Load FindZebra Summary
Disclaimer:
FindZebra Search conducts a search using our specialized medical search engine.
FindZebra Summary uses the text completions API
(subject to OpenAI’s API data usage policies)
to summarize and reason about the search results.
The search is conducted in publicly available information on the Internet that we present “as is”.
You should be aware that FindZebra is not supplying any of the content in the search results.
FindZebra Summary is loading...
-
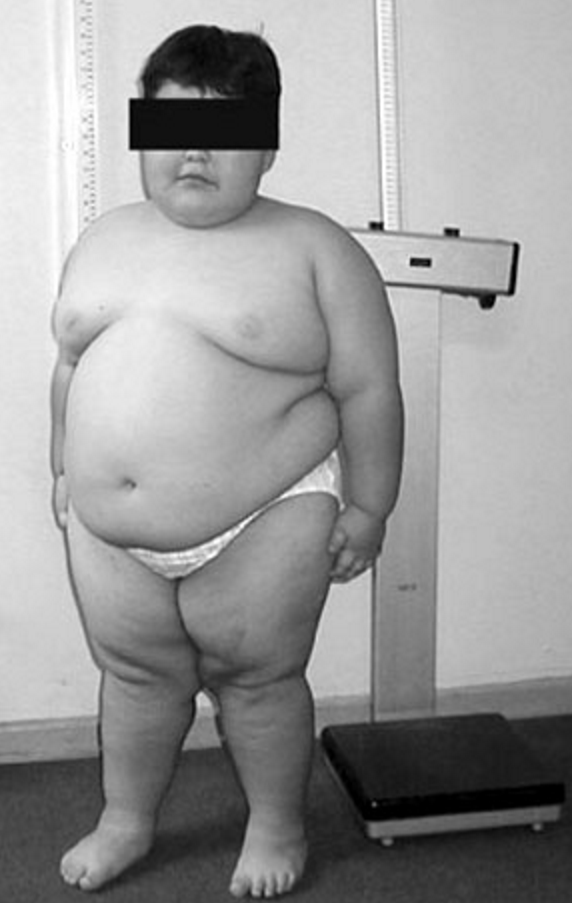
Pten Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome
Orphanet
The most important component seen in this group are malignancies and include breast carcinomas in women with an 85% lifetime risk, epithelial thyroid carcinomas with a 35% lifetime risk, endometrial carcinomas with a 28% lifetime risk, renal cell carcinomas with a 32% lifetime risk and colorectal carcinoma with a 10% lifetime risk.
-
Occupational Hearing Loss
Wikipedia
For example, a person continuously exposed to 85 dB(A) over an 8-hour work shift will reach 100% of their daily noise dose. ... It is important that workers are properly trained on the use of PPE to ensure proper protection. [28] A personal attenuation rating can be objectively measured through a hearing protection fit-testing system. ... Within the United States of America alone, 10 of the 28 million people that have experienced hearing loss related to noise exposure. ... Retrieved May 3, 2016 . ^ a b "CDC - NIOSH Topic: Occupational Hearing Loss (OHL) Surveillance" . www.cdc.gov . Retrieved 2016-03-28 . ^ a b "Ototoxic chemicals - chemicals that result in hearing loss" . Department of Commerce Western Australia . 2014-01-08 . Retrieved 2016-03-28 . ^ Campo P, Morata TC, Hong O (April 2013).
-
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Hypermobility Type
OMIM
Clinical Features Wenstrup et al. (2002) performed a prospective cohort study on 71 consecutive EDS patients. Twenty of 71, or 28%, had aortic root dilatation defined as greater than 2 serum deviations above population-based norms. ... Physical examination showed mild to moderate muscle weakness (85%) and reduction of vibration sense (60%) across all groups. ... Mild myopathic features were seen on muscle biopsy of 5 (28%) of 18 patients. Patients with the hypermobility type EDS caused by TNXB haploinsufficiency were least affected.
-
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Wikipedia
For adults the Hearing Handicap Inventory for Adults (HHIA) can be used [28] and for adolescents the modified 28-item Hearing Environments And Reflection on Quality of Life (HEAR-QL-28) can be used. [29] The HHIA, for example, is a 25-item questionnaire that asks both social and emotional-specific questions such as: Does a hearing problem cause you to avoid groups of people?" ... Response options are yes, no and sometimes. [28] [30] A greater score indicates greater perceived handicap. ... If subsequent monitoring shows that 85 dB is not surpassed for an eight-hour TWA, the employee is no longer required to wear hearing protection. [58] In the European Union , directive 2003/10/EC mandates that employers shall provide hearing protection at noise levels exceeding 80 dB(A), and that hearing protection is mandatory for noise levels exceeding 85 dB(A). [59] Both values are based on 8 hours per day, with a 3 dB exchange rate. ... Workers often will not exceed OSHA standards of 90 dBA, but NIOSH, whose focus is on best practice, has stricter standards which say that when exposed to noise at or exceeding 85 dBA workers need to be put on a hearing conservation program. ... An epidemiological study of 6557 automotive manufacturing workers in China (median age 28 years old) reported that in 62% of the settings where noise exposures were evaluated, levels exceeded the recommended level of 85 dBA. [146] The prevalence of hearing loss was 41% among auto part manufacturing workers, followed by 31% of power train workers and 24% in automotive manufacturing.
