Load FindZebra Summary
Disclaimer:
FindZebra Search conducts a search using our specialized medical search engine.
FindZebra Summary uses the text completions API
(subject to OpenAI’s API data usage policies)
to summarize and reason about the search results.
The search is conducted in publicly available information on the Internet that we present “as is”.
You should be aware that FindZebra is not supplying any of the content in the search results.
FindZebra Summary is loading...
-
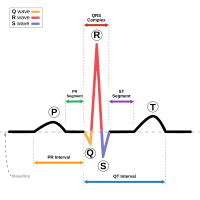
Torsades De Pointes
Wikipedia
Causes [ edit ] Torsades occurs as both an inherited (linked to at least 17 genes) [3] and as an acquired form caused most often by drugs and/or electrolyte disorders that cause excessive lengthening of the QT interval. [4] Common causes for torsades de pointes include drug-induced QT prolongation and less often diarrhea , low serum magnesium , and low serum potassium or congenital long QT syndrome. ... Please note that phase 0 leads to a net gain of Na + , while phases 1-3 lead to a net loss of K + . ... Torsades de pointes is associated with long QT syndrome , a condition whereby prolonged QT intervals are visible on an ECG. ... ISBN 978-0-7020-3084-0 . ^ a b Yap, Yee Guan; Camm, A John (2017-01-17). "Drug induced QT prolongation and torsades de pointes" . ... "Pharmacological treatment of acquired QT prolongation and torsades de pointes" .KCNH2, SCN5A, CYP3A4, KCNQ1, KCNE1, ANK2, KCNE2, NAA10, KCNJ5, SCN4B, SCN10A, SNTA1, ALG10B, CAV3, CALM2, CALM1, AKAP9, TRDN, C18orf21, NOS1AP, IL6, KCNK3, KCNA5, ATP12A, ATP4A, CYP19A1, KCNA4, ACE, SLC24A3, SLCO3A1, RAPGEF4, SLCO1B1, ATP5F1A, CRP, CYP2D6, NR1I2, TNF, SRL, SARDH, TLX2, HTR4, RYR2, RNPEP, ABCB1, ORM1, MSD, LBR, IL1A, ADRB1, IL1B, ADRA2C
-
Long Qt Syndrome 3
OMIM
Digenic inheritance has also been reported; see MOLECULAR GENETICS. Description Congenital long QT syndrome is electrocardiographically characterized by a prolonged QT interval and polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias (torsade de pointes). ... For a discussion of genetic heterogeneity of long QT syndrome, see LQT1 (192500). Clinical Features Wang et al. (1995) cited preliminary data suggesting that in chromosome 3-linked LQT the onset of the T wave is later and duration of the QT interval longer than in other forms. ... This family demonstrated that long QT syndrome-3 and Brugada syndrome appear to lie on a spectrum of cardiac electrophysiologic pathology caused by SCN5A mutation. ... Veldkamp et al. (2003) concluded that sodium channel mutations displaying an I-pst or a negative shift in inactivation may account for the bradycardia seen in LQT3 patients, whereas SA node pauses or arrest may result from failure of SA node cells to repolarize under conditions of extra net inward current. In a patient with long QT syndrome-3, Rivolta et al. (2001) identified a tyr1795-to-cys mutation in the SCN5A gene (Y1795C; 600163.0029). ... These results provided an explanation of the molecular mechanism for bradycardia-induced QT prolongation in patients carrying LQT3 mutations.
-
Afterdepolarization
Wikipedia
Early afterdepolarizations can result in torsades de pointes , tachycardia , and other arrhythmias . [1] EADs can be potentiated by hypokalemia and drugs that prolong the QT interval , including class Ia and III antiarrhythmic agents . ... They are due to elevated cytosolic calcium concentrations, classically seen with digoxin toxicity. [3] [4] The overload of the sarcoplasmic reticulum may cause spontaneous Ca 2+ release after repolarization, causing the released Ca 2+ to exit the cell through the 3Na + /Ca 2+ -exchanger. This results in a net depolarizing current. The classical feature is Bidirectional ventricular tachycardia .
-
Long Qt Syndrome
Wikipedia
Long QT syndrome ECG showing typical pattern of inherited Long QT syndrome (LQT1). A QT interval of >480ms is considered abnormally long. ... While some have QT intervals that are very prolonged, others have only slight QT prolongation, or even a normal QT interval at rest (concealed LQTS). ... Diagnosing long QT syndrome is challenging. Whilst the hallmark of LQTS is prolongation of the QT interval, the QT interval is highly variable among both those who are healthy and those who have LQTS. ... (November 2009). "The genetic basis of long QT and short QT syndromes: a mutation update" .KCNE1, KCNQ1, SCN5A, KCNH2, RYR2, KCNE2, SCN4B, KCNE3, POMC, PTEN, CYP1A1, CACNA1C, CAV3, ANK2, SNTA1, MYBPC3, AKAP9, KCNQ1OT1, DSP, TECRL, SLC2A5, KCNQ1-AS1, SSUH2, KCNJ2, CALM2, HRAS, NOS1AP, KCNA5, KCNA4, KCNK3, CALM1, CALM3, KCND3, SCD, LINC01672, KCND2, KCNQ2, RWS, PICALM, SCN1B, KCNQ4, SNAP91, HCN4, KCNB1, MINK1, PELI1, ACSBG1, TAT, SEC1P, CUZD1, MIR19B1, MIR133A2, KCNE5, MIR133A1, RNF207, CAVIN1, TRDN, LYPD4, ALG10B, TDP2, ABCC8, ALG10, FSD1L, TBX20, ABCC9, FSD1, PRDM6, ACADM, SQLE, HSPA1A, GJB3, GJA5, GAST, FXN, FLNC, DMBT1, CRX, COL4A5, COL4A2, CD59, CAV1, CAD, CACNB3, CACNA1D, AR, HFE, HSPA1B, SLN, HSPA2, SLC18A2, SCN10A, RPGR, PPARD, ADRB1, CNTN3, MYH7, MUC2, ND1, LDLR, KCNQ3, KCNJ11, KCNJ9, KCNJ5, HSPA4, PMP22
-
Andersen–tawil Syndrome
Wikipedia
Rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder Andersen–Tawil syndrome Other names Cardiodysrhythmic potassium-sensitive periodic paralysis, long QT syndrome type 7 This condition affects the QT interval (in blue). ... This, as in other forms of long QT syndrome, can lead to abnormal heart rhythms such as ventricular ectopy or ventricular tachycardia causing palpitations . [2] The ventricular tachycardia seen in Andersen–Tawil syndrome often takes a form known as bidirectional ventricular tachycardia. The arrhythmias seen in association with the condition can cause sudden cardiac death, but the risk of this is lower than in other forms of long QT syndrome. [1] Clinodactyly – abnormal curvature of 5th finger towards 4th finger The physical abnormalities associated with Andersen–Tawil syndrome typically affect the head, face, limbs and spine. ... This calcium release then leaves the cell through the sodium calcium exchanger in exchange for sodium, generating a net inward current and depolarising the cell membrane. [6] If this transient inward current is large enough, a premature action potential is triggered. ... National Library of Medicine External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : I45.8 ICD - 9-CM : 426.82 , 794.31 OMIM : 170390 MeSH : D050030 DiseasesDB : 700 External resources GeneReviews : Andersen-Tawil syndrome Orphanet : 37553 v t e Cardiovascular disease (heart) Ischaemic Coronary disease Coronary artery disease (CAD) Coronary artery aneurysm Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) Coronary thrombosis Coronary vasospasm Myocardial bridge Active ischemia Angina pectoris Prinzmetal's angina Stable angina Acute coronary syndrome Myocardial infarction Unstable angina Sequelae hours Hibernating myocardium Myocardial stunning days Myocardial rupture weeks Aneurysm of heart / Ventricular aneurysm Dressler syndrome Layers Pericardium Pericarditis Acute Chronic / Constrictive Pericardial effusion Cardiac tamponade Hemopericardium Myocardium Myocarditis Chagas disease Cardiomyopathy Dilated Alcoholic Hypertrophic Tachycardia-induced Restrictive Loeffler endocarditis Cardiac amyloidosis Endocardial fibroelastosis Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia Endocardium / valves Endocarditis infective endocarditis Subacute bacterial endocarditis non-infective endocarditis Libman–Sacks endocarditis Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis Valves mitral regurgitation prolapse stenosis aortic stenosis insufficiency tricuspid stenosis insufficiency pulmonary stenosis insufficiency Conduction / arrhythmia Bradycardia Sinus bradycardia Sick sinus syndrome Heart block : Sinoatrial AV 1° 2° 3° Intraventricular Bundle branch block Right Left Left anterior fascicle Left posterior fascicle Bifascicular Trifascicular Adams–Stokes syndrome Tachycardia ( paroxysmal and sinus ) Supraventricular Atrial Multifocal Junctional AV nodal reentrant Junctional ectopic Ventricular Accelerated idioventricular rhythm Catecholaminergic polymorphic Torsades de pointes Premature contraction Atrial Junctional Ventricular Pre-excitation syndrome Lown–Ganong–Levine Wolff–Parkinson–White Flutter / fibrillation Atrial flutter Ventricular flutter Atrial fibrillation Familial Ventricular fibrillation Pacemaker Ectopic pacemaker / Ectopic beat Multifocal atrial tachycardia Pacemaker syndrome Parasystole Wandering atrial pacemaker Long QT syndrome Andersen–Tawil Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Romano–Ward Cardiac arrest Sudden cardiac death Asystole Pulseless electrical activity Sinoatrial arrest Other / ungrouped hexaxial reference system Right axis deviation Left axis deviation QT Short QT syndrome T T wave alternans ST Osborn wave ST elevation ST depression Strain pattern Cardiomegaly Ventricular hypertrophy Left Right / Cor pulmonale Atrial enlargement Left Right Athletic heart syndrome Other Cardiac fibrosis Heart failure Diastolic heart failure Cardiac asthma Rheumatic fever v t e Diseases of ion channels Calcium channel Voltage-gated CACNA1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 1 Episodic ataxia 2 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-6 CACNA1C Timothy syndrome Brugada syndrome 3 Long QT syndrome 8 CACNA1F Ocular albinism 2 CSNB2A CACNA1S Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 1 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 1 CACNB2 Brugada syndrome 4 Ligand gated RYR1 Malignant hyperthermia Central core disease RYR2 CPVT1 ARVD2 Sodium channel Voltage-gated SCN1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 3 GEFS+ 2 Febrile seizure 3A SCN1B Brugada syndrome 6 GEFS+ 1 SCN4A Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 2 Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis Paramyotonia congenita Potassium-aggravated myotonia SCN4B Long QT syndrome 10 SCN5A Brugada syndrome 1 Long QT syndrome 3 SCN9A Erythromelalgia Febrile seizure 3B Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder Congenital insensitivity to pain Constitutively active SCNN1B / SCNN1G Liddle's syndrome SCNN1A / SCNN1B / SCNN1G Pseudohypoaldosteronism 1AR Potassium channel Voltage-gated KCNA1 Episodic ataxia 1 KCNA5 Familial atrial fibrillation 7 KCNC3 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-13 KCNE1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Long QT syndrome 5 KCNE2 Long QT syndrome 6 KCNE3 Brugada syndrome 5 KCNH2 Short QT syndrome KCNQ1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Romano–Ward syndrome Short QT syndrome Long QT syndrome 1 Familial atrial fibrillation 3 KCNQ2 BFNS1 Inward-rectifier KCNJ1 Bartter syndrome 2 KCNJ2 Andersen–Tawil syndrome Long QT syndrome 7 Short QT syndrome KCNJ11 TNDM3 KCNJ18 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 2 Chloride channel CFTR Cystic fibrosis Congenital absence of the vas deferens CLCN1 Thomsen disease Myotonia congenita CLCN5 Dent's disease CLCN7 Osteopetrosis A2, B4 BEST1 Vitelliform macular dystrophy CLCNKB Bartter syndrome 3 TRP channel TRPC6 FSGS2 TRPML1 Mucolipidosis type IV Connexin GJA1 Oculodentodigital dysplasia Hallermann–Streiff syndrome Hypoplastic left heart syndrome GJB1 Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease X1 GJB2 Keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome Ichthyosis hystrix Bart–Pumphrey syndrome Vohwinkel syndrome ) GJB3 / GJB4 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis Progressive symmetric erythrokeratodermia GJB6 Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Porin AQP2 Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus 2 See also: ion channels
