Load FindZebra Summary
Disclaimer:
FindZebra Search conducts a search using our specialized medical search engine.
FindZebra Summary uses the text completions API
(subject to OpenAI’s API data usage policies)
to summarize and reason about the search results.
The search is conducted in publicly available information on the Internet that we present “as is”.
You should be aware that FindZebra is not supplying any of the content in the search results.
FindZebra Summary is loading...
-
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 1
OMIM
In more than one-fourth of the pedigrees, linkage to no known locus could be established, suggesting the existence of a fifth BBS locus. Reviews Khan et al. (2016) reviewed the clinical spectrum and genetics of BBS, including genotype-phenotype correlations and contribution of each responsible gene to the total BBS mutational load. ... The authors conducted a comprehensive sequence analysis of all 14 BBS genes as well as the modifier gene CCDC28B (610162) in a cohort of 29 Arab BBS families. ... Croft et al. (1995) studied obesity and hypertension among nonhomozygous relatives of BBS patients, hypothesizing that BBS heterozygotes might be predisposed to these conditions. ... They concluded that the BBS gene may predispose male heterozygotes to obesity. ... In more than one-fourth of the pedigrees, linkage to no known locus could be established, suggesting the existence of a fifth BBS locus. Katsanis et al. (1999) collected a large number of BBS pedigrees of primarily North American and European origin and performed genetic analysis using microsatellites from all known BBS genomic regions.MKS1, BBS10, SDCCAG8, LZTFL1, BBIP1, CEP290, ARL6, IFT27, BBS2, MKKS, BBS4, BBS1, TTC8, ALMS1, IFT172, C8orf37, NPHP1, TMEM67, TBC1D32, BBS7, TRIM32, BBS9, BBS5, BBS12, TRAPPC3, ASTN2, PIGX, CEP19, ZDHHC24, CCDC28B, LEP, GLIS2, RTEL1, PLLP, PYY3, SULT1A4, PEG13, AZIN1, STOML3, RIN2, MAGEL2, CBLL2, MARVELD2, MYO3B, INPP5E, USP35, MUL1, WDPCP, IFT74, CEP131, SCAPER, INVS, NPY2R, NPY, NMB, NDN, MYO9A, MYO7A, RAB8A, KIFC3, KIF2A, INSR, IL18, GPT, GFAP, ERG, CCT, TNFRSF11B, PRKN, PCM1, ADIPOQ, CEP164, STUB1, FEM1B, RAPGEF5, IQCB1, FEZ1, TRPV1, PDE6B, VEGFA, SULT1A3, RHO, RFX1, RCVRN, PECAM1, SLX1A-SULT1A3
-
Mckusick-Kaufman Syndrome
GeneReviews
However, discrimination between MKS and BBS in the neonatal period is challenging, as the age-dependent features of BBS (including retinal dystrophy, obesity, and intellectual disability) have not developed [Slavotinek & Biesecker 2000]. ... Renal Anomalies and GI Malformations Although both renal anomalies and GI malformations have been identified in those with a clinical diagnosis of MKS, not all of these individuals have had molecular genetic testing nor were they followed to an age in which an eye exam could exclude the diagnosis of BBS. Since these physical findings are more common in those with a molecularly confirmed diagnosis of BBS, they should prompt screening for other clinical manifestations of BBS or molecular genetic testing for BBS. ... At least 26 genes are known to be associated with BBS. Pathogenic variants in MKKS (see Genetically Related Disorders) account for an estimated 6.3% of all BBS (see BBS Overview). ... Table 3 illustrates the phenotypic overlap between MKS and BBS [Schaefer et al 2011] (+ = major feature; ± = minor feature). ... Cardiac malformation Echocardiogram Specialist referral as appropriate Possible Bardet- Biedl syndrome (BBS) 2 Assessment of height, weight, & head circumference & initiation of a carefully maintained growth chart to document obesity If obesity or short stature present, this may indicate a diagnosis of BBS Determination of developmental status by standard screening tools to detect DD If present, this may indicate a diagnosis of BBS.
