZebra Summary is loading...
-
Nephrosis
Wikipedia
Epidemiology [ edit ] Disability-adjusted life year for nephritis and nephrosis per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004. [3] no data less than 40 40-120 120-200 200-280 280-360 360-440 440-520 520-600 600-680 680-760 760-840 more than 840 References [ edit ] ^ a b Elsevier , Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary , Elsevier. ^ a b c Nephrosis at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) ^ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates" .VIM, F2, DDIT3, NES, EDN1, NPHS2, ALB, REN, AGT, EDNRB, SOD1, ICAM1, ITGB2, HPSE, DES, LAMB2, HAVCR1, LRP2, NPPB, NPPA, CCL1, IL1B, CX3CL1, SREBF2, STAR, PTPRU, PDPN, CCL7, CYP3A43, ACE, CD59, CFH, CX3CR1, CYP3A5, ANGPT1, ANGPT2, CYP11A1, CD36, CYP27B1, TGFB1, APOA1, NPHS1, VEGFA, CLDN1, OLFM1, SGPL1, TNFSF10, LGALSL, NSD3, CLDN7, CST3, NDST1, CTSL, TRPC6, STAT5A, STAT3, CYP2C19, CCL13, SALL1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, HBEGF, EDNRA, MYOC, GATA3, ACTB
-
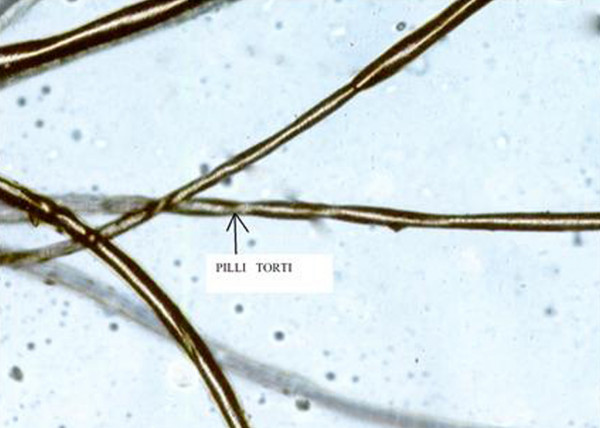
Pili Torti, Early-Onset
OMIM
Microscopic analysis showed flattened hair shafts that were twisted around the long axis, usually at 180 degrees, but ranging from 90 to 360 degrees. There were multiple broken hairs showing trichorrhexis nodosa (fractured hair with the ends stuck together resembling broomsticks). ... INHERITANCE - Autosomal dominant - Autosomal recessive - Isolated cases HEAD & NECK Teeth - Enamel hypoplasia may occur SKIN, NAILS, & HAIR Skin - Hyperkeratosis pilaris may occur Nails - Nail dystrophy may occur Hair - Brittle, dry hair - Flattened hair - Hair appears spangled in reflective light - Hair twists on long axis, 90 to 360 degrees - Hair fragility MISCELLANEOUS - Onset in early childhood - Hair may normalize at puberty ▲ Close
-
Brugada Syndrome 3
OMIM
The patient had a brother who died of cardiac arrest at 45 years of age, and 2 daughters with QTc intervals of 360 and 373 ms, respectively. The other proband was a 44-year-old man of European descent who had prominent ST segment elevation in V1, saddleback ST segment elevation in V2, a prominent J wave in lead III, and a QTc of 360 ms; he was also recently diagnosed with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (see 158900).SCN5A, SCN10A, PKP2, CACNA2D1, KCNE5, CACNA1C, KCND3, SCN1B, RANGRF, TRPM4, SCN3B, KCNJ8, SCN2B, ABCC9, CACNB2, KCNE3, SLMAP, KCNH2, GPD1L, HEY2, HCN4, AKAP9, CALM2, ANK2, LINC02523, KCNQ1, RYR2, VCL, MYH7, FGF11, NOS1AP, KCNE2, HARS1, GJA1, FGF14, FGF12, SEMA3A, EPHA3, BHLHE40, EGR3, DSP, DELEC1, DSG2, ATN1, XIRP1, LRRC10, HGS, NR4A3, KCNAB2, MFAP1, RRAD, ATXN2, SCD, KCNK1, APRT, SCN4B, KCNE1, KCND2, SRSF5, SKP1, TBX5, ELOC, ELOB, ELOA, IDS, SCN4A
-
Prepatellar Bursitis
Wikipedia
It generally does not produce a significant amount of pain unless pressure is applied directly. [4] The area may be red ( erythema ), warm to the touch, or surrounded by cellulitis , particularly if infection is present, often accompanied by fever . [5] : p. 608 Unlike arthritis , except in severe cases prepatellar bursitis generally does not affect the range of motion of the knee, though it may cause some discomfort in complete flexion of the joint. [6] : p. 360 Flexion and extension of the knee may be accompanied by crepitus , the audible grating of bones, ligaments, or particles within the excess synovial fluid. [7] : p. 20 Causes [ edit ] In human anatomy , a bursa is a small pouch filled with synovial fluid . ... The trauma can cause extravasation of nearby fluids into the bursa, which stimulates an inflammatory response. [2] This response occurs in two phases: The vascular phase, in which the blood flow to the surrounding area increases, and the cellular phase, in which leukocytes migrate from the blood to the affected area. [7] : p. 22 Other possible causes include gout , sarcoidosis , CREST syndrome , [6] : p. 359 diabetes mellitus , alcohol abuse , uremia , and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease . [7] : p. 22 Some cases are idiopathic , though these may be caused by trauma that the patient does not remember. [5] : pp. 607–8 The