-
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Wikipedia
., dilute urine). This condition results in a net concentrating effect on the serum (increasing its osmolarity). ... External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : N25.1 ICD - 9-CM : 588.1 OMIM : 304800 125800 MeSH : D018500 External resources MedlinePlus : 000511 GeneReviews : Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus v t e Kidney disease Glomerular disease See Template:Glomerular disease Tubules Renal tubular acidosis proximal distal Acute tubular necrosis Genetic Fanconi syndrome Bartter syndrome Gitelman syndrome Liddle's syndrome Interstitium Interstitial nephritis Pyelonephritis Balkan endemic nephropathy Vascular Renal artery stenosis Renal ischemia Hypertensive nephropathy Renovascular hypertension Renal cortical necrosis General syndromes Nephritis Nephrosis Renal failure Acute renal failure Chronic kidney disease Uremia Other Analgesic nephropathy Renal osteodystrophy Nephroptosis Abderhalden–Kaufmann–Lignac syndrome Diabetes insipidus Nephrogenic Renal papilla Renal papillary necrosis Major calyx / pelvis Hydronephrosis Pyonephrosis Reflux nephropathy v t e X-linked disorders X-linked recessive Immune Chronic granulomatous disease (CYBB) Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency X-linked agammaglobulinemia Hyper-IgM syndrome type 1 IPEX X-linked lymphoproliferative disease Properdin deficiency Hematologic Haemophilia A Haemophilia B X-linked sideroblastic anemia Endocrine Androgen insensitivity syndrome / Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy KAL1 Kallmann syndrome X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita Metabolic Amino acid : Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency Oculocerebrorenal syndrome Dyslipidemia : Adrenoleukodystrophy Carbohydrate metabolism : Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency Danon disease/glycogen storage disease Type IIb Lipid storage disorder : Fabry's disease Mucopolysaccharidosis : Hunter syndrome Purine–pyrimidine metabolism : Lesch–Nyhan syndrome Mineral : Menkes disease / Occipital horn syndrome Nervous system X-linked intellectual disability : Coffin–Lowry syndrome MASA syndrome Alpha-thalassemia mental retardation syndrome Siderius X-linked mental retardation syndrome Eye disorders: Color blindness (red and green, but not blue) Ocular albinism ( 1 ) Norrie disease Choroideremia Other: Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMTX2-3) Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease SMAX2 Skin and related tissue Dyskeratosis congenita Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (EDA) X-linked ichthyosis X-linked endothelial corneal dystrophy Neuromuscular Becker's muscular dystrophy / Duchenne Centronuclear myopathy (MTM1) Conradi–Hünermann syndrome Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 1 Urologic Alport syndrome Dent's disease X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Bone / tooth AMELX Amelogenesis imperfecta No primary system Barth syndrome McLeod syndrome Smith–Fineman–Myers syndrome Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome Mohr–Tranebjærg syndrome Nasodigitoacoustic syndrome X-linked dominant X-linked hypophosphatemia Focal dermal hypoplasia Fragile X syndrome Aicardi syndrome Incontinentia pigmenti Rett syndrome CHILD syndrome Lujan–Fryns syndrome Orofaciodigital syndrome 1 Craniofrontonasal dysplasia v t e Diseases of ion channels Calcium channel Voltage-gated CACNA1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 1 Episodic ataxia 2 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-6 CACNA1C Timothy syndrome Brugada syndrome 3 Long QT syndrome 8 CACNA1F Ocular albinism 2 CSNB2A CACNA1S Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 1 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 1 CACNB2 Brugada syndrome 4 Ligand gated RYR1 Malignant hyperthermia Central core disease RYR2 CPVT1 ARVD2 Sodium channel Voltage-gated SCN1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 3 GEFS+ 2 Febrile seizure 3A SCN1B Brugada syndrome 6 GEFS+ 1 SCN4A Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 2 Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis Paramyotonia congenita Potassium-aggravated myotonia SCN4B Long QT syndrome 10 SCN5A Brugada syndrome 1 Long QT syndrome 3 SCN9A Erythromelalgia Febrile seizure 3B Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder Congenital insensitivity to pain Constitutively active SCNN1B / SCNN1G Liddle's syndrome SCNN1A / SCNN1B / SCNN1G Pseudohypoaldosteronism 1AR Potassium channel Voltage-gated KCNA1 Episodic ataxia 1 KCNA5 Familial atrial fibrillation 7 KCNC3 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-13 KCNE1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Long QT syndrome 5 KCNE2 Long QT syndrome 6 KCNE3 Brugada syndrome 5 KCNH2 Short QT syndrome KCNQ1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Romano–Ward syndrome Short QT syndrome Long QT syndrome 1 Familial atrial fibrillation 3 