-
Normocytic Anemia
Wikipedia
Normocytic anemia is a type of anemia and is a common issue that occurs for men and women typically over 85 years old. Its prevalence increases with age, reaching 44 percent in men older than 85 years. [1] The most common type of normocytic anemia is anemia of chronic disease. [1] Contents 1 Classification 2 Diagnosis 3 Causes 4 Treatment 5 References 6 External links Classification [ edit ] A normocytic anemia is when the red blood cells are of normal size. ... MediGoo - Health Medical Tests and Free Health Medical Information . Retrieved 2020-12-28 . External links [ edit ] Entry on aafp.org v t e Diseases of red blood cells ↑ Polycythemia Polycythemia vera ↓ Anemia Nutritional Micro- : Iron-deficiency anemia Plummer–Vinson syndrome Macro- : Megaloblastic anemia Pernicious anemia Hemolytic (mostly normo- ) Hereditary enzymopathy : Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency glycolysis pyruvate kinase deficiency triosephosphate isomerase deficiency hexokinase deficiency hemoglobinopathy : Thalassemia alpha beta delta Sickle cell disease / trait Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin membrane : Hereditary spherocytosis Minkowski–Chauffard syndrome Hereditary elliptocytosis Southeast Asian ovalocytosis Hereditary stomatocytosis Acquired AIHA Warm antibody autoimmune hemolytic anemia Cold agglutinin disease Donath–Landsteiner hemolytic anemia Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria Mixed autoimmune hemolytic anemia membrane paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia Thrombotic microangiopathy Hemolytic–uremic syndrome Drug-induced autoimmune Drug-induced nonautoimmune Hemolytic disease of the newborn Aplastic (mostly normo- ) Hereditary : Fanconi anemia Diamond–Blackfan anemia Acquired: Pure red cell aplasia Sideroblastic anemia Myelophthisic Blood tests Mean corpuscular volume normocytic microcytic macrocytic Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration normochromic hypochromic Other Methemoglobinemia Sulfhemoglobinemia Reticulocytopenia
-
Tangier Disease
Wikipedia
Homozygous Tangier disease and cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 1994;107:85-98. ^ "Autosomal recessive: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia" . www.nlm.nih.gov . Retrieved 2015-09-28 . ^ Rust S, Rosier M, Funke H, et al. ... Genetics Home Reference . Retrieved 2015-09-28 . ^ Serfaty-Lacrosniere C, Civeira F, Lanzberg A, et al. Homozygous Tangier disease and cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 1994;107:85-98. ^ When a Gene Makes You Smell Like A Fish - Published 1990 Received From the Tangier History Museum" External links [ edit ] Tangier disease at NLM Genetics Home Reference Classification D ICD - 10 : E78.6 ICD - 9-CM : 272.5 OMIM : 205400 MeSH : D013631 DiseasesDB : 12901 External resources Orphanet : 31150 v t e Inborn error of lipid metabolism : dyslipidemia Hyperlipidemia Hypercholesterolemia / Hypertriglyceridemia Lipoprotein lipase deficiency/Type Ia Familial apoprotein CII deficiency/Type Ib Familial hypercholesterolemia/Type IIa Combined hyperlipidemia/Type IIb Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia/Type III Familial hypertriglyceridemia/Type IV Xanthoma/Xanthomatosis Hypolipoproteinemia Hypoalphalipoproteinemia/HDL Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency Tangier disease Hypobetalipoproteinemia/LDL Abetalipoproteinemia Apolipoprotein B deficiency Chylomicron retention disease Lipodystrophy Barraquer–Simons syndrome Other Lipomatosis Adiposis dolorosa Lipoid proteinosis APOA1 familial renal amyloidosis v t e Genetic disorder , membrane: ABC-transporter disorders ABCA ABCA1 ( Tangier disease ) ABCA3 ( Surfactant metabolism dysfunction 3 ) ABCA4 ( Stargardt disease 1 , Retinitis pigmentosa 19 ) ABCA12 ( Harlequin-type ichthyosis , Lamellar ichthyosis 2 ) ABCB ABCB4 ( Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 3 ) ABCB7 ( ASAT ) ABCB11 ( Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 2 ) ABCC ABCC2 ( Dubin–Johnson syndrome ) ABCC6 ( Pseudoxanthoma elasticum ) ABCC7 ( Cystic fibrosis ) ABCC8 ( HHF1 , TNDM2 ) ABCC9 ( Dilated cardiomyopathy 1O ) ABCD ABCD1 ( Adrenoleukodystrophy , Adrenomyeloneuropathy ) ABCG ABCG5 ( Sitosterolemia ) ABCG8 ( Gallbladder disease 4, Sitosterolemia ) see also ABC transporters
-
Lepidopterism
Wikipedia
Dermatol . 13 (5 Pt 1): 743–7. doi : 10.1016/S0190-9622(85)70216-2 . PMID 4078069 . Further reading [ edit ] Hossler EW (2009). ... J. Am. Acad. Dermatol . 62 (1): 13–28, quiz 29–30. doi : 10.1016/j.jaad.2009.08.061 .
-
Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma
Wikipedia
