-
Glaucoma
Wikipedia
From here, the trabecular meshwork drains aqueous humor via the scleral venous sinus ( Schlemm's canal ) into scleral plexuses and general blood circulation. [30] In open/wide-angle glaucoma, flow is reduced through the trabecular meshwork, due to the degeneration and obstruction of the trabecular meshwork, whose original function is to absorb the aqueous humor.MYOC, LTBP2, CDKN2B, SLC4A4, TGFB2, PITX2, BDNF, CDKN2A, TDRD7, MYLK, SH3PXD2B, CPAMD8, TNF, VEGFA, NTRK2, SNCG, CNTF, TXN, BAX, SQSTM1, CDKN1B, BECN1, NGF, BCL2, EPO, BAD, MAS1, CYP1B1, LGR4, BEX3, ATF2, NMNAT3, EPOR, FOXC1, CCND2, MAP1LC3A, ANXA3, NGFR, ACE2, TXNIP, NTRK1, LOXL1, GJA1, LMX1B, CDKN2B-AS1, SBF2, FBN1, TGFB1, NHS, ELN, ADAMTS10, COL1A1, TMCO1, COL11A1, PAX6, TEK, FAS, PLEKHA7, HLA-DRB1, PEX19, GNAQ, RPGR, PEX5, LIMK1, SRBD1, OCRL, FMNL2, COL2A1, NLRP3, PEX13, NOD2, FOXE3, RBBP8, ARHGEF12, AHR, ANGPT1, DDX58, TXNRD2, PRPF8, ATR, PROM1, TRAIP, OVOL2, PLXNA2, PLOD1, STUB1, RXYLT1, PIK3R1, MASP1, PIK3C2A, AFAP1, PEX14, YAP1, MERTK, PEX12, SLC7A14, PTCH1, PEX6, PRPF31, ROM1, RLBP1, RHO, RGR, RFC2, PRPH2, RBP3, OPTN, ZSWIM6, RASA1, RAD21, CNTNAP2, PEX2, TOPORS, TMEM98, KIAA1549, PEX10, PDE6B, PEX1, FAT4, PRPF6, B4GAT1, CCDC28B, PRDM5, ARL2BP, FKRP, CRB1, CEP152, AGBL5, SRD5A3, ZNF408, DHDDS, BICC1, PUS1, SNRNP200, ANKLE2, NDP, NEK2, NF1, ARHGEF18, IFT172, PDE6G, PDE6A, PCNT, POMT1, OPA1, EBP, PLK4, NRL, XYLT1, IFIH1, SEMA4A, GZF1, NIPBL, FSCN2, RP9, PTPN22, SCAPER, BEST1, BUB3, WT1, WFS1, CLIP2, LARGE1, NDUFB11, LRAT, VHL, PRPF4, TRIP13, RBFOX1, TRIM44, PDE7B, CLRN1, USH2A, UFD1, PRPF3, IFT88, RECQL4, PTCH2, PEX11B, POMT2, GMPPB, HERC2, CCDC22, BAZ1B, IMPG2, PEX3, SUFU, OFD1, YARS2, SMC3, LOH19CR1, DERA, NAA10, SMC1A, AHI1, HIRA, RP1, DHX38, KLHL7, CEP57, ANKH, IFT140, BTNL2, SKIV2L, RAPGEF5, SAG, KIZ, RS1, RREB1, RPS19, RPE65, WASHC5, RP2, NR2E3, HDAC8, CENPJ, TULP1, TBL2, TUB, KMT2A, PEX16, SETD5, ADAMTS3, ELP4, TIMP3, POMGNT1, SPATA7, GTF2IRD1, SEC24C, PEX26, AGK, TTC37, EXOC2, TBX1, BCOR, ZEB1, DHCR7, CANT1, MECOM, WDR36, FKTN, EYS, CBS, ZNF513, KDSR, CERKL, GJB3, PCARE, TBC1D20, GJB4, TTC8, HGSNAT, DNAJC24, GP1BB, CA4, GSTM1, BUB1B, BUB1, BBS2, BBS1, GTF2I, GUCA1B, HCCS, ARVCF, ETS1, FREM2, ARL3, ESCO2, VCAN, JMJD1C, THSD7A, CRYAA, CRX, ADAMTS17, CREBBP, CADM2, COX7B, COMT, DAG1, C8orf37, COL5A2, C14orf39, COL5A1, COL4A1, COL3A1, B3GALNT2, CCBE1, CNGA1, CNGB1, CLN3, RDH12, B3GLCT, EP300, CENPE, ARSB, GSN, ATRIP, ZNF469, CDHR1, ARL6, PRSS56, KIF11, CRPPA, CHRDL1, FAM161A, IDH3B, SLC25A4, ANTXR1, MAK, POMGNT2, IDH3A, ACVR1, REEP6, PRCD, MFRP, RNU4ATAC, IMPDH1, ADAMTSL1, MYOCOS, CHST14, POMK, LOXL1-AS1, ABCA4, CISD2, IDUA, IL6, GSTT1, HCAR2, TP53, TBK1, HCA1, ADCY10, MAGEC3, MMP9, MAGEE1, HCAR1, TLR4, APOE, IL1A, ACTB, FN1, CA2, EDNRB, MMRN1, MTHFR, EDN1, NOS3, HSD11B1, SIX6, CAV1, IL1B, P2RX7, ANGPTL7, CCN2, TYRP1, NR3C1, GSTP1, SPARC, MMP1, SIX1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, DBA2, ATOH7, TTR, CAV2, MMP3, WWTR1, TGM2, HSPA4, AMD1P2, ASB10, NFKB1, NFE2L2, S100B, AMD1, HPGDS, NPPA, SIRT1, ADRB2, VDR, CP, AQP4, CNR1, VAV3, APRT, MIR93, MIR29B2, MIR29B1, BCHE, HEYL, RNU1-1, IL17B, SIGMAR1, SPAG11B, GSTK1, AKT1, RUNX1T1, CCT, CDK9, CDKN1A, CDR1, SPAG11A, POSTN, AKR1C4, CISH, CLU, IL20, MAP3K5, PRSS55, SPZ1, IGF1, PTEN, SLC1A3, PTGER2, PTGFR, SFRP1, GAS5, ISG20, HSPA1B, P2RY6, GABPA, CXCL8, SLCO6A1, IL2RA, FOXO1, BIRC6, EDNRA, SOD2, HSPA1A, CYP2B6, MGP, CRISP2, MAPK3, THBS1, MEG3, HIF1A, MAPK8, ABCA1, MFAP1, MTOR, OPTC, GLCCI1, B3GAT3, GPR166P, VN1R17P, HPSE2, GLC1I, CYGB, LGR6, MRGPRX3, GPATCH3, ELOVL5, MIR483, PART1, MVB12B, CPLANE1, MAP1LC3B, COL18A1, LOC110599580, TRPM3, WLS, MAGT1, LPAR3, MIR1298, CARD14, WNK2, DAPK2, MT1IP, MIR760, WNK1, IL1F10, MARCKSL1, CCR2, GORASP1, DNLZ, LINGO1, IL22RA1, PLXDC2, IL21, NLRC4, MRGPRX4, DOK5, SLC12A9, DPYSL5, FOXP3, ASAH2, ASCC1, LRRC8A, NSMCE3, TNFRSF12A, HSD17B7, GPRC5C, IL20RB, MIR29A, PDIK1L, PLB1, TMTC2, GPRC5D, MRGPRX1, OXER1, GPHA2, GPRC6A, ARID2, MARCHF1, RPGRIP1, PAK5, IL22, GPR151, MIR215, MIR211, MIR204, MIR200A, FOXD3, TUG1, NGB, MIR182, MIR149, GBA2, MIR141, MIR122, GPR158, MALAT1, TAF8, PTCHD3, MRTFB, BBS5, AICDA, GJD2, TMEM182, ANAPC1, AAVS1, RIMS1, FUT8, TLX2, HNF4A, HDAC1, HBB, GSTM3, GSTM2, GNAS, GLC3B, GLC1C, GLC1B, GLA, GDNF, FLT4, HTR1A, FOXC2, FANCF, PTK2B, FAAH, F9, ERG, EPHB6, EPHB1, ELK3, ELAVL2, EDN2, DOCK3, HSPD1, IAPP, MGLL, LTBP3, MT1F, MT1E, MT1B, MT1A, ABCC1, MMP2, CD46, MAPT, MAOA, SMAD4, SMAD3, SH2D1A, LPA, ICA1, LOX, LGALS9, LCN2, LAMC2, LAMA4, ITGAM, ITGA4, INPP5B, IL17A, IGFALS, IFNA13, IFNA1, COCH, DMXL1, DBN1, ANGPT2, BMP4, BMP2, BGLAP, BCL2L1, BAK1, ALDH7A1, ASAH1, ARSD, AQP9, AQP1, APCS, ANXA5, AMT, DBH, ALPP, ALPI, ALDH1A1, ALB, APLNR, AGTR1, AGT, AGER, AP2B1, ADCYAP1