KCNQ2 BFNS1 Inward-rectifier KCNJ1 Bartter syndrome 2 KCNJ2 Andersen–Tawil syndrome Long QT syndrome 7 Short QT syndrome KCNJ11 TNDM3 KCNJ18 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 2 Chloride channel CFTR Cystic fibrosis Congenital absence of the vas deferens CLCN1 Thomsen disease Myotonia congenita CLCN5 Dent's disease CLCN7 Osteopetrosis A2, B4 BEST1 Vitelliform macular dystrophy CLCNKB Bartter syndrome 3 TRP channel TRPC6 FSGS2 TRPML1 Mucolipidosis type IV Connexin GJA1 Oculodentodigital dysplasia Hallermann–Streiff syndrome Hypoplastic left heart syndrome GJB1 Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease X1 GJB2 Keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome Ichthyosis hystrix Bart–Pumphrey syndrome Vohwinkel syndrome ) GJB3 / GJB4 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis Progressive symmetric erythrokeratodermia GJB6 Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Porin AQP2 Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus 2 See also: ion channels v t e Cell surface receptor deficiencies G protein-coupled receptor (including hormone ) Class A TSHR ( Congenital hypothyroidism 1 ) LHCGR ( Luteinizing hormone insensitivity , Leydig cell hypoplasia , Male-limited precocious puberty ) FSHR ( Follicle-stimulating hormone insensitivity , XX gonadal dysgenesis ) GnRHR ( Gonadotropin-releasing hormone insensitivity ) EDNRB ( ABCD syndrome , Waardenburg syndrome 4a , Hirschsprung's disease 2 ) AVPR2 ( Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus 1 ) PTGER2 ( Aspirin-induced asthma ) Class B PTH1R ( Jansen's metaphyseal chondrodysplasia ) Class C CASR ( Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia ) Class F FZD4 ( Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy 1 ) Enzyme-linked receptor (including growth factor ) RTK ROR2 ( Robinow syndrome ) FGFR1 ( Pfeiffer syndrome , KAL2 Kallmann syndrome ) FGFR2 ( Apert syndrome , Antley–Bixler syndrome , Pfeiffer syndrome , Crouzon syndrome , Jackson–Weiss syndrome ) FGFR3 ( Achondroplasia , Hypochondroplasia , Thanatophoric dysplasia , Muenke syndrome ) INSR ( Donohue syndrome Rabson–Mendenhall syndrome ) NTRK1 ( Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis ) KIT ( KIT Piebaldism , Gastrointestinal stromal tumor ) STPK AMHR2 ( Persistent Müllerian duct syndrome II ) TGF beta receptors : Endoglin / Alk-1 / SMAD4 ( Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia ) TGFBR1 / TGFBR2 ( Loeys–Dietz syndrome ) GC GUCY2D ( Leber's congenital amaurosis 1 ) JAK-STAT Type I cytokine receptor : GH ( Laron syndrome ) CSF2RA ( Surfactant metabolism dysfunction 4 ) MPL ( Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia ) TNF receptor TNFRSF1A ( TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome ) TNFRSF13B ( Selective immunoglobulin A deficiency 2 ) TNFRSF5 ( Hyper-IgM syndrome type 3 ) TNFRSF13C ( CVID4 ) TNFRSF13B ( CVID2 ) TNFRSF6 ( Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome 1A ) Lipid receptor LRP : LRP2 ( Donnai–Barrow syndrome ) LRP4 ( Cenani–Lenz syndactylism ) LRP5 ( Worth syndrome , Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy 4 , Osteopetrosis 1 ) LDLR ( LDLR Familial hypercholesterolemia ) Other/ungrouped Immunoglobulin superfamily : AGM3, 6 Integrin : LAD1 Glanzmann's thrombasthenia Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia EDAR ( EDAR hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia ) PTCH1 ( Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome ) BMPR1A ( BMPR1A juvenile polyposis syndrome ) IL2RG ( X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency ) See also cell surface receptorsAQP2, AVPR2, PRKCA, CLCNKB, AQP3, GRN, SIRT1, SLC4A4, RNF40, AVP, BBS1, CCDC28B, ARHGAP4, L1CAM, GPRC6A, SCT, VWF, FZD4, KEAP1, LGR6, LPAR3, VN1R17P, OXER1, MRGPRX3, MRGPRX1, GPR151, MRGPRX4, GPR166P, AQP1, ARHGAP1, COX8A, LNPEP, NFE2L2, ADRA2B, AQP8, AQP5, GPBAR1, BRS3, CALCA, MINDY4, CANX, CLCNKA, PDZD4, ACKR3, DMD, WDTC1, CXCR6, EDNRA, ELF3, LPAR2, EPHA3, G6PD, GABPA, ST14, SSTR4, SLC12A1, GPR42, REN, ADRA1A, ADCY6
-
Bartter Syndrome
Wikipedia
Potassium, however, is able to diffuse back into the tubule lumen through apical potassium channels, returning a net positive charge to the lumen and establishing a positive voltage between the lumen and interstitial space. ... External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : E26.8 ICD - 9-CM : 255.13 OMIM : 601678 241200 607364 602522 MeSH : D001477 DiseasesDB : 1254 SNOMED CT : 707742001 External resources MedlinePlus : 000308 eMedicine : med/213 ped/210 Orphanet : 93604 v t e Adrenal gland disorder Hyperfunction Aldosterone Hyperaldosteronism Primary aldosteronism Conn syndrome Bartter syndrome Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism AME Liddle's syndrome 17α CAH Pseudohypoaldosteronism Cortisol Cushing's syndrome Pseudo-Cushing's syndrome Steroid-induced osteoporosis Sex hormones 21α CAH 11β CAH Hypofunction Aldosterone Hypoaldosteronism 21α CAH 11β CAH Cortisol CAH Lipoid 3β 11β 17α 21α Sex hormones 17α CAH Inborn errors of steroid metabolism Adrenal insufficiency Adrenal crisis Adrenalitis Xanthogranulomatous Addison's disease Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome v t e Kidney disease Glomerular disease See Template:Glomerular disease Tubules Renal tubular acidosis proximal distal Acute tubular necrosis Genetic Fanconi syndrome Bartter syndrome Gitelman syndrome Liddle's syndrome Interstitium Interstitial nephritis Pyelonephritis Balkan endemic nephropathy Vascular Renal artery stenosis Renal ischemia Hypertensive nephropathy Renovascular