Specialty Oncology , ENT surgery Symptoms Various upper respiratory symptoms such as difficulty breathing Usual onset Ages 24-85 (Average of 52 years) Diagnostic method Biopsy Differential diagnosis Synovial sarcoma , Fibrosarcoma , and other related sarcomas of the ENT Treatment Surgery with radiation Prognosis Good Frequency Very Rare Deaths 0 Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma is a newly recognized, very rare, low grade malignant tumor of the nasal cavity which was formerly probably included in fibrosarcoma and synovial sarcoma cases. ... Patients present over a wide age range (24–85 years), with a mean age of 52 years. ... "Low-grade sinonasal sarcoma with neural and myogenic features: a clinicopathologic analysis of 28 cases". Am J Surg Pathol . 36 (4): 517–25. doi : 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182426886 .
-
Acoustic Shock
Wikipedia
Devices which solely limit noise levels to about 85 dB have been shown in field trials to be ineffective (data from these trials has not been released into the public domain). ... BBC News . 12 February 2001. [ needs update ] ^ Coleman, Clive (28 March 2018). "Musician wins landmark ruling over ruined hearing" .
-
Prader–willi Syndrome
Wikipedia
The PW genes are the SNRPN and NDN necdin genes, along with clusters of snoRNAs : SNORD64 , SNORD107, SNORD108 and two copies of SNORD109, 29 copies of SNORD116 (HBII-85) and 48 copies of SNORD115 (HBII-52). ... "Prader-Willi syndrome: a review with special attention to the cognitive and behavioral profile". Birth Defects Orig. Artic. Ser . 28 (1): 99–104. PMID 1340242 . ^ a b c Cassidy SB (1997). ... "Prader-Willi phenotype caused by paternal deficiency for the HBII-85 C/D box small nucleolar RNA cluster" . ... PMID 18500341 . ^ Ding F, Li HH, Zhang S, Solomon NM, Camper SA, Cohen P, Francke U (March 2008). "SnoRNA Snord116 (Pwcr1/MBII-85) deletion causes growth deficiency and hyperphagia in mice" . ... PMID 18320030 . ^ Ding F, Prints Y, Dhar MS, Johnson DK, Garnacho-Montero C, Nicholls RD, Francke U (2005). "Lack of Pwcr1/MBII-85 snoRNA is critical for neonatal lethality in Prader-Willi syndrome mouse models".MAGEL2, SNRPN, NDN, MKRN3, NPAP1, IPW, PWAR1, SNORD116-1, MKRN3-AS1, PWRN1, SNORD115-1, MRAP2, HERC2, HTR2C, CEP63, CENPJ, SOS1, PTPN11, RIT1, KRAS, RAF1, LZTR1, ATR, GH1, UBE3A, GABRB3, SNORD116@, UROD, SNURF, LEP, SNORD14D, SNORD14B, SNORD35B, SNORD14E, SNORD14C, GHRL, SNORD15A, IGF1, HCRT, GHR, SLC52A2, OCA2, F2R, NR1I2, ADIPOQ, PCSK1, ATP10A, POMC, SETDB1, IL6, GHRH, SNHG14, MAGED1, PWAR5, DMD, BEST1, ZNF274, FMR1, GNAQ, GLP1R, EHMT1, STOML3, HSPG2, STS, RASA1, TNFSF11, CRP, SLC6A4, LEPR, MARK2, TNFRSF11B, EHMT2, METAP2, NHLH2, GHSR, GABRA5, SOST, SIM1, PIK3CA, DKK1, PROCR, PADI4, EID1, RNF13, CIT, ABCB6, GREM1, CYFIP1, ACADS, ADIPOR1, RCBTB1, ZGLP1, MIR23A, MIR122, GOLGA8EP, RBMY1D, ENHO, PWARSN, RBMY2DP, GOLGA6A, WHAMMP3, SNORD109B, SNORD109A, NIPA1, TUBGCP5, LMLN, TMPRSS13, NIPA2, DHDDS, POM121, ADIPOR2, ANKRD36B, CHPT1, PRDM9, RETN, NSMCE3, ANGPTL8, ZNF654, DHX40, SMN2, PREPL, MSMB, MECP2, STMN1, HTR2B, HTC2, NR4A1, HDC, GCG, GAPDH, GABRG3, FRAXA, FMO2, EPHB1, EFNB2, DIO3, DAZ1, DAG1, CNR1, CD36, BTF3P11, BRAF, BGLAP, BDNF, BCR, AVP, ARSD, ARSA, AR, APOC3, ALCAM, MEN1, MST1, DLK1, CYTB, SCG2, VEGFA, TYR, TWIST1, TSPY1, TNF, THAS, STATH, STAR, AGRP, SMN1, SLC5A2, CCL5, SAG, RBMY1A1, PYY, PRNP, PRL, PRKCA, PTPA, PML, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PGC, PDPK1, NPY2R, NPY, HNRNPM, FMR1-IT1
-
Duodenal Lymphocytosis
Wikipedia
Absence of HLA-DQ2 (and the rarer HLA-DQ8) makes coeliac disease most unlikely. [5] As antibody-negative coeliac disease is recognised, HLA status, persistence or progression of the duodenal IEL numbers following a gluten challenge, followed by symptomatic improvement on a gluten-free diet, has been used to be more certain about the diagnosis, which was made in 22% of one series of over 200 adult cases. [5] Helicobacter infection is a common finding at endoscopy and although duodenal IEL counts were found to be slightly higher with this infection, this was not considered to be a meaningful cause in children. [6] Other infections, including Cryptosporidiosis and Giardiasis can also be associated with an increase in IELs. [2] Management [ edit ] The management is that of any identified associated disorder such as a gluten free diet for cases with coeliac disease [5] or treatment of associated infections. [2] Prognosis [ edit ] When duodenal lymphocytosis is associated with other features of coeliac disease, in particular positive antibodies, or HLA-DQ2/8 and a family history, treatment with a gluten -free diet produces an improvement in IEL numbers. [5] Diarrhoea, thyroiditis, weakness and folate deficiency were other predictors of the development of gluten sensitivity and coeliac disease, which developed in 23 of 85 patients over 2 years in one series. [7] References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f Lauwers, Gregory Y; Fasano, Alessio; Brown, Ian S (2015). "Duodenal lymphocytosis with no or minimal enteropathy: much ado about nothing?" . Modern Pathology . 28 (S1): S22–S29. doi : 10.1038/modpathol.2014.135 . ... S2CID 22316105 . ^ Losurdo, Giuseppe; Piscitelli, Domenico; Giangaspero, Antonio; Principi, Mariabeatrice; Buffelli, Francesca; Giorgio, Floriana; Montenegro, Lucia; Sorrentino, Claudia; Amoruso, Annacinzia; Ierardi, Enzo; Leo, Alfredo Di (2015-06-28). "Evolution of nonspecific duodenal lymphocytosis over 2 years of follow-up" .