-
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome
MedlinePlus
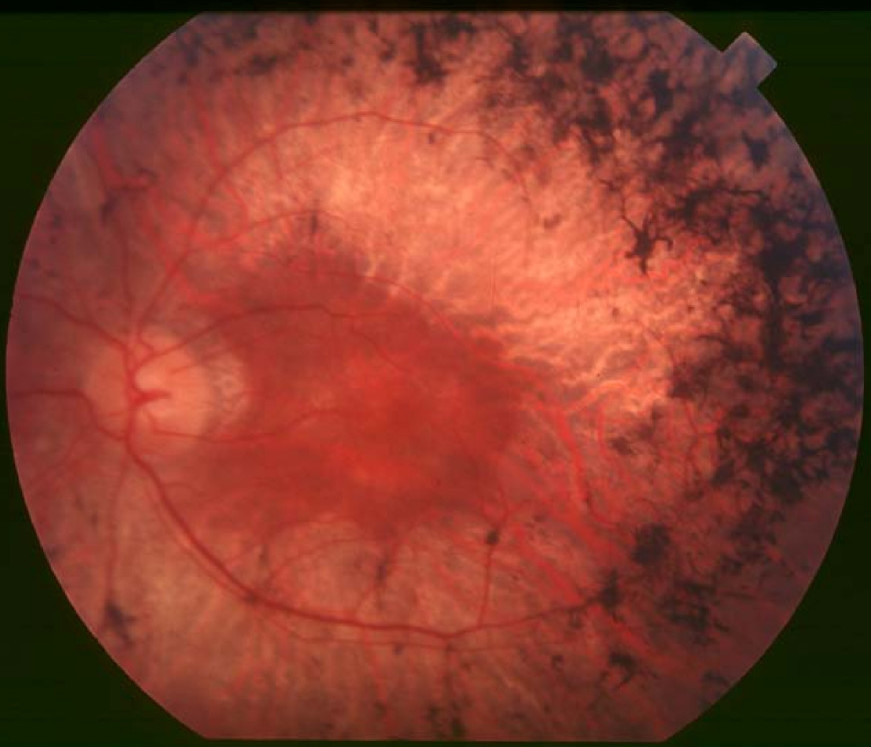
Cilia are also necessary for the perception of sensory input (such as sight, hearing, and smell). The proteins produced from BBS genes are involved in the maintenance and function of cilia. Mutations in BBS genes lead to problems with the structure and function of cilia. ... Another 20 percent of cases are caused by mutations in the BBS10 gene. The other BBS genes each account for only a small percentage of all cases of this condition. ... In affected individuals who have mutations in one of the BBS genes, mutations in additional genes may be involved in causing or modifying the course of the disorder. Studies suggest that these modifying genes may be known BBS genes or other genes. The additional genetic changes could help explain the variability in the signs and symptoms of Bardet-Biedl syndrome.
-
Laurence–moon Syndrome
Wikipedia
Physical therapy aims at improving the strength and ability using assisting tools such as ankle-foot orthitic braces, weight-bearing walkers and regular exercise. [ citation needed ] Eponym and nomenclature [ edit ] It is named after the physicians John Zachariah Laurence and Robert Charles Moon who provided the first formal description of the condition in a paper published in 1866. [3] [4] In the past, LMS has also been referred to as Laurence–Moon–Bardet–Biedl or Laurence–Moon–Biedl–Bardet syndrome, but Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS) is now usually recognized as a separate entity. [5] Recent advances in genetic typing of the phenotypically -wide variation in patients clinically diagnosed with either Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS) or Laurence-Moon Syndrome (LMS) have questioned whether LMS and BBS are genetically distinct. For example, a 1999 epidemiological study of BBS and LMS reported that "BBS proteins interact and are necessary for the development of many organs." "Two patients [in the study] were diagnosed clinically as LMS but both had mutations in a BBS gene. The features in this population do not support the notion that BBS and LMS are distinct." [6] A more recent 2005 paper also suggests that the two conditions are not distinct. [7] References [ edit ] ^ a b Farag, T.
-
Stature Quantitative Trait Locus 3
OMIM
Molecular Genetics Lorentzon et al. (2000) investigated the vitamin D receptor (VDR; 601769) gene polymorphisms, BsmI and TaqI, in 90 healthy Caucasian males. Boys with the BB genotype were shorter at birth (p = 0.01) and grew less from birth to age 16.9 +/- 0.3 (p = 0.01) than their Bb and bb counterparts. Both during puberty (age 16.9 +/- 0.3) and after puberty (age 19.3 +/- 0.7), the BB boys were shorter (p = 0.005 - 0.008).