hypertension Renal cortical necrosis General syndromes Nephritis Nephrosis Renal failure Acute renal failure Chronic kidney disease Uremia Other Analgesic nephropathy Renal osteodystrophy Nephroptosis Abderhalden–Kaufmann–Lignac syndrome Diabetes insipidus Nephrogenic Renal papilla Renal papillary necrosis Major calyx / pelvis Hydronephrosis Pyonephrosis Reflux nephropathy v t e Diseases of ion channels Calcium channel Voltage-gated CACNA1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 1 Episodic ataxia 2 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-6 CACNA1C Timothy syndrome Brugada syndrome 3 Long QT syndrome 8 CACNA1F Ocular albinism 2 CSNB2A CACNA1S Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 1 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 1 CACNB2 Brugada syndrome 4 Ligand gated RYR1 Malignant hyperthermia Central core disease RYR2 CPVT1 ARVD2 Sodium channel Voltage-gated SCN1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 3 GEFS+ 2 Febrile seizure 3A SCN1B Brugada syndrome 6 GEFS+ 1 SCN4A Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 2 Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis Paramyotonia congenita Potassium-aggravated myotonia SCN4B Long QT syndrome 10 SCN5A Brugada syndrome 1 Long QT syndrome 3 SCN9A Erythromelalgia Febrile seizure 3B Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder Congenital insensitivity to pain Constitutively active SCNN1B / SCNN1G Liddle's syndrome SCNN1A / SCNN1B / SCNN1G Pseudohypoaldosteronism 1AR Potassium channel Voltage-gated KCNA1 Episodic ataxia 1 KCNA5 Familial atrial fibrillation 7 KCNC3 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-13 KCNE1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Long QT syndrome 5 KCNE2 Long QT syndrome 6 KCNE3 Brugada syndrome 5 KCNH2 Short QT syndrome KCNQ1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Romano–Ward syndrome Short QT syndrome Long QT syndrome 1 Familial atrial fibrillation 3 KCNQ2 BFNS1 Inward-rectifier KCNJ1 Bartter syndrome 2 KCNJ2 Andersen–Tawil syndrome Long QT syndrome 7 Short QT syndrome KCNJ11 TNDM3 KCNJ18 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 2 Chloride channel CFTR Cystic fibrosis Congenital absence of the vas deferens CLCN1 Thomsen disease Myotonia congenita CLCN5 Dent's disease CLCN7 Osteopetrosis A2, B4 BEST1 Vitelliform macular dystrophy CLCNKB Bartter syndrome 3 TRP channel TRPC6 FSGS2 TRPML1 Mucolipidosis type IV Connexin GJA1 Oculodentodigital dysplasia Hallermann–Streiff syndrome Hypoplastic left heart syndrome GJB1 Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease X1 GJB2 Keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome Ichthyosis hystrix Bart–Pumphrey syndrome Vohwinkel syndrome ) GJB3 / GJB4 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis Progressive symmetric erythrokeratodermia GJB6 Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Porin AQP2 Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus 2 See also: ion channelsKCNJ1, CLCNKB, SLC12A1, BSND, REN, CLCNKA, SLC12A3, SCNN1B, CYP17A1, CASR, MAGED2, CLC, GH1, SHBG, ESPN, SLC12A2, SSTR4, SELENBP1, IGAN1, AP3B1, LPAR2, PTGS2, CXCR6, ACKR3, CCHCR1, TRIP13, ADRA1A, PTH, PPP1R12A, AGT, AGTR1, BRS3, CLCN5, CYP11B1, DBP, DCT, SLC26A3, EDNRA, EPHA3, FGL1, GJB2, GPR42, HPS1, HSD11B2, ADRA2B, KCNJ10, ARHGEF25
-
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor
GARD
However in some cases, a pancreatic NET occurs outside of the pancreas. A NET arises from cells that produce hormones, so the tumor can also produce hormones. ... Pancreatic NETs are called either functional or nonfunctional. A functional pancreatic NET causes specific symptoms because it makes extra hormones, such as gastrin, insulin, or glucagon. ... Pancreatic NETs can be hard to diagnosis, often not identified until 5 to 10 years after they begin to grow. Most pancreatic NETs are not inherited and occur sporadically in people with no family history of NETs.MEN1, PCSK1, ATM, BRCA2, C11orf65, IGF2, SST, TP53, CDKN2A, SLC6A2, MTOR, EPHB1, POMC, GH1, GCGR, DAXX, ELK3, KRT19, SSTR2, CHGA, SSTR5, UCHL1, FZD4, GCM2, DLGAP1, DCLK1, SSTR4, INA, STK11, EIF2AK3, TFE3, THBD, CXCR4, PAX8, TSC1, TTR, TYMS, VEGFA, ABO, CNPY2, MRGPRX4, GPR166P, VN1R17P, MIR196A1, GADL1, MRGPRX1, GPRC6A, OXER1, GPR119, GPR151, MRGPRX3, SEMA3A, AZIN2, ACCS, STK33, LGR6, ACSS2, MEG3, NEUROG3, LPAR3, LILRB1, PLA2G15, RET, SLC2A3, INSM1, GRN, FFAR1, GHRH, GAST, FGFR4, F3, EGFR, DHCR24, CSF1, CRH, CHGB, CD44, CCK, CALCA, VPS51, ATRX, ASS1, ASCL1, ANGPT2, HSF1, PDX1, SLC2A2, KIT, SLC2A1, SEA, SDHB, SDHA, AKT1, PYGM, PTH, PTEN, PPY, PTPA, PGR, PCYT1A, PCNA, NFKB1, NEUROD1, MUC1, SMAD4, STMN1, KRAS, H3P10
-
Neuroendocrine Tumor
GARD
A neuroendocrine tumor (NET) is a rare type of tumor that arises from specialized body cells called neuroendocrine cells . ... Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (also called islet cell tumors) - NETs that typically arise in the pancreas, although they can occur outside the pancreas. A p heochromocytoma is another, rarer type of NET that usually develops in the adrenal gland , but can also arise in other parts of the body. ... Functional NETs produce a specific set of symptoms due to the production of excess hormones, while non-functional NETs generally do not cause specific symptoms. In many cases, a person has no symptoms until the tumor spreads to the liver and/or impairs the function of an organ or system. This can make NETs very hard to diagnose. The majority of NETs are not inherited and occur sporadically in people with no family history of NETs.