-
Cerebral Autosomal Recessive Arteriopathy With Subcortical Infarcts And Leukoencephalopathy
Wikipedia
. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Carasil. (2013). Retrieved 1/28, 2015, from http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php? ... Retrieved 2019-11-05 . ^ a b c d e Cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. (2011). Retrieved 1/28, 2015 ^ a b Devaraddi, Navalli; Jayalakshmi, G.; Mutalik, Narayan R. (2018-01-01). ... Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 20(2), 85-86,87,88,89,90,91. ^ a b Reference, Genetics Home. ... "Characteristic features and progression of abnormalities on MRI for CARASIL" . Neurology . 85 (5): 459–463. doi : 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001803 .
-
Myocardial Infarction
Wikipedia
Pain radiates most often to the left arm, but may also radiate to the lower jaw, neck, right arm, back, and upper abdomen . [28] [29] The pain most suggestive of an acute MI, with the highest likelihood ratio , is pain radiating to the right arm and shoulder. [30] [29] Similarly, chest pain similar to a previous heart attack is also suggestive. [31] The pain associated with MI is usually diffuse, does not change with position, and lasts for more than 20 minutes. [24] It might be described as pressure, tightness, knifelike, tearing, burning sensation (all these are also manifested during other diseases). ... Spasm of coronary arteries, such as Prinzmetal's angina may cause blockage. [24] [28] Tissue death [ edit ] Drawing showing anterior left ventricle wall infarction If impaired blood flow to the heart lasts long enough, it triggers a process called the ischemic cascade ; the heart cells in the territory of the blocked coronary artery die ( infarction ), chiefly through necrosis , and do not grow back. ... Treatment aims to preserve as much heart muscle as possible, and to prevent further complications. [28] Treatment depends on whether the myocardial infarction is a STEMI or NSTEMI. [69] Treatment in general aims to unblock blood vessels, reduce blot clot enlargement, reduce ischemia, and modify risk factors with the aim of preventing future MIs. [28] In addition, the main treatment for myocardial infarctions with ECG evidence of ST elevation (STEMI) include thrombolysis or percutaneous coronary intervention , although PCI is also ideally conducted within 1–3 days for NSTEMI. [69] In addition to clinical judgement , risk stratification may be used to guide treatment, such as with the TIMI and GRACE scoring systems. [16] [69] [111] Pain [ edit ] The pain associated with myocardial infarction may be treated with nitroglycerin or morphine . [28] Nitroglycerin (given under the tongue or intravenously) may improve the blood supply to the heart, and decrease the work the heart must do. [28] It is an important part of therapy for its pain relief, despite there being no benefit to overall mortality. [28] [112] Morphine may also be used, and is effective for the pain associated with STEMI. [28] The evidence for benefit from morphine on overall outcomes, however, is poor and there is some evidence of potential harm. [113] [114] Antithrombotics [ edit ] Aspirin , an antiplatelet drug , is given as a loading dose with the goal of reducing the clot size and reduce further clotting in the affected artery. [28] [69] It is known to decrease mortality associated with acute myocardial infarction by at least 50%. [69] P2Y12 inhibitors such as clopidogrel , prasugrel and ticagrelor are given concurrently, also as a loading dose , with the dose depending on whether further surgical management or fibrinolysis is planned. [69] Prasugrel and ticagrelor are recommended in European and American guidelines, as they are active more quickly and consistently than clopidogrel. [69] P2Y12 inhibitors are recommended in both NSTEMI and STEMI, including in PCI, with evidence also to suggest improved mortality. [69] Heparins , particularly in the unfractionated form, act at several points in the clotting cascade , help to prevent the enlargement of a clot, and are also given in myocardial infarction, owing to evidence suggesting improved mortality rates. [69] In very high-risk scenarios, inhibitors of the platelet glycoprotein α IIb β 3a receptor such as eptifibatide or tirofiban may be used. [69] There is varying evidence on the mortality benefits in