-
Barber-Say Syndrome
Orphanet
Barber Say syndrome (BSS) is a rare ectodermal dysplasia with neonatal onset characterized by congenital generalized hypertrichosis, atrophic skin, ectropion and microstomia. Epidemiology BBS is a rare entity described in eleven patients to date. Clinical description BBS presents with congenital generalized hypertrichosis, facial dysmorphism (typically with bilateral ectropion, absent or sparse eyebrows and lashes, hypertelorism/telecanthus, broad nasal bridge, bulbous nose, anteverted nostrils, macrostomia, thin lips and misshapen ears), hyperlaxity and redundancy of the skin with deep folds, nipple hypoplasia and absence of mammary glands.
-
Bogart–bacall Syndrome
Wikipedia
Individuals who speak or sing outside of their normal range can develop BBS over a long period of misuse. Individuals who develop this syndrome tend to speak or perform with poor breath support and laryngeal muscle tension. ... Teachers may also be susceptible to BBS depending on their volume and how much they talk on a regular basis. ... Women are more likely than men to develop BBS due to the tendency of lowering their voices in a professional environment. ... ISBN 9780810887923 . ^ "RightDiagnosis: BBS Symptoms" . Retrieved 2011-09-03 . ^ Rubin, John S.; Sataloff, Robert T.; Korovin, Gwen S. (2014). ... Retrieved 2011-09-03 . ^ "RightDiagnosis: BBS Treatment" . Retrieved 2011-09-03 . ^ Gordon, Kate; Reed, Ona.
-
Shot Hole Disease
Wikipedia
Cherry leaves with a mild shot hole disease infection Shot hole disease (also called Coryneum blight ) is a serious fungal disease that creates BB -sized holes in leaves, rough areas on fruit, and concentric lesions on branches. The pathogen that causes shot hole disease is Wilsonomyces carpophilus . [1] Contents 1 Hosts and symptoms 2 Disease cycle 3 Management 4 Importance 5 References Hosts and symptoms [ edit ] Peach tree leaves displaying various stages of the shot hole disease: brown spots on the leaf with conidium holders in the middle (center) that eventually fall off, leaving BB-sized holes behind (left) Shot hole disease of apricot leaves The fungal pathogen Wilsonomyces carpophilus affects members of the Prunus genera. ... As the disease progresses the damaged areas become slightly larger and then dry up and fall away, leaving BB-sized holes behind. As the fungus spreads, more leaf tissue is damaged until the leaf falls.
-
Congenital Heart Defects, Hamartomas Of Tongue, And Polysyndactyly
OMIM
Because mutation in a Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS; see 209900)-related gene was found, the patient was investigated for ocular, renal, and pelvic abnormalities; none of these was found (see MOLECULAR GENETICS). ... Because the WDPCP gene is mutated in BBS, Saari et al. (2015) referred their patient for a screen for ocular abnormalities. At age 3 years there were no signs of retinal degeneration, symptoms of nyctalopia, or peripheral vision loss. However, BBS-related retinal dystrophy typically occurs later than age 3 years.
-
Vaginal Atresia
Wikipedia
Abnormal androgen production is also induced, eventually leading to hyperandrogenism and Müllerian aplasia. [7] Bardet-Biedl Syndrome [ edit ] Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a cliopathic human genetic disorder that can affect various parts of the body. Parts of the urogenital system where the effects of BBS are seen include: ectopic urethra , kidney failure , uterus duplex , hypogonadism , septate vagina , and hypoplasia of the fallopian tubes , uterus , ovaries . [8] Some of the common characteristics associated with this syndrome include intellectual disorders, loss of vision, kidney problems, and obesity. [2] [9] [10] The mechanism that causes BBS is still remains unclear. Mutations in more than 20 genes can cause BBS and is an inherited recessive condition. Some of the gene mutations that occur in BBS are listed below: BBS1 , BBS2 , ARL6 (BBS3) , BBS4 , BBS5 , MKKS (BBS6) , BBS7 , TTC8 (BBS8) , BBS9 , BBS10 , TRIM32 (BBS11) , BBS12 , MKS1 (BBS13) , CEP290 (BBS14) , WDPCP (BBS15) , SDCCAG8 (BBS16) , LZTFL1 (BBS17) , BBIP1 (BBS18) , IFT27 (BBS19) , IFT72 (BBS20) , and C8ORF37(BBS21 ) [11] The majority of the genes that are related to BBS encode proteins which are called cilia and basal bodies, which are related structures. [11] Fraser Syndrome [ edit ] Fraser syndrome is a disorder that affects the development of the child prior to birth.