-
Neuroendocrine Tumor
Wikipedia
H&E stain Specialty Endocrine oncology Neuroendocrine tumors ( NETs ) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine ( hormonal ) and nervous systems . ... G1 and G2 neuroendocrine neoplasms are called neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) – formerly called carcinoid tumours. ... Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. ( November 2015 ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message ) NETs from a particular anatomical origin often show similar behavior as a group, such as the foregut (which conceptually includes pancreas, and even thymus, airway and lung NETs), midgut and hindgut ; individual tumors within these sites can differ from these group benchmarks: Foregut NETs are argentaffin negative. ... Bone metastasis is uncommon. Hindgut NETs are argentaffin negative and rarely secrete 5-HT, 5-HTP, or any other vasoactive peptides. ... Not all cells are immediately killed; cell death can go on for up to two years. [ citation needed ] PRRT was initially used for low grade NETs. It is also very useful in more aggressive NETs such as Grade 2 and 3 NETs [83] [84] provided they demonstrate high uptake on SSTR imaging to suggest benefit.MEN1, CDKN1B, SSTR2, DAXX, ATRX, BRAF, TYMS, PTHLH, SSTR3, SSTR1, BAP1, MTOR, SST, GAST, SLC6A2, INSM1, CTNNB1, RET, PIK3CA, DNMT3A, POMC, EPHB1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, CHGA, ELK3, CHEK2, PIK3CB, GRN, CD274, SMUG1, AKT1, GNA12, TP53, SYP, VEGFA, CDKN2A, ASCL1, BCL2, ENO2, NCAM1, GCG, MYCN, EGFR, MGMT, KIT, RASSF1, VHL, SCLC1, SSTR5, FOLH1, NKX2-1, KRAS, CALCA, CCND1, TAC1, PTPRF, VIP, NTS, PAX5, RHBDF2, GRP, IGF1, SDHD, GOT1, MAP2K7, CCK, ERBB2, DLL3, PPY, CXCL12, TP63, SMAD4, MUC1, INS, GCGR, CKAP4, NEUROD1, ISL1, MYC, NGF, SATB2, GLP1R, HSP90AA1, H3P10, HRAS, CHGB, CALR, NTRK1, TEK, DLK1, CDK4, CDX2, TGFA, UCHL1, RPE65, PGR, PDGFRA, CARTPT, CRH, UVRAG, SLC5A5, CXCR4, IGF1R, OTP, IL6, PHLDA3, TTF1, PAX8, TACR1, STK11, TRIM21, PLA2G15, SCG2, SQLE, SLC18A2, TERT, HDAC9, SLC2A1, PROM1, BCL2L11, NTSR1, PAX6, NAMPT, NOCT, INA, PLCB3, CD200, MKI67, PDX1, MAPK1, NES, HPSE, PTEN, STMN1, ABO, RIPK1, RORC, RAF1, IL1B, TRPV1, GATA3, ANGPT2, FOXM1, PTK2B, SDHAF2, ACCS, BDNF, EPAS1, EGF, ACSS2, MIB1, DNMT1, CCN2, TRPM8, CLDN4, CPE, CD34, CD44, FLNA, CEACAM5, B3GAT1, GH1, GIP, GHSR, GIPR, ADCY2, ALB, H3P28, TPPP2, H4C5, GGH, MIR1290, TMEM209, ELOA3, H4C13, H4C14, GPR151, SRPX, LGR5, TNFSF11, PSMG1, DCBLD2, H4-16, NRP1, MRGPRX4, SOCS1, H4C2, MIR3137, MRGPRX3, TNFRSF25, H3P12, CYYR1, AZIN2, DNER, AK6, MLIP, LMLN, NRP2, GPR68, MIR1246, H4C8, MAFK, MIR150, MIR155, MBOAT4, H4C9, MIR21, POTEKP, VN1R17P, SNORD95, GPR166P, ARID1A, EID3, SLC7A5, MIR375, H4C15, FZD4, MIRLET7C, OXER1, H4C12, HMGA2, H4C3, ARX, ELOA3B, GPRC6A, H4C11, H4C6, C17orf97, POTEM, MRGPRX1, ARMH1, H4C1, GADL1, ACTBL2, H4C4, BRI3, SQSTM1, ISYNA1, GHRL, ACOT7, KLF12, KRT20, SLC27A4, TET2, BCOR, EBNA1BP2, RALBP1, PGRMC1, LAMTOR1, FBXW7, MEG3, MAML3, TMEM127, NTNG1, ATRAID, KHDRBS1, DCTN4, SNORD61, NUP62, SNORD48, NTSR2, LPAR3, MAPK8IP2, SRRM2, BRD4, TRAM1, SPINK4, XIST, PPWD1, RBMS3, SETD1B, ZHX2, TNFSF13B, USE1, MAK16, UBE2Z, ONECUT2, FHL5, GCM2, DCLK1, ZBED1, ARHGEF2, PALB2, ALG9, SNED1, TET1, PDCD1LG2, TMPRSS13, MTA1, RPAIN, H1-10, EEF1E1, LGR6, PRMT5, NEUROD4, YAP1, SCML2, LANCL1, PAK4, RABEPK, ZNF197, CTNNBL1, PNO1, INSL5, EPB41L5, HDAC5, AKT3, CD302, GBA3, DCAF1, ATAT1, SERPINA3, VCL, CGA, ESR1, ERBB4, EPHB2, E2F1, DUSP2, DSG3, DPT, DPP4, DMBT1, DDC, DAD1, VCAN, CREB1, CRABP1, KLF6, CLU, FOXN3, CEACAM7, CEACAM3, ESR2, ETFA, EZH2, GHRH, HSPA4, AGFG1, HMOX1, HMGA1, GTF2H1, GSN, GNAS, GNA15, GFRA1, F3, GDNF, FSHR, FLT4, FLII, FLI1, FOXO1, FHIT, FGFR4, CGB3, CFL1, UQCRFS1, CDKN2C, FAS, APRT, APLP1, XIAP, APC, SLC25A6, SLC25A4, ANGPT1, ALK, AKT2, AFP, PARP1, ADCYAP1R1, ADCYAP1, ACVRL1, ACTN4, ACTG2, ACTG1, ACR, AQP4, ARF1, ATM, CASP3, CDK6, CD40LG, CD36, CD33, CCNE1, CCKBR, SERPINA6, CAV1, CA9, ATOH1, VPS51, C5, BRS3, BRCA2, DST, BAX, AVP, ATP4A, HTC2, HTR2A, TNC, IAPP, SDC1, SCT, SORT1, RNASE3, RARB, PTPRZ1, PTPRM, PTBP1, PSMD7, PSG2, PRKAR1A, PPP4C, POU4F1, PNN, PKD2, PITX2, PCYT1A, SERPINA5, PAX4, SDCBP, SDHB, SDHC, ST2, UBE2I, TPM3, TPH1, TNF, TM7SF2, TERC, TAT, STAT3, SSTR4, SEMA3F, SSR2, SOX11, SOX4, SOX2, SLPI, SLC3A2, SLC1A5, SFRP1, PAK3, PAK1, TNFRSF11B, KIF11, MDK, MAOA, LCN2, RPSA, L1CAM, KRT19, KRT7, KRT5, IL12A, MET, IL9, CXCL8, IL2, IL1A, IGFBP1, IGF2, IFNA13, IFNA1, MDM2, MFAP1, ODC1, MUTYH, NTRK2, NT5E, NRAS, NOTCH3, NPY, NOTCH1, NFKB1, NEFM, MUC4, CD99, NUDT1, COX2, MTAP, MST1R, MST1, MSMB, MMP7, MLH1, PTPRC