prepatellar bursa and the olecranon bursa are the two bursae that are most likely to become infected, or septic . [10] Septic bursitis typically occurs when the trauma to the knee causes an abrasion , though it is also possible for the infection to be caused by bacteria traveling through the blood from a pre-existing infection site. [11] In approximately 80% of septic cases, the infection is caused by Staphylococcus aureus ; other common infections are Streptococcus , Mycobacterium , and Brucella . [6] : p. 359 It is highly unusual for septic bursitis to be caused by anaerobes , fungi , or Gram-negative bacteria . [5] : p. 608 In very rare cases, the infection can be caused by tuberculosis . [12] Diagnosis [ edit ] There are several types of inflammation that can cause knee pain , including sprains , bursitis, and injuries to the meniscus . [9] A diagnosis of prepatellar bursitis can be made based on a physical examination and the presence of risk factors in the person's medical history ; swelling and tenderness at the front of the knee, combined with a profession that requires frequent kneeling, suggest prepatellar bursitis. [2] Swelling of multiple joints along with restricted range of motion may indicate arthritis instead. [5] : p. 608 A physical examination and medical history are generally not enough to distinguish between infectious and non-infectious bursitis; aspiration of the bursal fluid is often required for this, along with a cell culture and Gram stain of the aspirated fluid. [6] : p. 360 Septic prepatellar bursitis may be diagnosed if the fluid is found to have a neutrophil count above 1500 per microliter , [5] : p. 608 a threshold significantly lower than that of septic arthritis (50,000 cells per microliter). [6] : p. 360 A tuberculosis infection can be confirmed using a radiograph of the knee and urinalysis . [12] Prevention [ edit ] It is possible to prevent the onset of prepatellar bursitis, or prevent the symptoms from worsening, by avoiding trauma to the knee or frequent kneeling. [5] : p. 610 Protective knee pads can also help prevent prepatellar bursitis for those whose professions require frequent kneeling and for athletes who play contact sports , such as American football , basketball , and wrestling . [13] Treatment [ edit ] Non-septic prepatellar bursitis can be treated with rest, the application of ice to the affected area, and anti-inflammatory drugs , particularly ibuprofen . Elevation of the affected leg during rest may also expedite the recovery process. [13] Severe cases may require fine-needle aspiration of the bursa fluid, sometimes coupled with cortisone injections. [11] However, some studies have shown that steroid injections may not be an effective treatment option. [14] After the bursitis has been treated, rehabilitative exercise may help improve joint mechanics and reduce chronic pain . [15] : p. 2320 Opinions vary as to which treatment options are most effective for septic prepatellar bursitis. [6] : p. 360 McAfee and Smith recommend a course of oral antibiotics , usually oxacillin sodium or cephradine , and assert that surgery and drainage are unnecessary. [5] : p. 609 Wilson-MacDonald argues that oral antibiotics are "inadequate", and recommends intravenous antibiotics for managing the infection. [1] Some authors suggest surgical irrigation of the bursa by means of a subcutaneous tube. [6] : p. 360 [16] Others suggest that bursectomy may be necessary for intractable cases; the operation is an outpatient procedure that can be performed in less than half an hour. [17] : p. 357 Epidemiology [ edit ] The various nicknames associated with prepatellar bursitis arise from the fact that it commonly occurs among those individuals whose professions require frequent kneeling , such as carpenters, carpet layers, gardeners, housemaids , mechanics, miners, plumbers, and roofers. [2] [4] [5] : p. 607 The exact incidence of the condition is not known; it is difficult to estimate because only severe septic cases require hospital admission, and mild non-septic cases generally go unreported. [5] : p. 607 Prepatellar bursitis is more common among males than females.