-
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Orphanet
Management and treatment Lifestyle changes such as limitation of physical activity, avoidance of strong emotion and stressful environments should be recommended to all CPVT patients. Beta blockers (BB; particularly nadolol) are the first treatment option for patients with CPVT and the maximum tolerated dose should be administered to control arrhythmias. Flecainide, a sodium channel blocker, can be considered in patients with BB-resistant arrhythmias. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is recommended in CPVT patients who survived a cardiac arrest, and in those experiencing recurrent syncope or breakthrough arrhythmias despite compliance to an optimal medical treatment.
-
Leprosy
Orphanet
Borderline forms exist: borderline tuberculoid, borderline borderline and borderline lepromatous (BT, BB, BL). Tuberculoid leprosy (TLep) or paucibacillary form includes TT and BT and lepromatous leprosy (LLep) or multibacillary form includes LL, BL and BB.CCDC88B, SLC11A1, TLR2, TLR1, IL23R, RAB32, BATF3, LTA, HLA-DRB1, LACC1, CCDC122, TNFSF15, C1orf141, HLA-B, PRKN, TNF, RIPK2, SIGLEC5, IL18R1, IL10, IL1RL1, LINC02571, DELEC1, FILIP1, BBS9, COX4I1, CDH18, SLC2A13, RMI2, SNX20, LINC01091, WASF5P, UBE2V1P15, LINC00690, IFNG, NOD2, VDR, LRRK2, SDHD, PACRG, IL6, MBL2, RBM45, TLR4, MICA, ERBB2, IL4, IL12B, BTNL2, HLA-A, HSPD1, HLA-DQA1, IL2, GEM, S100A6, DDX39A, SLC26A3, MRC1, NGF, CFP, CCL4, CFH, DDX39B, TOLLIP, TGFBR2, KIR3DL1, CTLA4, IL17F, SLC7A9, IL2RA, HSD11B2, APOE, IL1B, IL10RB, CXCL10, IL17A, IL12RB2, BCHE, CD209, ACTG2, IL22, CCR2, TOR1B, FOXP3, NT5C3A, POTEM, CD274, IL37, CYP2E1, PARL, CYP19A1, ACAD8, RNU1-1, NUPR1, H3C9P, SPAG8, PTPN22, NLRP1, ACOT7, ACTG1, POTEKP, EMC3, CR1, ADGB, PWAR1, CASP8, APOA1, STING1, CD14, TNFSF8, CD40, IRGM, TIRAP, CD40LG, DEFB1, ACTBL2, IL26, GAL3ST4, SLC52A2, PINK1, CCR5, ANXA2, ZNF410, HAMP, MAVS, AKR1B10, ANXA1, FMNL1, HLA-DQB1, SOCS1, MASP2, MFN2, PCK1, HIF1A, PAEP, NOS2, NFKBIL1, MPZ, MNAT1, MICB, CIITA, LTB, LGALS3, LDLR, KIR3DL2, KIR2DS1, KDR, ISG20, IL15, IL13RA1, IL13, IL10RA, HLA-C, CXCR2, IL5RA, IL1RN, IL1A, IGF1, HSPE1, POLG, PREP, RNU1-4, FLNA, BMS1, FHL5, IL32, MAP3K14, BCL10, NR1I2, F2R, FCN1, FCN2, HLA-DRB4, FCN3, VEGFA, TOP2A, S100A1, CXCR3, GSTM1, TGFBR1, TGFB1, TFAM, TAP1, STAT3, SOD2, SLAMF1, ACACA, CCL3, S100B, SERPINA3
-
Senior-Loken Syndrome
Orphanet
Differential diagnosis SLS presents genetic and clinical overlap with other ciliopathies, in particular with isolated NPH and Joubert syndrome related diseases (JSRD) such as Joubert syndrome with oculorenal defect, Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) and Alström syndrome. Physical examination should consider the presence of the main clinical signs of JSRD (hypotonia, ataxia and breathing abnormalities in infants) and BBS (polydactyly and obesity).