-
Brugada Syndrome 1
OMIM
Brugada syndrome-3 (611875) and Brugada syndrome-4 (611876), the phenotypes of which include a shortened QT interval on ECG, are caused by mutation in the CACNA1C gene (114205) on chromosome 12p13 and CACNB2 gene (600003) on chromosome 10p12, respectively. ... Some living members of this family demonstrated ECG features compatible with Brugada syndrome and QT prolongation characteristic of long QT syndrome-3 (LQT3; 603830). ... This family demonstrated that the long QT syndrome type-3 and Brugada syndrome appear to lie on a spectrum of cardiac electrophysiologic pathology caused by SCN5A mutation. ... In a patient with Brugada syndrome, Rivolta et al. (2001) identified a tyr1795-to-his mutation mutation in the SCN5A gene (Y1795H; 600163.0030). In a patient with Long QT syndrome-3, they identified a different mutation at the same codon (Y1795C; 600163.0029). They concluded that these findings provided further evidence of the close interrelationship between Brugada syndrome and long QT syndrome type 3 at the molecular level.SCN5A, SCN10A, PKP2, CACNA2D1, KCNE5, CACNA1C, KCND3, SCN1B, RANGRF, TRPM4, SCN3B, KCNJ8, SCN2B, ABCC9, CACNB2, KCNE3, SLMAP, KCNH2, GPD1L, HEY2, HCN4, AKAP9, CALM2, ANK2, LINC02523, KCNQ1, RYR2, VCL, MYH7, FGF11, NOS1AP, KCNE2, HARS1, GJA1, FGF14, FGF12, SEMA3A, EPHA3, BHLHE40, EGR3, DSP, DELEC1, DSG2, ATN1, XIRP1, LRRC10, HGS, NR4A3, KCNAB2, MFAP1, RRAD, ATXN2, SCD, KCNK1, APRT, SCN4B, KCNE1, KCND2, SRSF5, SKP1, TBX5, ELOC, ELOB, ELOA, IDS, SCN4A
-
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome Due To Net Deficiency
Orphanet
A rare, genetic, primary orthostatic disorder characterized by dizziness, palpitations, fatigue, blurred vision and tachycardia following postural change from a supine to an upright position, in the absence of hypotension. A syncope with transient cognitive impairment and dyspnea may also occur. The norepinephrine transporter deficiency leads to abnormal uptake and high plasma concentrations of norepinephrine.
-
Neuroendocrine Neoplasm Of Esophagus
Orphanet
A group of esophageal epithelial neoplasms characterized by neuroendocrine differentiation, comprising well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas (NECs), and mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasms, an umbrella category including mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma. ... NECs may also arise in other parts of the esophagus. On endoscopy, NETs usually appear as small polypoid or nodular submucosal masses, while NECs are large, infiltrative, and ulcerated. Patients most commonly present with dysphagia, pain, weight loss, and sometimes melena. Metastatic NETs may be associated with carcinoid syndrome.
-
Drug-Induced Qt Prolongation
Wikipedia
In males, the presence of testosterone upregulates IKr channels and therefore decreases QT interval. [2] Stated otherwise, estrogens prolong the QT interval, while androgens shorten it and decrease the response to IKr-blocking agents. ... The ischemia that results from myocardial infarctions also induce QT prolongation. Pathophysiology [ edit ] IKr blockade On EKG , the QT interval represents the summation of action potentials in cardiac muscle cells . ... Because of its multiple actions, amiodarone causes QT prolongation but TdP is rarely observed. ... "Mechanisms, risk factors, and management of acquired long QT syndrome: a comprehensive review" . ... "Mechanisms, risk factors, and management of acquired long QT syndrome: a comprehensive review" .