, ACHE, ABO, BTC, C3, C4BPA, CA9, CYP2J2, CYBB, CYBA, CXADR, CUX1, CSTA, CSF2, CRYBB2, CRYAB, CRMP1, CREB1, COX8A, COL8A2, CHM, CEBPD, CEBPB, CDSN, CD47, CD40, CASP3, CAPG, CAMP, CACNA2D1, CACNA1C, CA12, MT1G, MT1H, MT1JP, CDC7, MTMR2, ARHGEF7, APLN, DPM2, TNFSF14, RIPK1, AKR1C3, DENR, NCK2, SRPX, HYAL3, FZD4, USP9X, TGFBR3, XRCC1, VWF, VTN, VAV2, UTRN, TYR, PHLDA2, TRPC5, HSP90B1, TNNT3, TNFRSF1B, CLDN5, SELENBP1, PKD2L1, DCLK1, XPR1, POU6F2, PADI2, DDX20, KERA, STIP1, PDIA5, HPSE, FRS2, ARFGEF1, FST, PRG4, DHRS9, DNM1L, ABCB6, HDAC6, SLC23A2, MFN2, PRDX6, NRG2, TBPL1, GDF15, ROCK2, AIM2, CD163, S1PR2, TH, TGFBR1, MT1M, OGN, MAPK10, MAPK9, PPARG, PON1, POLG, PLG, PLA2G4A, SERPINA1, SERPINF1, PDK1, PDGFRB, PBX1, NTF3, TFRC, NRF1, NPHS1, NOS2, NMB, NFATC3, NEFL, MYP2, MTNR1A, MTHFD1, CYTB, MT1X, MT1L, PRNP, PSD, PTPN9, PTPN11, TFAP2B, PRDX2, TAP2, TAP1, TAC3, SYT1, STAT3, SPRR2A, SPINK1, SOD1, SNCA, SLCO2A1, SLC6A2, SLC1A1, SELE, CXCL6, CCL2, SALL1, SAA2, ROS1, RNASE3, RLN2, RELA, RAN, PTPRB, H3P40
- Dental Trauma Wikipedia
-
Calculus (Dental)
Wikipedia
F. nucleatum P. gingivalis P. intermedia T. forsythia T. denticola Red complex Entamoeba gingivalis (amoebic) Trichomonas tenax Other Calculus Clinical attachment loss Edentulism Fremitus Furcation defect Gingival enlargement Gingival pocket Gingival recession Gingivitis Horizontal bony defect Linear gingival erythema Occlusal trauma Periodontal pocket Periodontal disease Periodontitis Plaque Vertical bony defect Treatment and prevention Periodontal examination Ante's law Brushing Bleeding on probing Chlorhexidine gluconate Flossing Hydrogen peroxide Mouthwash Oral hygiene Tetracycline Triclosan Host modulatory therapy Treatment Conventional therapy Debridement Scaling and root planing Full mouth disinfection Full mouth ultrasonic debridement Surgery Apically positioned flap Bone graft Coronally positioned flap Crown lengthening Free gingival graft Gingival grafting Gingivectomy Guided bone regeneration Guided tissue regeneration Enamel matrix derivative Implant placement Lateral pedicle graft Open flap debridement Pocket reduction surgery Socket preservation Sinus lift Subepithelial connective tissue graft Tools Curette Membrane Probe Scaler Important personalities Tomas Albrektsson Frank Beube Per-Ingvar Brånemark Robert Gottsegen Gary Greenstein Jan Lindhe Brian Mealey Preston D.