NSTEMI. ... These medications include tissue plasminogen activator , reteplase , streptokinase , and tenecteplase . [28] Thrombolysis is not recommended in a number of situations, particularly when associated with a high risk of bleeding or the potential for problematic bleeding, such as active bleeding, past strokes or bleeds into the brain, or severe hypertension . Situations in which thrombolysis may be considered, but with caution, include recent surgery, use of anticoagulants, pregnancy, and proclivity to bleeding. [28] Major risks of thrombolysis are major bleeding and intracranial bleeding . [28] Pre-hospital thrombolysis reduces time to thrombolytic treatment, based on studies conducted in higher income countries, however it is unclear whether this has an impact on mortality rates. [123] Other [ edit ] In the past, high flow oxygen was recommended for everyone with a possible myocardial infarction. [81] More recently, no evidence was found for routine use in those with normal oxygen levels and there is potential harm from the intervention. [124] [125] [126] [127] [128] Therefore, oxygen is currently only recommended if oxygen levels are found to be low or if someone is in respiratory distress. [28] [81] If despite thrombolysis there is significant cardiogenic shock , continued severe chest pain, or less than a 50% improvement in ST elevation on the ECG recording after 90 minutes, then rescue PCI is indicated emergently. [129] [130] Those who have had cardiac arrest may benefit from targeted temperature management with evaluation for implementation of hypothermia protocols.TNF, NOS3, ACE, TGFB1, HMGB1, IL1B, AGT, MMP2, MMP9, CASP3, NPPA, GSK3B, ICAM1, GATA4, CAT, PPARGC1A, S100B, BECN1, SOD2, PLN, PLAU, LTA, MIAT, BCL2L1, IL10, HSD11B2, MYH7, PSMA6, OLR1, PHACTR1, BRAP, MIA3, SH2B3, WDR12, ESR1, THBD, IL6, EPO, CXCL12, APOE, ITGB3, TNFSF4, PLAT, BCL2, F7, F5, LGALS2, F2, REN, P2RY12, NR3C2, TNNI3, KIF6, LGALS3, F13A1, ATM, LRP8, IL1RN, HP, TP53, KLK1, BAX, SOD1, NOS2, HSPA5, MIR145, JAK2, PAPPA, TIMP2, DDIT3, TM6SF2, GCLM, IL6R, GCLC, SELL, CKM, LAMP2, PRKCE, NRIP1, ACTA2, CRP, NPPB, MIR423, ATP1A1, SIRT1, CKB, MIR125B2, VWF, EDN1, DGKZ, CREB1, CREM, CCN2, VDAC1, BAK1, ACE2, IGF1, KLF13, ADRB2, PDE3A, AGTR1, LDHA, ADORA3, CCL2, MIR761, MFF, ANGPT1, IFNA2, GJA1, ADORA1, DAB2IP, GGT1, ADIPOQ, HMOX1, SERPINE1, MMP1, HIF1A, TNFRSF12A, MAPK1, NFE2L2, AKT1, SELP, THBS1, SIRT3, F3, CYBB, IL17A, SMAD2, FN1, POSTN, ADRB1, ANGPT2, AGER, CD36, C3, TNC, PDE5A, TNFRSF1A, CCL5, CYBA, CD59, REG1A, FLT1, ANXA5, CDKN1B, CSF2, CASR, EDNRA, CTSB, MTOR, MIF, COL3A1, NFKBIA, TBX5, TNFRSF1B, PGF, HSPD1, UTS2, PLAUR, ITGB1, TGFBR1, MYH6, TRPV1, MDH2, MDK, IGF1R, MEF2C, EDNRB, SFRP2, EGLN3, HAMP, KCNK2, MMP14, BNIP3, MMP13, SOCS1, SDC1, SMAD4, ADAMTS1, SPARC, OPA1, VCAN, BDKRB2, CAV3, BDKRB1, MAP1LC3A, EGLN1, APOH, TFPI, SLC27A1, VDAC2, CSNK2A1, DCN, CSNK2B, DAB2, EPOR, ATP5F1D, MFN2, EPAS1, AVPR1A, ITGA3, CACYBP, DVL1, DAG1, EDN2, AK1, CYP11B1, KCNJ2, RAD50, TXNRD1, PDGFD, APOB, RPS6KB1, LPA, SLPI, HADH, LPL, GSR, FIS1, TBX3, UTS2R, TEK, GJA5, TGFB2, GHRH, TGFBR2, TTN, LDLR, SHH, RANBP1, YBX1, G6PD, FZD2, LCAT, MEF2A, TLR4, PCSK9, MAP3K5, BIRC5, IL4R, SLC27A6, PTN, PLCB3, OPRK1, ATG7, CCR3, TNFRSF14, COL1A1, ABO, CFL1, PPARG, PLCB1, CCNA2, OPRD1, PEBP1, C7, C8A, C8B, AIMP1, ABCA1, BTN2A1, SMAD3, CDKN2B-AS1, COL4A2, CTNNB1, ENPP1, ILF3, CLEC16A, LAMA3, FOS, ELN, MEFV, LDLRAP1, FAS, GLA, CAV1, GUCY1A1, IL23R, CBS, AP3D1, LRPAP1, IL12B, LIPA, ATP2B1, IRF5, LRP6, RNF13, STAT4, CFTR, MAPKAP1, PLCL2, ATL1, ITIH3, SMARCA4, CALR, BCHE, LMNA, HLA-B, JCAD, CYP17A1, ABCG5, DNAJC6, SPTBN5, RAF1, PLA2G6, MB, GCG, SORCS2, CXCR4, EMC8, PON1, MARCHF10, BAZ1B, THOC2, PIK3CG, PIGQ, OSGIN1, ZC3H3, GJA4, DYRK1B, PIGA, LZTR1, IVD, GTF2IRD1, CETP, PTPN11, ZC3HC1, ACSS1, CYP2C19, SCNN1A, CAD, YTHDF3, NLRP3, CDKN2A, ITGA1, NDST1, PLPP3, PECAM1, TSPO, ITPK1, NUP210, PTPRN2, FUT7, ABCC6, C20orf181, CD14, GLP1R, JPH3, TSPAN9, GTF2I, ABCG8, STAT3, CEP19, LARGE2, SRP54, PIK3CB, PML, MORF4L1, BRAF, HGD, HGF, NRG1, PIK3CD, DNAJC21, PITRM1, CSF3, SBDS, CST2, APOA1, TFF1, PIK3CA, GNB3, RFC2, APOC3, MAPK14, SLC2A10, TET2, MLX, PLA2G3, KLRC4, RGS12, LTBP2, VOPP1, CUL9, GP6, TAF4, GDF15, COL13A1, PDZD2, LIMK1, ERGIC1, POM121L9P, FGF2, BHMG1, ATXN2, SELE, CLCN1, SLC7A8, AVP, CELSR2, MTHFR, PSMB4, ALOX5, ALOX5AP, UGGT2, ZNF536, WNK2, ABCC1, VEGFA, MPO, AGPAT2, NCOR2, MPL, MALAT1, ANKUB1, SBF1, C9orf139, MYH9, BSCL2, TBL2, IL12A-AS1, MCCC2, TENM3, TRDMT1, IL12A, MMRN1, DPP4, GPR160, WRN, EIF2AK1, PSMA4, CLIP2, SEC24D, ALDH2, CCR1, PGR-AS1, BIN1, BCRP1, UBAC2, ARVCF, PLA2G2A, CCR2, POU2F3, MIR21, PLA2G1B, GPR135, PTGS2, TP73, CAVIN1, CPLX2, TCF25, SEPTIN9, DIDO1, UHRF1, FES, PLA2G7, FGB, SLC5A2, F10, TRAPPC9, C4A, SERPINA5, MMP3, SCNN1G, ERAP1, CYP27A1, CHRM3, SCNN1B, CCT2, IL1A, IKZF1, PLG, ITGA2, POLDIP2, AIMP2, RNF19A, AHSA1, APOA5, CRK, GRAP2, ADD1, ACCS, DECR1, GABPA, MIR499A, ACSS2, CCR5, ABCB1, PLA2G15, FSD1L, FSD1, ACTB, AGTR2, IKZF5, TM7SF2, PTEN, ADM, TNNT2, CYP2J2, CYP2C9, MTCO2P12, FGF23, TIMP1, CHDH, COX2, CX3CR1, ALB, PARP1, TXN, CFH, CYP2C8, THBS4, KDR, MIR34A, MSC, BDNF, LTA4H, FSTL1, ADAMTS13, CXCL8, GH1, MIR208A, TRS-AGA2-3, ADRA2B, MTR, ESR2, PTGIS, MAPK3, PROC, AHSG, IL4, MIR143, HFE, TBPL1, MBL2, GSTM1, CASP1, ITGA2B, SLC33A1, HPSE, GP1BA, CD34, HSPB3, EHMT1, HSPB1, IL18, MIR155, PPARA, APLN, CDKN2B, LCN2, ANXA1, PTK2B, FABP3, SORT1, OR10A4, MAPK8, S100A4, PTH, TNFRSF11B, ADAM8, NOS1, NM, NGF, ADH1C, OSM, FTO, PTGS1, AKR1A1, CIITA, MDM2, NT5E, PTX3, RLN2, ROS1, LIPC, LEP, MMP12, GPT, ARNTL, F2R, APOA4, SPP1, ST2, NR3C1, NOX4, NR1I2, TH, RIPK3, THPO, TIMP3, TLR2, FGA, COPD, C1QTNF9, VCAM1, LRPPRC, CHI3L1, ENG, MIR210, EGFR, DSPP, MIR126, DNASE1, MIR144, MIR17, CST3, CLU, CNR2, CPB2, SMUG1, SOAT1, COL4A1, MIR325, IL6ST, NTN1, IFNG, VPS51, HSPB2, SLC6A4, SHBG, ID2, MST1, GPR162, KLF4, EGR1, KIT, E2F1, ALOX12, HAVCR1, ATG5, ALOX15, C4B, PTGER4, VDR, GDF11, CCL11, EPRS1, PRKAB1, PRKAA2, TNFRSF4, SLC7A9, PCYT1A, DDX39A, KCNMA1, DES, BMI1, XRCC1, TREM1, INSRR, MYDGF, TLR9, BGN, NPR3, ABCG1, SERPINB2, ILK, NPY, GAS5, TRIB1, CTSD, CYP1A2, NFKBIL1, DDX39B, NFKB1, MIR146A, CYP11B2, SCG2, ADAMTS7, SERPINA3, MME, F11, TTR, BRCA1, THBS2, LBP, FABP4, ZGLP1, DNM1L, MIR208B, YAP1, PROM1, TFAM, COL18A1, SERPINF1, ACKR3, PER2, CD151, GSTP1, GSTT1, SELENBP1, SOCS3, CD40, SEMA6A, RUNX1, XPR1, AQP9, ITGAM, MIR223, MIR22, FAP, PRKAA1, S100A9, S100A8, FGF1, MGP, PDE4D, TMSB4X, RETN, FGG, TIMP4, ARG1, ANPEP, FUS, FPR2, CXCR6, DDAH2, PROCR, CLOCK, APOM, CREG1, LPAR2, CD163, MRAS, PRKCB, PRKCA, TXNRD2, PPIA, PADI4, TNFSF10, LIPG, ACSL6, UTRN, DENR, UGT1A1, TCP1, DUOX2, BAG3, DELEC1, KCNQ1OT1, SSTR4, SREBF2, NR1H3, INSIG2, SOD3, SMN2, RYR2, TGFBR3, SMN1, SLC25A37, EBI3, S100A1, SLC2A1, ACSL5, SEMA3F, CCHCR1, ATXN1, SDC4, DUOX1, SEMA3A, SLC52A1, DDAH1, BEST1, BHLHE40, FCN3, APOL1, DAPK2, KLK4, HDAC4, KDM3A, MTHFD1L, NES, RAPGEF5, XPO1, MEG3, MOK, INTU, PDCD4, UCP2, ANGPTL3, KCNE2, SETD2, NEIL3, PTPN1, TLR3, RCBTB1, THY1, PTGES, LOX, FBN1, BRS3, IL33, COL4A3, GLI3, C5AR1, IL15, C5, CXCL10, INS, PDX1, MIR326, GIPR, GHSR, COMT, BSG, MIR375, IGF2, COX8A, KCNQ1, KNG1, BMP2, ZNF627, GAP43, LIF, CRMP1, MIR183, CCND1, FNDC5, FLNA, LTC4S, FOXM1, IGF2R, CNR1, ADM2, CCND2, GSTM2, MIR29B1, MIR29B2, GSN, MIR23A, MIR30A, MIR30B, CD68, CYP2R1, CD40LG, ENTPD1, SCARB1, CD28, LRG1, CXCL1, PRRT2, MIR98, HSPA4, CGAS, CMA1, CAST, PLB1, GPR42, TXNRD3, GPER1, MIR203A, ZFAS1, AZIN2, IFNA1, IFNA13, SMAD1, LIFR, SERPINC1, CYP4A11, BTBD8, ENPEP, CYP1B1, ELANE, ACHE, MTAP, MIR150, F13B, MIR711, F2RL1, BRINP3, ETV2, CYP19A1, AIRE, CXCL16, GOLGA6A, NCAM1, NPPC, ACVR1B, GRK2, NPR1, PCSK1, NANOS3, NUCB2, ADRA1A, EPHX1, MPI, HPSE2, FOXO4, CTSK, PKD1, MIR590, PIM1, MIR106B, MCAM, ARSA, MIR100, TAS2R50, FCN2, AR, FCN1, MIR132, CTSG, DNTT, PF4, KMT2A, APEX1, APOC1, MIRLET7I, PFN2, MIR134, MIR140, MIR204, MIR221, MIR224, MIR139, MIR212, MIR130A, ERAL1, MIR206, AATF, MIR24-1, SIRT4, ADGRL3, MIR214, LPAR3, VPS33B, MIR199A1, MIR181A2, SH2B1, SOSTDC1, MIR181C, MIR185, MIR26A1, TXN2, GCA, MIR186, MIR15A, MIR188, MIR192, MIR197, MIR199A2, CLEC4E, MIR154, MIR19A, MIR19B1, DGCR5, PHGDH, MIR149, MIR15B, MIR20A, POFUT1, MIR142, MIR200A, BRD4, ANGPTL2, ARC, PALLD, MIR26B, KIF28P, MIR4306, MIR762, TMED7-TICAM2, LYVE1, CPSF4, MIR1908, JTB, MIR1825, MIR1231, MIR298, LILRB1, KIF2C, HOTAIR, WWP2, HNRNPUL1, MIR577, KIF3A, MIR421, CXADRP1, POTEM, APELA, MICA, MIR519D, NFAT5, H3P10, DCTN6, H3P24, H3P23, B3GNT2, LOC110806262, NRG3, RN7SL263P, OGA, TCFL5, PPR1, CST12P, TRAF3IP2, CERNA3, ARPP21, TP53COR1, APOC4-APOC2, TUBGCP2, COMMD3-BMI1, KLRC4-KLRK1, MIR486-1, SLC2A6, MIR27A, MIR34C, GPR166P, FAIM2, DNAI1, KDM1A, VN1R17P, POTEKP, EIF2AK4, PHLPP2, MIR93, MIR31, MIR148B, TBC1D9, MIR30E, MPRIP, STAB1, ABRAXAS2, METAP1, MLC1, MIR301A, MIR29A, MIR133B, SCAP, WIF1, FCMTE2, AKAP10, PADI2, MIR525, MIR498, MIR497, CHP1, ACOT7, MIR494, MIR146B, MIR424, MIR151A, MGLL, MIR370, MIR367, MIR328, CARD8, KLRK1, CD93, ATF6, SIRT2, MIR125A, TENM2, MIR122, AGGF1, DDIT4, TCHP, KBTBD7, REG4, TSPAN10, HMCN1, ROPN1L, FERMT3, TRPM4, CELF1, CNNM2, SESN2, NCAPG2, CASZ1, MAP1LC3B, TET1, ELOVL2, SARS2, ZC3H12A, TUG1, AGBL2, COQ5, CCDC93, AKT1S1, TSLP, HDAC7, GDE1, IL17F, GHRL, CLEC6A, MYOCD, DERL3, ZNF160, WNT3A, ABCC11, HHIPL1, TERF2IP, XRN1, ATAD1, ADTRP, PSRC1, RNASE7, IL1F10, DOT1L, PCDH18, KLF3-AS1, RMDN3, MIR10A, RHBDF2, EAF2, GREM2, STRA6, TINAGL1, MOAP1, ELOVL5, LGR6, BTNL2, ZNF77, CREBZF, SLC2A9, CELF4, STARD7, NGB, PTBP2, TRIB3, TBX20, MRTFA, JPH2, PELI1, CFAP97, ST6GALNAC1, TTTY15, GINGF2, PPP6R3, NDNF, ADIPOR2, OGFOD1, SLC52A2, CDC73, PAGR1, NOX5, ELOVL6, TRPM8, NBEAL1, NUCKS1, ACD, FEM1A, CDCA7L, MRPS6, CDCP1, AIDA, SMPD4, SYBU, SLC30A6, RAB14, TMEM54, SIRT6, ISYNA1, TMOD4, NCR3, COL6A5, IL27, SPESP1, GPRC6A, ZBTB12, DIPK2A, LINC00528, MLKL, DCP1B, RHOV, THAP5, OXER1, NENF, HFM1, CITED4, CCDC63, TMTC3, SPAAR, ZNF746, MRGPRX1, ASPM, NEAT1, OSTN, HSPB7, MIRLET7D, PEAR1, IL37, DISC1, GSTK1, TICAM2, SLC6A18, ACTBL2, HPGDS, EMC10, TNRC6A, CPP, STING1, RABGEF1, PPP1R42, SGSM3, MAT2B, REM1, ATP10D, IL19, PPM1L, A1CF, CPA4, GPR151, SLCO6A1, ANGPTL4, HSPB6, EARS2, JDP2, MRGPRX4, PLEKHO1, HSPA14, MRGPRX3, MUC17, HSPA12B, LRRC3B, BFAR, OMA1, TLR7, FBXO32, PLA1A, C1QTNF5, TRPV2, RMDN1, ADIPOR1, KCNIP2, ASCC1, RMDN2, ERFE, COMMD7, GNAS-AS1, MOB3C, IL22, NTM, MMVP1, TMED5, TMED7, TNNI3K, GLRX2, PTPRVP, B3GNTL1, IL34, PWAR1, APIP, GAL, CACUL1, TRPM6, A2M, CX3CL1, TXNIP, GCH1, GLO1, GFAP, GDF10, MSTN, GDF1, GCKR, GCGR, FXN, GC, GATA3, GAS6, GARS1, FYN, FUT4, GLRA2, GOLGA4, GPI, GPLD1, CXCR3, GPR17, GRK4, GPX1, GPX4, GRB2, GRIA1, CXCL2, GUCY1B1, GYS1, GZMB, HABP2, SERPIND1, GAST, FPR1, SLCO1B1, EPHB4, F9, EZH2, ESRRA, ERBB4, ERBB2, EPHX2, EPHB2, FOLR2, ENO2, ENO1, MARK2, EIF4EBP1, EFNA3, S1PR3, FABP2, FANCD2, FAT1, FBP1, FCAR, FCGR2A, FCGR3A, FCGR3B, FER, FGF9, FGFR1, FGFR3, FOXO1, FOXO3, FLT4, FOLH1, FOLR1, HDAC1, HHEX, HIC1, KLKB1, LCP1, RPSA, LAIR1, LAD1, KRT16, KRT1, KCNN4, HLA-C, KCNJ11, KCNE1, ITIH4, ITGB2, ISL1, IRF6, LCT, LEPR, LGALS3BP, LIPE, LRP1, LTB, CYP4F3, CD180, LYN, TACSTD2, SMAD7, MAG, MAP4, MAPT, MAS1, MBNL1, MCL1, IRF3, ITGA6, IPP, HTR1D, HLA-DMB, HLA-DPB2, HMGB2, HMGCR, HMGA1, NR4A1, HRG, HSD11B1, HSF1, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, HSPA1L, HSPA9, HSP90AA1, HTR2A, INHBA, ICAM3, IRF8, IFI27, IFNAR1, IFNGR2, IGFBP1, IGFBP3, IGFBP4, IGFBP7, IL2RB, CXCR1, CXCR2, IL11, TNFRSF9, S1PR1, ECM1, ECE1, BACH1, BMP6, CXCR5, BID, CEACAM1, CFB, BCL2A1, BAAT, RUNX3, B2M, AZU1, ATR, ATP5PF, ATOH1, ATF3, BNIP3L, BPI, BRCA2, KLF9, BTK, SERPING1, C3AR1, C9, CA2, CA3, SLC25A20, CALCR, CALM2, CAMP, CANX, CASP7, CASP8, ASPA, ASIP, ARR3, APLNR, ABCA4, AOC1, ACACA, ACACB, ACTG1, ACTG2, ADA, ADAM10, ADH1B, ADH5, ADORA2B, ADRB3, AGRP, JAG1, AHR, AREG, AKT2, ALCAM, AMPD1, ANG, ANK2, ANXA7, APAF1, APC, APOA2, APOC2, APOC4, APOD, APP, APRT, CASP9, CCK, E2F4, CTSZ, DBH, CYP7A1, CYP3A4, CYP2D6, CYP1A1, CXADR, CTSE, CD5L, NKX2-5, CSH2, CSH1, CRY2, CRX, CR1, DBP, DCC, DDT, DHCR24, SEPTIN1, DIO3, DLD, DMD, DNMT1, DNMT3A, DRD1, ATN1, RCAN1, TSC22D3, HBEGF, DUSP1, DYRK1A, CPT2, CPT1A, CPOX, CENPC, CD27, CD44, CD69, CDK1, CDC42, CDH2, CDH11, CDH13, CDKN1A, CDKN1C, CDX2, CEACAM5, CEBPD, CECR, CEACAM3, CPA3, CEACAM7, CHAT, CHGA, CHRNA4, CHRNA5, CHUK, CKMT2, ERCC8, CCR7, CNP, COL1A2, COL5A2, COMP, CP, CD46, MEIS2, MAP3K3, SF3A2, GPR65, LOH19CR1, FZD7, FZD4, FZD1, MIA, ECB2, FGF16, GHS, ALMS1, PXDN, DNALI1, ZNF202, YWHAZ, RAE1, RGS5, PPM1D, CYP4F2, MAPKAPK5, DEGS1, TNFSF11, PDE8B, RTCA, AOC3, SLC4A4, VAMP8, RIPK1, TNFSF13, DLK1, TNFRSF11A, IL18R1, XRCC3, XIST, XBP1, TPD52, TAC1, ADAM17, TBXA2R, TBXAS1, ZEB1, TRA, PPP1R11, TERT, TGFB3, TGM2, CLDN5, TNFAIP6, TNNI2, TNXB, TRPC3, WT1, TRPC4, TTC3, TTPA, TYR, SUMO1, UCP3, VEGFB, VEGFC, VIM, VIP, VLDLR, WARS1, WNT1, WNT11, FGF18, NRP1, ABCC8, HDAC6, NAMPT, BCAP31, PPIF, ABCC9, ABCB6, GJC1, NR2E3, TMEM11, DGCR2, NR1H4, NR1I3, MVP, GFPT2, TOMM70, ATP6AP2, MPZL2, TRIM13, STX6, RAMP1, CNPY2, WARS2, PRMT5, GPNMB, MERTK, FST, CARM1, ZNRD2, UBD, ANP32B, SLC35A1, GNLY, KEAP1, BMS1, SNX17, KL, CFLAR, CCN4, PER3, IER3, ARHGEF7, FUBP1, WASF1, TRPA1, ARTN, DNAJA3, LRRFIP1, AURKB, IL32, PPIG, COX5A, PIEZO1, RECQL5, FADS2, MED23, QKI, GSTO1, FHL5, GAL3ST1, SPTLC2, GOSR1, GOSR2, AKAP12, PRORP, PPP6R2, EIF4A3, SUV39H1, STXBP2, MET, PIK3C2G, PMM2, SERPINF2, PLD1, PLCB2, PLA2G4A, PITX3, SERPINA4, PROX1, PI3, PFN1, SLC26A4, PDK4, PDHB, PDGFRA, PNMT, POLD1, PON2, PPARD, PPID, PPP1R1A, PRF1, PRH1, PRH2, PRKAR1A, PKN1, PRKD1, MAPK10, MAP2K1, MAP2K6, PRL, PRNP, PDGFA, PDCD1, PCSK2, MYD88, MFAP1, KITLG, CXCL9, MITF, MMP7, MMP8, MRE11, MSRA, MT1JP, COX1, MTHFD1, ND2, MTTP, MYBL2, MYLK, PCNA, NAB1, NDUFA2, NTRK2, OGG1, OGN, SLC22A18, P2RX7, P2RY1, P2RY2, P4HB, PAK1, PAM, PRKN, PC, PROS1, MASP1, STXBP1, SLC5A5, SLN, SLC25A1, SLC16A1, SLC6A8, SLC6A6, SLC6A3, SLC5A3, PSEN1, SMTN, SLC5A1, SLC2A4, ST3GAL4, SIAH2, SGK1, SMARCA1, SMPD1, SMPD2, SNAI1, SNRNP70, SOX9, SP1, SP3, SPG7, SPRR2A, AKR1D1, SRY, SSTR2, STAT6, SULT1E1, ELOVL4, STIM1, SRSF3, SELENOP, SELPLG, RFC1, PSG2, PSMD9, PSMD10, PTBP1, PTGDS, PTGER2, PTK2, PTPRA, PTPRC, PZP, RAC1, RAP1A, RASGRF2, RENBP, RNASE1, CXCL6, RNASE2, RPGR, RPS19, RPS20, RRAD, RYR3, S100A12, SAA1, SAFB, SCN5A, CCL19, CCL20, CCL21, CCL22, H3P40
-
Vaso-Occlusive Crisis
Wikipedia
"The burden of emergency department use for sickle-cell disease: an analysis of the national emergency department sample database" . Am. J. Hematol . 85 (10): 797–9. doi : 10.1002/ajh.21807 . ... American Family Physician (12 ed.). 92 : 1069-1076A. ^ Rees, David C.; Gibson, John S. (28 November 2011). "Biomarkers in sickle cell disease" .
-
X-Linked Opitz G/bbb Syndrome
GeneReviews
Major (more frequent) findings Hypertelorism and/or telecanthus (present in virtually all affected individuals) All degrees of hypospadias that, in the most severe form, can be associated with renal malformations (85%-90%) Laryngotracheoesophageal abnormalities, primarily laryngeal cleft, resulting in swallowing difficulties and respiratory dysfunction (60%-70%) A family history consistent with X-linked inheritance – although variable expressivity among affected individuals, even within the same family, should be taken into consideration Minor findings (found in ≤50% of individuals) Intellectual disability and developmental delay Cleft lip and/or palate Congenital heart defects (e.g., ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, persistent left superior vena cava, patent ductus arteriosus) Imperforate or ectopic anus Midline defects of the brain including agenesis of the corpus callosum and cerebellar vermis agenesis or hypoplasia Establishing the Diagnosis Male proband. ... Incidence of Clinical Features in Males with X-OS with an Identified MID1 Pathogenic Variant View in own window Clinical Feature # of Males with Clinical Feature / Total # of Males Hypertelorism 82/82 Hypospadias 65/85 Laryngotracheoesophageal defects 46/85 Intellectual disability and/or developmental delay 28/85 Cleft lip//palate 42/85 Congenital heart defects 20/85 Anal defects 18/85 Brain abnormalities 18/35 1 Fontanella et al [2008], Li et al [2015] 1.MID1, MID2, AKT1, BMP2, KLK3, PTPA, TP53, TMSB10, TOPBP1, CTCF, KEAP1, NPEPPS, CXCR4, TP63, COIL, SMUG1, UBE2V1, NR2C2, MAP3K7, RFPL1, SPECC1L, PSAT1, PROS1, ASXL1, MIR675, MIR592, MIR367, MIR211, MIR106A, TMEM189-UBE2V1, TMEM189, AFAP1-AS1, TRIM17, CALN1, CD276, PIF1, MID1IP1, HERC6, SOX18, SHC3, RAG1, PRKAA2, MAPK1, ITGA3, IGBP1, IBSP, HMOX1, HMGB1, HK2, GPC3, GABPA, FRA16D, F3, ERCC2, ERCC1, EPHB2, EGFR, DLX3, RUNX2, IGF2, JAG2, PRKAB1, JAK2, PRKAA1, PPP2CA, PLAG1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, SERPINF1, NFE2L2, MYC, MTX1, MTHFR, MMP9, MGMT, MEFV, CCAT2
-
Developmental Delay With Variable Intellectual Impairment And Behavioral Abnormalities
OMIM
Other features included movement disorder (44%), such as ataxia or spasticity, sleep disturbances (38%), seizures (25%), structural brain abnormalities (22%), growth delay (13%), macrocephaly (25%), digital anomalies (34%), somatic overgrowth (28%), and inverted nipples (13%). Dysmorphic facial features were common, although variable, and included tented upper lip, brachycephaly, midface hypoplasia, and low-set ears; there was no recognizable gestalt. In addition to the monozygotic twins (patients 27 and 28), there were 3 families in which a less severely affected parent carried the same heterozygous mutation as the proband (patients 1, 5, and 7). ... Common features included global developmental delay with intellectual disability (mean IQ of 69), autistic features (69%), attention disorders or hyperactivity (67%) or other behavioral abnormalities (85%), and hypotonia (63%). Patient had mild motor delay, with an average age at walking around 20 months and spoken words around 23 months, although most had speech difficulties. ... The patients were ascertained from a cohort of 313 individuals with intellectual disability who underwent trio-based whole-exome sequencing. In 28 patients from 27 unrelated families, including a set of monozygotic twins (patients 27 and 28), with DDVIBA, Vetrini et al. (2019) identified 25 heterozygous mutations in the TCF20 gene (see, e.g., 603107.0004-603107.0006).
-
Candidiasis
Wikipedia
February 13, 2014 . Retrieved 28 December 2014 . ^ a b c d e "Oral Candidiasis Statistics" . cdc.gov . ... Archived from the original on 29 December 2014 . Retrieved 28 December 2014 . ^ "Symptoms of Oral Candidiasis" . cdc.gov . ... Archived from the original on 29 December 2014 . Retrieved 28 December 2014 . ^ "Candidiasis" . cdc.gov . ... Archived from the original on 29 December 2014 . Retrieved 28 December 2014 . ^ a b c Walker M (2008). ... Archived from the original on 29 December 2014 . Retrieved 28 December 2014 . ^ a b Dolin GL, Mandell JE, Bennett R (2010).AIRE, IL17A, CARD9, DEFB4A, DEFB4B, STAT1, IL1B, IL22, NUDT11, S100A1, S100B, SLC5A2, IL10, TNF, IL17RA, IL23A, PSAP, CSF2, DEFB103B, CLEC7A, DEFB103A, SLPI, ADAM17, SYK, IL17F, STAT3, SCLT1, DDX43, TGFA, CCL2, RNA18SN5, RORC, RFX2, RASGRF1, PLB1, TLR1, LRRCC1, NOD2, TRAF3, LAT2, NR4A3, IRS4, PPIG, SETD1A, PTPRH, YME1L1, LRRC7, SIRT3, CCL28, TOR1AIP1, CAP1, NAT1, SRGN, CDR2, DECR1, CYP51A1, CX3CR1, CSH2, CSH1, CSF3, ERCC8, CHEK1, CDR1, EGF, CEACAM1, BCR, APCS, ANPEP, ALS3, ALB, ADM, ADAM10, DEFB1, EGFR, PRB3, IL15, NAT2, MYD88, CYTB, MPO, MBL2, SH2D1A, LGALS3, INPP5D, IL12RB1, ELK3, IL10RB, IL4, IGHG3, HSPA9, HSPA8, HSPA4, FUT2, ELK4, PLCG2
-
Opitz G/bbb Syndrome
Wikipedia
Opitz G/BBB syndrome. Meroni, G. (2011, July 28). X-Linked Opitz G/BBB Syndrome. GeneReviews . ... Seattle, Washington, USA: University of Washington, Seattle. ^ Meroni, G. (2011, July 28). X-Linked Opitz G/BBB Syndrome. GeneReviews . ... Cleveland, Ohio, USA: Johns Hopkins University. ^ Meroni, G. (2011, July 28). X-Linked Opitz G/BBB Syndrome. GeneReviews . ... Cleveland, Ohio, USA: Johns Hopkins University. ^ Meroni, G. (2011, July 28). X-Linked Opitz G/BBB Syndrome. GeneReviews . ... (Health Grades, Inc.) Retrieved July 28, 2015, from Right Diagnosis from healthgrades: http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/o/opitz_g_bbb_syndrome/complic.htm ^ Meroni, G. (2011, July 28).
-
Deafness, Autosomal Recessive 85
OMIM
Clinical Features Shahin et al. (2010) reported a large consanguineous Palestinian family with autosomal recessive prelingual nonsyndromic hearing loss. Mapping By genomewide linkage analysis of a consanguineous Palestinian family with hearing loss, Shahin et al. (2010) found linkage to an 11.1-Mb region on chromosome 17p12-q11.2 (lod score of 7.25) between markers rs230884 and rs12603885, which they designated DFNB85. Although the MYO15A gene (602666) lies in this region, full sequencing revealed no functional mutations. Shahin et al. (2010) concluded that a second gene for hearing loss lies in this region. INHERITANCE - Autosomal recessive HEAD & NECK Ears - Hearing loss, prelingual bilateral MISCELLANEOUS - Based on one consanguineous Palestinian family (last curated August 2015) ▲ Close
-
Winter-Over Syndrome
Wikipedia
It is completely cut off during winter, the mean temperature is −51 °C (−60 °F), and the lowest recorded temperature is −85 °C (−121 °F). [4] For these reasons, the immobility, monotony, harsh physical environment, sexual deprivation, and the general isolation, are believed to contribute to increased anxiety and depression among the residents of the station. [1] Several studies have been done over the years to determine the contributing causes, or stresses, of "winter-over" syndrome. ... Retrieved 11 April 2017 . ^ "How cold is the Antarctic?" . NIWA . 2007-02-28 . Retrieved 2019-09-21 . ^ Palinkas LA, Reed HL, Do NV (1997).