-
Doege–potter Syndrome
Wikipedia
Actual rates of hypoglycemia associated with a fibrous tumor are quite rare (a 1981 study of 360 solitary fibrous tumors of the lungs found that only 4% caused hypoglycemia [8] ), and are linked to large tumors with high rates of mitosis . [9] Removal of the tumor will normally resolve the symptoms. [1] [9] Tumors causing DPS tend to be quite large; [10] in one case a 3 kg (6.6 lb), 23×21×12 cm (9.1×8.3×4.7 in) mass was removed, sufficiently large to cause a collapsed lung . [5] In X-rays , they appear as a single mass with visible, defined borders, appearing at the edges of the lungs or a fissure dividing the lobes of the lungs. [10] Similar hypoglycemic effects have been related to mesenchymal tumors. [6] References [ edit ] ^ a b Balduyck B, Lauwers P, Govaert K, Hendriks J, De Maeseneer M, Van Schil P (July 2006). ... "Solitary fibrous tumors of the pleura: eight new cases and review of 360 cases in the literature". Cancer . 47 (11): 2678–89. doi : 10.1002/1097-0142(19810601)47:11<2678::AID-CNCR2820471126>3.0.CO;2-9 .
- Dyserythropoiesis Wikipedia
- Ring Dermoid Of Cornea OMIM
-
Prefibrotic Primary Myelofibrosis
Wikipedia
British Journal of Haematology . 186 (2): 358–360. doi : 10.1111/bjh.15840 . ISSN 1365-2141 . ... British Journal of Haematology . 186 (2): 358–360. doi : 10.1111/bjh.15840 . ISSN 1365-2141 .
- Limb Body Wall Complex Wikipedia
- Short Qt Syndrome 3 OMIM
-
Nephritis
Wikipedia
Loss of these proteins can result in blood clots, causing sudden stroke. [16] Diagnosis [ edit ] The diagnosis depends on the cause of the nephritis, in the case of lupus nephritis, blood tests , X-rays and an ultrasound can help ascertain if the individual has the condition. [3] Treatment [ edit ] Disease burden of nephritis/ nephrosis worldwide in 2004. [17] no data less than 40 40–120 120–200 200–280 280–360 360–440 440–520 520–600 600–680 680–760 Treatment (or management) of nephritis depends on what has provoked the inflammation of the kidney(s).LGALS3, ALB, LGALS9, LGALS1, LEPR, HLA-B, CCR5, FAS, PLAU, CXCR2, ICAM1, IL4, CYP2J2, CASP8, ITGA4, CCL3, CCND2, ITGB2, ITGAL, PTK2B, SNRPD1, SERPINB7, PTK2, SMAD6, SMAD7, AGTR1, EDN1, COL4A5, MYH9, FCGR2A, DNASE1, FCGR2B, C1QA, SPP1, STAT4, COL4A3, THY1, CTLA4, COL4A4, TREX1, DNASE1L3, PTPN22, UMOD, PLG, CD151, ALMS1, IRAK1, CASP10, C1R, TNF, FCGR3A, CCL2, IGAN1, ACE, HSP90B2P, HLA-DRB1, IGHA1, IL6, IL10, TGFB1, CXCL8, IL1B, CXCR3, IL17A, LTA, MPO, IL22, FLI1, NLRP3, CD40LG, FCGR3B, MIR155, RBM45, TLR9, ITGAM, NLRP1, UCHL1, CD40, IL10RA, TNFRSF1B, IL18, CXCL12, MYD88, CAMK4, CST3, LCN2, C3, SOX9, ANXA2, TLR4, CCR2, MBL2, TNFSF13B, MMP3, PTEN, NFE2L2, CD274, TLR7, CFH, PAX2, NEIL3, IGHG3, GAS6, NPHS2, FOXP3, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, FCN2, IL23A, IFNA1, IFNA13, IKBKG, AIMP1, TLR5, ST8SIA4, ADIPOQ, TLR3, AIM2, THEMIS2, KLK4, RAPGEF5, CLDN2, SOCS1, DDX39B, LST1, TM7SF2, SEMA5A, FGF23, YWHAZ, TNFSF10, XK, BAP1, TRAP1, SCGB1A1, VCAM1, VDR, VEGFA, IL18BP, SIRT1, DDX39A, PLB1, GAS5, ERVK-6, GORASP1, WNK1, VTCN1, HVCN1, IL17F, LRRK2, SLC15A4, EMB, GPBAR1, IL21, NLRP6, SUMO4, MIR146A, MIR193A, MIR20A, MIR21, MT1IP, SPAG11A, ERVK-20, THRA1/BTR, ACE2, HAMP, TNIP1, PTGDR2, IKZF1, SEMA3A, SPAG11B, PROCR, CXCL13, TXNIP, PPARGC1A, BTG3, IL24, SLC7A9, CIC, VANGL2, PADI4, RASGRP3, GREM1, HAVCR1, ERVW-1, MBL3P, TNFRSF12A, IL17RD, OTUB1, ALG1, TIMP4, ACR, THRA, IL1A, CCN2, ATN1, EGFR, ELANE, ENO1, ERN1, ESR1, ETS1, FCAR, FGF2, FLII, FN1, GABPA, GAPDH, GATA3, GSTT1, HLA-A, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HSPE1, IRF8, IFN1@, IGBP1, CRYGD, CRP, CR1, CAST, AGT, AIF1, ALOX15, ANGPT1, AXL, B2M, BCL2, BGN, BRAF, BTK, CASP1, COL4A2, CASP3, CAV1, CD1C, CD28, CD86, CD34, CD44, CDKN2A, CCR1, ACKR2, IKBKB, IL1RN, TGFBR2, IL2, NOS2, NOS3, CCN3, YBX1, OGG1, SERPINE1, PDCD1, PDGFB, PF4, PLA2G1B, PODXL, MAPK3, PTGER2, PTGS1, PTGS2, PTPRC, PTPRO, PTX3, RELA, CCL5, SNRPA, SYT1, TRBV20OR9-2, NFKB1, NEU1, ACTN4, MT1B, IL5, IL7R, IL11, CXCL10, KDR, CD46, MAP3K5, MET, MMP8, MT1A, MT1E, MTNR1A, MT1F, MT1G, MT1H, MT1JP, MT1M, MT1L, MT1X, MT2A, COX1, COX2, MTCO2P12
- Cataract, Microcephaly, Failure To Thrive, Kyphoscoliosis Syndrome OMIM
-
Age-Related Hearing Impairment 2
OMIM
In 1,332 non-Finnish European individuals, the authors found a significant association between ARHI and rs11928865 within the GRM7 gene (604101) on chromosome 3p26.1-p25.1, which was replicated in 130 non-Finnish Europeans. In 360 Finnish individuals, rs779706 and rs779701 in the GRM7 gene showed significant association.
- Cementoblastoma Wikipedia
-
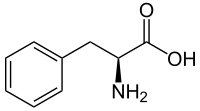
Phenylketonuria
Orphanet
According to the European guidelines for the management of PKU, the recommended maintenance level is usually between 120 and 360 micromol/L in newborns, with treatment considered essential in older patients with levels above 600 micromol/L.PAH, QDPR, G6PD, CAT, HNF1A, NEFH, PTS, LRIT1, SHCBP1, PAM, PRDM6, CACNA1A, PELI1, TTR, DMD, LAT, SPR, GCH1, MBP, SLC7A5, TH, GRAP2, SART3, BEST1, AIMP2, OLFM1, TBX1, SOD1, FARP2, PART1, AHSA1, SDS, TPX2, SLC3A2, RNF19A, MMACHC, POLDIP2, SND1, SLC38A7, NIF3L1, ASCC2, COL25A1, NAGS, SLC6A19, MCCD1, SLC22A5, ACADM, PMEL, SAA1, GRM5, GFAP, GCHFR, FN1, NQO1, DECR1, CUX1, MAPK14, CRP, CRK, CNP, CGA, ATR, ASS1, APP, HBB, MAOB, NBN, PGM1, RET, REN, ALB, PTH, MAPK1, POLG, PCNA, NFKB2, PCBD1, PAEP, OXCT1, OTC, OAS3, NME1, NCF1
-
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Deficiency
GeneReviews
However, since evidence suggests that individuals with classic PKU have demonstrable neurophysiologic changes when Phe levels are between 360 and 600 μmol/L (6 to 10 mg/dL), other experts recommend Phe restriction for any individual who has Phe levels >360 μmol/L (6 mg/dL) on an unrestricted diet. ... Risks include the following [Vockley et al 2014]: Intellectual disability (>90%).The threshold for this finding is a maternal Phe concentration consistently above 360 µmol/L during pregnancy with an inverse relationship between cognitive function and maternal Phe level above 360 µmol/L. ... Singh et al [2014] provide the following dietary recommendations: Maintain blood Phe between 120 and 360 μmol/L throughout the life span. ... Treatment in individuals with Phe levels consistently <600 μmol/L but >360 μmol/L remains controversial [Weglage et al 2001, Hanley 2011, van Spronsen 2011]. ... Maternal Phe concentration of 120-360 µmol/L during pregnancy is recommended.
- Maternal Phenylketonuria Orphanet
-
Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder
Wikipedia
Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences . 36 : 333–360. doi : 10.1007/7854_2016_457 . ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2 . ... Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 36 . pp. 333–360. doi : 10.1007/7854_2016_457 . ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2 .
- Infectious Necrotic Hepatitis Wikipedia
- Autosomal Dominant Vitreoretinochoroidopathy Orphanet