-
Otitis Media
Wikipedia
While less than 7 days of antibiotics have fewer side effects, more than seven days appear to be more effective. [51] If there is no improvement after 2–3 days of treatment a change in therapy may be considered. [1] Azithromycin appears to have less side effects than either high dose amoxicillin or amoxicillin/clavulanate. [52] Tympanostomy tube [ edit ] Tympanostomy tubes (also called "grommets") are recommended with three or more episodes of acute otitis media in 6 months or four or more in a year, with at least one episode or more attacks in the preceding 6 months. [1] There is tentative evidence that children with recurrent acute otitis media (AOM) who receive tubes have a modest improvement in the number of further AOM episodes (around one fewer episode at six months and less of an improvement at 12 months following the tubes being inserted). [53] [54] Evidence does not support an effect on long-term hearing or language development. [54] [55] A common complication of having a tympanostomy tube is otorrhea, which is a discharge from the ear. [56] The risk of persistent tympanic membrane perforation after children have grommets inserted may be low. [53] It is still uncertain whether or not grommets are more effective than a course of antibiotics. [53] Oral antibiotics should not be used to treat uncomplicated acute tympanostomy tube otorrhea. [56] They are not sufficient for the bacteria that cause this condition and have side effects including increased risk of opportunistic infection. [56] In contrast, topical antibiotic eardrops are useful. [56] Otitis media with effusion [ edit ] The decision to treat is usually made after a combination of physical exam and laboratory diagnosis, with additional testing including audiometry , tympanogram , temporal bone CT and MRI . [57] [58] [59] Decongestants, [60] glucocorticoids, [61] and topical antibiotics are generally not effective as treatment for non-infectious, or serous , causes of mastoid effusion. [57] Moreover, it is recommended against using antihistamines and decongestants in children with OME. [60] In less severe cases or those without significant hearing impairment, the effusion can resolve spontaneously or with more conservative measures such as autoinflation . [62] [63] In more severe cases, tympanostomy tubes can be inserted, [55] possibly with adjuvant adenoidectomy [57] as it shows a significant benefit as far as the resolution of middle ear effusion in children with OME is concerned. [64] Chronic suppurative otitis media [ edit ] Topical antibiotics are of uncertain benefit as of 2020. [65] Some evidence suggests that topical antibiotics may be useful either alone or with antibiotics by mouth. [65] Antiseptics are of unclear effect. [66] Topical antibiotics (quinolones) are probably better at resolving ear discharge than antiseptics. [67] Alternative medicine [ edit ] Complementary and alternative medicine is not recommended for otitis media with effusion because there is no evidence of benefit. [26] Homeopathic treatments have not been proven to be effective for acute otitis media in a study with children. [68] An osteopathic manipulation technique called the Galbreath technique [69] was evaluated in one randomized controlled clinical trial; one reviewer concluded that it was promising, but a 2010 evidence report found the evidence inconclusive. [70] Outcomes [ edit ] Disability-adjusted life year for otitis media per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004. no data < 10 10–14 14–18 18–22 22–26 26–30 30–34 34–38 38–42 42–46 46–50 > 50 Deaths from otitis media per million persons in 2012 