-
Retinitis Pigmentosa 71
OMIM
Clinical Variability Bujakowska et al. (2015) reported 2 sisters, 15 and 22 years of age, with RP as well as systemic features suggesting a Bardet-Biedl-like ciliopathy (BBS; see 209900). Both were obese and had a history of delayed speech development and elevated liver transaminases. ... Molecular Genetics In 2 sisters with RP and obesity, who were negative for mutation in 12 BBS-associated genes, Bujakowska et al. (2015) performed whole-exome sequencing (WES) and identified compound heterozygosity for a missense mutation (H1567Q; 607386.0013) and a splice site mutation (607386.0014) in the IFT172 gene.C8orf37, PDE6B, PDE6A, CRX, RPGR, RPE65, PDE6G, LRAT, ABCA4, EYS, MERTK, IMPDH1, ROM1, RHO, USH2A, CRB1, CNGB1, RPGRIP1, GUCY2D, RP2, NRL, RBP3, CLRN1, RDH12, SAG, SPATA7, CNGA1, ARL6, AIPL1, REEP6, RGR, DHX38, GUCA1B, OFD1, IDH3A, IDH3B, PRPF8, RP1, FAM161A, TULP1, SNRNP200, PRPF31, CERKL, NR2E3, CA4, MAK, PRCD, PRPF3, RLBP1, PROM1, PCARE, CHM, ARL2BP, TOPORS, BBS1, CYP4V2, BEST1, DHDDS, KLHL7, IMPG2, HGSNAT, IFT140, PRPF6, BBS2, TTC8, AHI1, SCAPER, CLN3, IFT172, CDHR1, KIZ, FLVCR1, TTPA, ARL3, PRPF4, AGBL5, RP9, SLC7A14, FSCN2, POMGNT1, ZNF513, ZNF408, RBP4, ABHD12, UNC119, NEK2, AHR, TUB, SEMA4A, ATF6, IFT88, FOXI2, UBAP1L, CCZ1B, CROCC, PDAP1, FAM71A, KIAA1549, IRX5, ARHGEF18, C1QTNF5, PRTFDC1, SLC37A3, NAALADL1, CRB2, NGF, CEP250, CWC27, CCDC66, GRIN2B, PRPH2, AGTPBP1, SLC6A6, AIFM1, FGFR2, KL, MT2A, PTEN, MYO7A, CEP290, GUCA1A, RDH5, CDH23, IQCB1, MSTO1, CACNA1A, BBS4, ATXN7, USH1C, CFAP410, ATP6, PANK2, MKKS, BBS9, SLC24A1, PEX1, RP1L1, HADHA, PNPLA6, SDCCAG8, BBS12, NDUFAF5, RRM2B, PDHA1, NDUFS8, NDUFV2, LZTFL1, FOXRED1, POMT2, RCBTB1, TST, FKRP, BBS7, CNGB3, NCAPG2, NPHP1, MKS1, NDUFB11, SURF1, SDHB, PEX2, WDPCP, PRPH, NDUFV1, NDUFA13, SCN1A, SCO1, SDHA, SDHD, PHYH, TACO1, LIPT1, SLC19A1, NDUFA12, PEX5, NGLY1, ALMS1, LARGE1, NDUFS4, PRDX1, NDUFS3, POLR3A, MFSD8, ZDHHC24, RNASEH1, CTNS, ARL13B, TRIM32, NIPAL1, ECHS1, FASTKD2, ERCC3, POMT1, ERCC6, ERG, IFT27, NDUFAF6, BBS5, NDUFS2, CLRN1-AS1, COX20, CYGB, COX15, COX10, COX8A, COX7B, CDH23-AS1, ACOX1, C8orf37-AS1, MMACHC, JAG1, AMACR, AIRE, PET100, SDHAF1, ZFYVE26, PHF3, ATP1A2, BCS1L, NDUFS7, CAV1, TTLL5, VSX2, ERCC8, COX6B1, PRRT2, MTFMT, GSS, COL18A1, GMPPB, HADHB, ND1, ND2, ND3, ND4, ND5, ND6, TRNK, TRNL1, TRNN, TRNS1, TRNV, TRNW, TRIM37, BBS10, NDUFA2, NDUFA4, NDUFA9, NDUFA10, NDUFS1, SLC19A3, WFS1, BBIP1, COA8, HCCS, NDUFAF2, HADH, TMEM14B, COX14, PLXNA2, LSM2, TRNT1, CLU, MFRP, PCDH15, DHX16, PTPRC, SLU7, KLK3, SIGMAR1, NXNL1, CLTA, CNTF, NT5C2, RPE, PROS1, PLAG1, NPHP4, TIMP3, PSAT1, NPEPPS, MYP2, CXCR6, RIMS1, RRH, SLC19A2, EXOSC2, ADIPOR1, LPAR2, USP9X, COG4, VCP, EDN1, LCA5, PDC, ATN1, OTX2, OTC, CNOT3, MVK, LPCAT1, MMP9, EDNRA, RCC1, EPO, INS, FANCF, HSPA4, HK1, GNAT1, HIF1A, OPN4, GSN, SERPINF1, GPR42, NSMCE3, GRK1, ALDH3A2, SFRP2, ACKR3, ADRA1A, ARL2, ATXN2, CC2D2A, ADRA2B, WDR19, SOD3, PLIN2, SSTR4, BRS3, STC1, ACTB, NRG4, TWIST2, GRK7, POC5, ARMS2, MFT2, SAMD11, SAMD7, NOC2L, JAKMIP1, MIR204, POLDIP2, GUCY2EP, LIN28B, NPHP3, ARSI, RD3, CENPV, PITPNM3, INVS, CENPK, TENT5A, CYCS, DCUN1D1, TWNK, SLC2A4RG, TBX20, RDH11, PNPLA2, KIDINS220, NGB, MPP4, NYX, TNMD, ENFL2, TUT1, DNER, FTO, ELOVL6, ALG12, RNF19A, COQ8B, SETD2, KLF15, PDZD7, HKDC1, C5AR2, DNAJC17, ADGRV1, CEP78, GNPTG, AAVS1, THBS2, WHRN, MMP2, HMOX1, HK2, HGF, GRM5, GRM1, GRB10, GLO1, GK, GJB2, GDNF, GDF2, G6PD, FRZB, FN1, FGF5, FGF2, FBN2, HSP90AA1, IDH2, IFNG, INSR, MEIS2, MDH1, MAP1A, SMAD4, LTB, LAMP1, ISG20, ING1, IGF1, IMPA1, CXCL8, IL6, IL2RA, IL1B, IL1A, CCN1, FASN, ETV5, ERN1, ALDH7A1, CACNA1F, C5AR1, C3, C1QBP, BSG, BMP4, BCL2, ARRB2, CANX, ARR3, ABCC6, APOE, APOB, AMFR, ADH7, ABO, CACNA1S, CCT, ERBB2, CYBB, EGF, E2F1, DUSP6, DNMT3A, CFD, ACE, CYLD, CTNNB1, CD44, MAPK14, CRYAB, CRK, CP, CORD1, COL2A1, CD74, RAB8A, MSR1, SH3BP4, CYTB, SYNJ1, FGF18, HSD17B6, DGKE, BRAP, SMC1A, USP11, AIMP2, PAX8, ZNF132, ZFP36, USH1E, TSC1, TP53, TNF, TMPRSS2, TSPAN7, SMC3, ARHGEF2, CRLF1, AKT3, TMED3, SIRT1, ARC, MAPRE3, ARPP21, AHSA1, PPIH, HEPH, SNAP29, PLEKHM1, PHYHIP, HDAC4, KNTC1, EIF2AK3, GRAP2, EFTUD2, TIMP2, TIMP1, DYNLT3, PKNOX1, HTRA1, PRNP, MAPK1, PRKCG, POLG, PMM2, PLAU, PIM1, RAC1, PGF, CFP, PDGFRB, NPTX2, NFE2L2, NAGLU, MYC, ALDH18A1, RASGRF1, ELOVL4, SFTPD, STATH, SOS1, SOD1, SNRPB, SNCA, SLC2A1, SGSH, SFRP5, RBP1, SEC14L1, CX3CL1, CCL2, S100A6, RPS6KB1, RPS6, RCVRN, H3P22
-
Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome
OMIM
Ataxia-telangiectasia variant-1 is the designation applied to the Nijmegen breakage syndrome and AT variant-2 is the designation for the Berlin breakage syndrome, which differ only in complementation studies. Cells from NBS/BBS patients are hypersensitive to ionizing radiation with cytogenetic features indistinguishable from those of ataxia-telangiectasia (AT; 208900), but NBS/BBS patients have a distinct clinical phenotype. ... Saar et al. (1997) performed a whole-genome screen in 14 NBS/BBS families and localized the causative gene to a 1-cM interval on 8q21, between markers D8S271 and D8S270, with a peak lod score of 6.86 at D8S1811. This marker also showed strong allelic association to both Slavic NBS and German BBS patients, suggesting the existence of one major mutation of Slavic origin. The authors stated that since the same allele is seen in both complementation groups, genetic homogeneity of NBS/BBS can be considered as proved. Matsuura et al. (1997) used microcell-mediated chromosome transfer followed by complementation assays based on radiosensitivity to demonstrate that only chromosome 8 complements the sensitivity to ionizing radiation in NBS cell lines.NBN, TP53, MRE11, ATM, NLRP2, RAD50, NME1, MKKS, BRCA1, LIG4, MYC, PTEN, PARP1, XRCC1, XRCC3, SIRT1, TMED3, UBASH3B, BBS12, MDM2, H3P22, XRCC6, ANXA6, ATR, BBS1, MS4A1, IKZF1, TBPL1, POLQ, KLF4, BBS4, SLC12A9, BBS2, CBX5, RAD54B, IFT172, PHGDH, HCAR1, KRT20, BBS7, IGF1, MRPL36, MIB1, CDKN1A, MCPH1, LIN28A, BBS10, NHEJ1, NANOG, BRIP1, ARL6, ARID5B, TTC8, PEG13, XRCC6P5, POU5F1P3, POU5F1P4, SMC1A, CDKN2A, IGF1R, KMT2A, PECAM1, PDGFRB, TNFRSF11B, FANCD2, FANCB, FANCF, H2AX, PIK3CB, IDH1, LCK, KPNA2, IL18, IL5, IL2, PIK3CA, PIK3CD, COL11A2, TERF2, XPC, VEGFA, TRH, ELANE, TMPRSS2, TERT, TERF1, PIK3CG, AFP, SOX2, RAD52, ERG, POU5F1, POLH, TRBV20OR9-2