-
Qt Interval, Variation In
OMIM
Very long or short QT intervals occur in a heterogeneous collection of mendelian disorders, the various forms of long QT syndrome (LQTS; see 192500) and short QT syndrome (SQTS; see 609620). ... Mapping To identify genetic mechanisms by which an altered QT interval may contribute to SCD risk, Arking et al. (2006) examined the QT interval directly as opposed to the SCD phenotype, treating the QT interval as a quantitative trait that could be accurately and reliably measured in large samples from standard ECG recordings. In a genomewide study involving 200 individuals at the extremes of a population-based QT interval distribution of 3,966 subjects from the KORA cohort in Germany, the authors found an association between QT interval and common genetic variants in noncoding regions of the NOS1 regulator NOS1AP (605551) on chromosome 1q23.3. Post et al. (2007) replicated the association between variants in the NOS1AP gene and QT interval (p = 0.006) in a genetically homogeneous population of Old Order Amish. ... Associations Pending Confirmation Kim et al. (2012) performed a genomewide association study of 6,805 Asian individuals (Korean, Japanese, and Chinese) and found significant association between a SNP (rs13017846) near the SLC8A1 gene (182305) and shorter QT intervals (p = 8.0 x 10(-14)). Using a genomewide association and replication study in up to 100,000 individuals, Arking et al. (2014) identified 35 common variant loci associated with QT interval that collectively explain approximately 8 to 10% of QT interval variation and highlight the importance of calcium regulation in myocardial repolarization.
-
Short Qt Syndrome
MedlinePlus
Short QT syndrome is a condition that can cause a disruption of the heart's normal rhythm (arrhythmia). ... In people with this condition, the part of the heartbeat known as the QT interval is abnormally short. If untreated, the arrhythmia associated with short QT syndrome can lead to a variety of signs and symptoms, from dizziness and fainting (syncope) to cardiac arrest and sudden death. ... Frequency Short QT syndrome appears to be rare. At least 70 cases have been identified worldwide since the condition was discovered in 2000. ... Learn more about the genes associated with Short QT syndrome CACNA1C KCNH2 KCNJ2 KCNQ1 Inheritance Pattern Short QT syndrome appears to have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Some affected individuals have a family history of short QT syndrome or related heart problems and sudden cardiac death.
-
Short Qt Syndrome
Wikipedia
The precise QT duration used to diagnose the condition remains controversial with consensus guidelines giving cutoffs varying from 330 ms, [11] 340 ms or even 360 ms when other clinical, familial, or genetic factors are present. [11] [12] The QT interval normally varies with heart rate , but this variation occurs to a lesser extent in those with short QT syndrome. [1] It is therefore recommended that the QT interval is assessed at heart rates close to 60 beats per minute. [1] Other features that may be seen on the ECG in short QT syndrome include tall, peaked T-waves and PR segment depression. [10] Other features supporting diagnosis [ edit ] Other features that support a diagnosis of short QT syndrome include: a history of ventricular fibrillation]or ventricular tachycardia despite an apparently structurally normal heart; a family history of confirmed short QT syndrome; a family history of sudden cardiac death aged <40 years; and identification of a genetic mutation consistent with short QT syndrome. [12] [11] Invasive electrophysiological studies , in which wires are passed into the heart to stimulate and record the heart's electrical impulses, are not currently recommended for diagnosing short QT syndrome or predicting the risk of sudden cardiac death. [11] [12] Treatment [ edit ] The treatment for short QT syndrome is aimed at preventing abnormal heart rhythms and reducing the risk of sudden cardiac death. ... "Short QT syndrome" . Cardiovascular Research . 67 (3): 357–66. doi : 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.03.026 . ... R.; Bjerregaard, P. (2000). "Idiopathic short QT interval: a new clinical syndrome?" ... "Sudden death associated with short-QT syndrome linked to mutations in HERG" . ... PMID 12925462 . External links [ edit ] "Short QT syndrome" . Genetics Home Reference .
-
Long Qt Syndrome 1
GARD
Romano-Ward syndrome is the most common form of inherited long QT syndrome . Symptoms include arrhythmia , fainting, cardiac arrest , and sudden death. There are six different types of this syndrome, long QT 1 through 6. Each type is caused by a change in a different gene. The most prevalent form of long QT syndrome is long QT type 1. Long QT type 1 is caused by changes in the KCNQ1 gene.
-
Short Qt Syndrome 2
OMIM
A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that short QT syndrome-2 (SQT2) is caused by heterozygous mutation in the KCNQ1 gene (607542) on chromosome 11p15. Description Short QT syndrome is a cardiac channelopathy associated with a predisposition to atrial fibrillation and sudden cardiac death. Patients have a structurally normal heart, but electrocardiography (ECG) exhibits abbreviated QTc (Bazett's corrected QT) intervals of less than 360 ms (summary by Moreno et al., 2015). ... A short QT interval on a subsequent ECG (290 ms) and on every ECG through 3 years of follow-up was noted. ... ECG showed atrial fibrillation (AF) with slow ventricular response and short QT interval (280 ms). Electrical cardioversion did not terminate the AF.
-
Familial Gastric Type 1 Neuroendocrine Tumor
Orphanet
A rare neoplastic disease characterized by occurrence of atypical and aggressive gastric type 1 neuroendocrine tumors (NET) in early adulthood. The tumors often show nodal infiltration requiring total gastrectomy. ... Patients present high serum gastrin concentrations and iron-deficiency anemia (rather than megaloblastic anemia, which is a typical feature in patients with sporadic gastric type 1 NET, where the tumor usually arises on the background of autoimmune atrophic gastritis).