0 1 2–4 Complications of acute otitis media consists of perforation of the ear drum, infection of the mastoid space behind the ear ( mastoiditis ), and more rarely intracranial complications can occur, such as bacterial meningitis , brain abscess , or dural sinus thrombosis . [71] It is estimated that each year 21,000 people die due to complications of otitis media. [13] Membrane rupture [ edit ] In severe or untreated cases, the tympanic membrane may perforate , allowing the pus in the middle-ear space to drain into the ear canal .RSPH4A, TNF, A2ML1, IL6, MUC5AC, IL1B, IL10, FBXO11, BPIFA1, RPL38, SH3PXD2B, MUC4, TGIF1, MUC1, IL1A, FGFR1, MECOM, EYA4, NF2, E2F4, NAGLU, SCGB1A1, DNAH5, TP73, BTC, CTSL, TBX1, CTSK, CTSB, CBY1, SCN2B, EDARADD, IDUA, LMNA, PHEX, ENPP1, CAT, SALL4, NOS2, CXCR4, PNP, TNFSF11, CD3D, CYBC1, CCDC47, DCLRE1C, NSD1, SLC2A1, NCF1, PRX, TCIRG1, BTK, WAS, NBN, NCF2, NCF4, ALMS1, CD3E, CD247, IKBKB, TLK2, FGFR3, DNAAF3, RPGR, IL2RG, RAG2, NIPBL, RAG1, IL7R, RNF168, CYBB, CYBA, CLCN7, PTPRC, SNX10, STX17-AS1, CCDC39, MBL2, TLR2, TLR4, CD14, TLR9, CASP3, DUSP1, COPD, PYCARD, MBL3P, DEFB4A, STS, MCPH1, DHRS2, DEFB4B, MPO, MUC5B, CCR2, CAPN14, SFTPA2, TRAP, SFTPA1, KAT5, MIR146B, SMC2, POLD4, ADAMTS13, NISCH, MIR146A, CFAP97, FLVCR1, TIPRL, CRYGEP, SLC25A21, ITFG1, METTL8, PACC1, PPP2R2D, GALNT14, POLE4, PORCN, ABO, PIK3CD, VEGFA, ELANE, KRT5, ITGB2, ITGAM, ITGAL, ITGA5, CXCL8, IL6R, IL5, IL2, IFNG, FUT2, ATN1, CD46, CRYGC, COL2A1, CD44, CASP9, CASP1, VPS51, C7, BPI, AQP1, AQP8, AKT1, LIMK1, MEFV, TLR5, PIK3CG, SLC11A1, CCL3, CCL2, S100B, S100A12, S100A9, S100A8, S100A1, RAC1, PTEN, PIP, JAG1, MIF, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, PAX9, PAK1, SERPINE1, OPHN1, NT5E, MUC2, MMP9, MMP8, MMP2, H3P5
-
Influenza
Wikipedia
Influenza Other names Flu, the flu, Grippe Influenza virus, magnified approximately 100,000 times Specialty Infectious disease Symptoms Fever , runny nose , sore throat , muscle and joint pain , headache , coughing , feeling tired [1] Usual onset One to four days after exposure [1] Duration ~1 week [1] Causes Influenza viruses [2] Prevention Hand washing , influenza vaccine , surgical masks [1] [3] Medication Neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir [1] Frequency 3–5 million severe cases per year [1] Deaths Up to 650,000 respiratory deaths per year [1] [4] Influenza , commonly known as " the flu ", is an infectious disease caused by an influenza virus . [1] Symptoms can be mild to severe. [5] The most common symptoms include: high fever , runny nose , sore throat , muscle and joint pain , headache , coughing , and feeling tired . [1] These symptoms typically begin two days after exposure to the virus and most last less than a week. [1] The cough, however, may last for more than two weeks. [1] In children, there may be diarrhea and vomiting , but these are not common in adults. [6] Diarrhea and vomiting occur more commonly in gastroenteritis , which is an unrelated disease sometimes referred to as "stomach flu" or the "24-hour flu". [6] Complications of influenza may include viral pneumonia , secondary bacterial pneumonia , sinus infections , and worsening of previous health problems such as asthma or heart failure . [2] [5] Three of the four types of influenza viruses affect humans: Type A, Type B, and Type C. [2] [7] Type D has not been known to infect humans, but is believed to have the potential to do so. [7] [8] Usually, the virus is spread through the air from coughs or sneezes. [1] This is believed to occur mostly over relatively short distances. [9] It can also be spread by touching surfaces contaminated by the virus