-
Mental Retardation, Truncal Obesity, Retinal Dystrophy, And Micropenis Syndrome
OMIM
The phenotype was similar to Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS; 209900) and Cohen syndrome (COH1; 216550) but could be distinguished by the age of onset and nonprogressive nature of the visual impairment, and the lack of several characteristics, including dysmorphic facies, skin or gingival infection, microcephaly, 'mottled retina,' polydactyly, and testicular anomalies.
-
Martorell's Ulcer
Wikipedia
"Topical Treatment of Hypertensive Leg Ulcers With Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB A Randomized Controlled Trial" . Archives of Dermatology . 147 (8): 926–930. doi : 10.1001/archdermatol.2011.84 .
-
Meckel Syndrome, Type 1
OMIM
Karmous-Benailly et al. (2005) speculated that fetuses with an antenatal diagnosis of Meckel or 'Meckel-like' syndrome (see 208540), because of the presence of cystic kidneys and polydactyly and/or hepatic fibrosis but no encephalocele, might be instances of Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS; 209900). They sequenced the 8 BBS genes in a series of 13 such cases. In 6, they identified a recessive mutation in a BBS gene: 3 in BBS2 (606151), 2 in BBS4 (600374), and 1 in BBS6 (604896). ... The results indicated that the antenatal presentation of BBS may mimic Meckel syndrome. Inheritance Numerous examples of affected sibs, concordance in presumedly monozygotic twins (Stockard, 1921), roughly equal occurrence in males and females, and parental consanguinity in some instances (Tucker et al., 1966; Walbaum et al., 1967) make autosomal recessive inheritance quite certain.
-
Osteopetrosis, Autosomal Dominant 2
OMIM
Biochemical Features Yoneyama et al. (1989) found elevated creatine kinase of the so-called BB type (CKB; 123280) in 3 adults with osteopetrosis. Yoneyama et al. (1992) demonstrated marked elevation of BB isozyme fraction of serum creatine kinase for male sibs with this disorder. ... Individuals with autosomal dominant osteoporosis type II (OPTA2) have elevated serum levels of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP; 171640) and the BB isoenzyme of creatine kinase (CKBB).
-
Embolic Stroke Of Undetermined Source
Wikipedia
. ^ a b Adams HP, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE (January 1993). ... PMID 22498329 . ^ Gupta A, Gialdini G, Lerario MP, Baradaran H, Giambrone A, Navi BB, et al. (June 2015). "Magnetic resonance angiography detection of abnormal carotid artery plaque in patients with cryptogenic stroke" .