and then touching the eyes, nose, or mouth. [5] [9] [10] A person may be infectious to others both before and during the time they are showing symptoms. [5] The infection may be confirmed by testing the throat, sputum , or nose for the virus. [2] A number of rapid tests are available; however, people may still have the infection even if the results are negative. [2] A type of polymerase chain reaction that detects the virus's RNA is more accurate. [2] Frequent hand washing reduces the risk of viral spread, as does wearing a surgical mask . [3] [ needs update ] Yearly vaccinations against influenza are recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for those at high risk, [1] and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for those six months of age and older. [11] The vaccine is usually effective against three or four types of influenza. [1] It is usually well tolerated. [1] A vaccine made for one year may not be useful in the following year, since the virus evolves rapidly. [1] Antiviral medications such as the neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir , among others, have been used to treat influenza. [1] The benefit of antiviral medications in those who are otherwise healthy do not appear to be greater than their risks. [12] No benefit has been found in those with other health problems. [12] [13] Influenza spreads around the world in yearly outbreaks , resulting in about three to five million cases of severe illness and about 290,000 to 650,000 deaths. [1] [4] About 20% of unvaccinated children and 10% of unvaccinated adults are infected each year. [14] In the northern and southern parts of the world, outbreaks occur mainly in the winter, while around the equator , outbreaks may occur at any time of the year. [1] Death occurs mostly in high risk groups—the young, the old, and those with other health problems. [1] Larger outbreaks known as pandemics are less frequent. [2] In the 20th century, three influenza pandemics occurred: Spanish influenza in 1918 (17–100 million deaths), Asian influenza in 1957 (two million deaths), and Hong Kong influenza in 1968 (one million deaths). [15] [16] [17] The World Health Organization declared an outbreak of a new type of influenza A/H1N1 to be a pandemic in June 2009 . [18] Influenza may also affect other animals, including pigs, horses, and birds. [19] Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Symptoms of influenza 1.2 Emergency warning signs 1.2.1 Signs of dehydration 2 Virology 2.1 Types of virus 2.1.1 Influenzavirus A 2.1.2 Influenzavirus B 2.1.3 Influenzavirus C 2.1.4 Influenzavirus D 2.2 Structure, properties, and subtype nomenclature 2.3 Replication 3 Mechanism 3.1 Transmission 3.2 Pathophysiology 4 Prevention 4.1 Vaccination 4.2 Infection control 5 Diagnosis 6 Treatment 6.1 Antivirals 6.1.1 Neuraminidase inhibitors 6.1.2 M2 inhibitors 7 Prognosis 7.1 Neurological complications 8 Epidemiology 8.1 Seasonal variations 8.2 Mortality 8.3 Outbreaks 9 History 9.1 Etymology 9.2 Pandemics 10 Society and culture 11 Research 12 Other animals 12.1 Bird flu 12.2 Swine flu 13 References 14 Further reading 15 External links Signs and symptoms Most sensitive symptoms for diagnosing influenza [20] Symptom: Sensitivity Specificity Fever 68–86% 25–73% Cough 84–98% 7–29% Nasal congestion 68–91% 19–41% All three findings, especially fever, were less sensitive in people over 60 years of age. ... People over 65 years old, pregnant women, very young children and people of any age with chronic medical conditions are more likely to get complications from influenza, such as pneumonia, bronchitis , sinus , and ear infections . [174] Neurological complications Influenza encephalitis MRI In some cases, an autoimmune response to an influenza infection may contribute to the development of Guillain–Barré syndrome . [175] However, as many other infections can increase the risk of this disease, influenza may only be an important cause during epidemics. [175] [176] This syndrome has been believed to also be a rare side effect of influenza vaccines.DDX58, IFITM3, MX1, CXCL10, IRF7, LAMP3, CCL2, EIF2AK2, RSAD2, STAT1, ISG15, TNFSF10, IFIH1, PLSCR1, OAS2, IFIT5, ATF3, OAS1, IFI44L, TNFAIP6, APOL6, OASL, OAS3, DDX60, RTP4, HERC6, SLC22A8, IFI44, UBE2L6, ZCCHC2, SAMD9, XAF1, SERPING1, CCL8, SCO2, MX2, GBP1, PARP12, IFI6, HERC5, IFI27, IFIT3, XIST, TOR1B, IFI35, TRIM22, IFIT2, SIGLEC1, TDRD7, TREX1, IFIT1, LY6E, SFTPD, RAB39B, IL1B, IL2, IVNS1ABP, SARS2, ERVK-6, TNF, IFNG, IFNB1, IFNA13, IFNA1, PTPN11, IL10, ROBO3, PLAAT4, IL17A, SARS1, TLR4, IL6, HLA-A, PBRM1, TLR7, LINC01672, ERVK-32, TLR2, COPD, KRT31, CRP, ZMYND10, CD248, CPVL, TLR9, TLR3, VHLL, IRF3, HMOX1, CD40LG, MAPK1, LSAMP, IGHA1, IL22, ARIH1, CSF2, MAPK14, IL4, NLRP3, ACTB, PIK3CA, NR1I2, TRIM25, MED1, IL2RA, DOCK3, PPBP, ISG20, TMPRSS2, CASP1, ST14, IL33, GRN, PKD1, PEBP1, HLA-C, RNPC3, MYD88, NCR1, MAVS, DHX9, PRNP, MRC1, ACE2, GZMB, FOLH1, TRBV20OR9-2, MBL2, ICAM1, HSPA4, HCL2, RPS19, PIK3CG, IL27, POLDIP2, CCR5, CD28, GRAP2, CD80, CFTR, RNF19A, IL5, CRK, AHSA1, LOH19CR1, SRL, IL1A, CCR2, CXCL8, SARDH, PER2, AIMP2, IFNL1, ATN1, PIK3CD, IFNAR1, PIK3CB, EIF4G1, HLA-B, TLR5, PRDX2, CFH, HLA-DRB1, HMGB1, TNFRSF9, TXN, MYO1G, IL7R, ERVW-1, IL15, KRT32, NM, HCRT, EPHA3, NHS, EGFR, DHFR, ST6GAL1, CTLA4, RAB11A, CCL5, CD86, PLG, ANP32B, POTEF, CASP3, B3GAT1, CAP1, IL17D, C4BPA, PPARG, BST2, IRF9, ABCB6, ALB, CD274, PTGS2, SDS, CARD14, EPHB2, FPR2, MPO, SPINT1, CBLIF, CFAP97, GPI, SOD1, GABPA, XPO1, NFE2L2, COX2, MFAP1, FOXP3, IPO5, RELA, NS2, CMPK1, ICOS, PPIA, MMP9, SEC14L2, MPPE1, BRD4, LNPEP, LRIT1, TGFB1, NOS2, VTRNA1-1, STAT3, PAM, SEA, XCL1, GOLPH3, SERPINB6, LAMP1, LAMC2, MUC5AC, MUC1, SMS, MYDGF, NT5C2, PAGR1, RBM45, ANP32A, PRDM1, STING1, NR4A3, BCL2, AREG, EIF4A2, APRT, ESCO2, F2RL1, FGF2, MLANA, FN1, GAST, VTN, GALNS, GAPDH, RTL1, SLC9A6, CTAA1, TNFSF9, CD79A, HACD1, CDC42, IL18R1, SORBS1, TNFRSF18, MIR223, MBTPS1, NCR2, TNFSF13B, CLK1, IL32, CPT2, CD163, MIR155, MIR146A, RIPK3, ERVK-20, ABHD2, HLA-DQB1, TRAF6, DOT1L, TRAF3, MTCO2P12, ADAR, IFNA2, IFNAR2, IGF1, LINC02605, IL7, CXCR2, IL18, ILF3, ABO, ITGAE, ITGAM, SHCBP1, EBI3, TTR, TIRAP, LOC102724971, APCS, XCR1, BATF2, LOC102723407, ANXA1, UCK2, IL17F, SOCS3, MTSS2, ATG7, ZMPSTE24, RIDA, PRPF8, B3GNT3, FLVCR1, ATP2C1, RTN3, BET1, TRIM3, PPIE, DLL1, RBMS3, IL17C, CLEC10A, DISC1, TBK1, SLC35A1, IL37, NXF1, CFDP1, BAMBI, KHDRBS1, SLC27A4, IL24, TPPP, ADAMTS7, IRAK3, PADI4, CHP1, USP18, ARHGAP45, SRRM2, MORC3, ECD, P2RX2, SNRNP200, WDTC1, TRAM1, MPRIP, SIRT1, CLEC5A, BACE1, CXCR6, SLC27A5, PTPN22, CTCF, POLD3, PLK4, BACE2, CCL27, KLK5, LILRB1, MALT1, MCF2L, CPSF4, JTB, SUGT1, IL17RA, TMED2, CKAP4, SGK3, ABCA1, IL22RA1, CD207, MIR192, TICAM2, CCL4L1, PRSS57, LINC01194, MIR144, MIR15A, MIR184, MIR198, CYCSP51, MIR200C, MIR205, MIR206, MIR21, MIR29A, MIR29B1, MIR29B2, HLA-P, RAB7B, MIR30C1, NRSN1, TARS3, B4GALNT2, NMS, IL31RA, EGFLAM, ASZ1, TRIM69, MUC15, TREML4, TICAM1, DEFT1P, BCL6B, PTF1A, IFNL3, CLEC9A, BTBD8, MIR29C, MIR30C2, CTHRC1, ERVK-21, MFT2, MIR1260A, TMED7-TICAM2, PSMB8-AS1, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, ERVK-10, ERVK-9, ERVK-18, MIR744, ERVK-25, ERVK-24, MYMX, GATD3B, ERVK-19, CST12P, H3P24, EGOT, GGTLC4P, MIR31, MIR146B, MIR34A, MIR34C, DEFB103A, MIR328, ERVK-7, MIR451A, MIR485, MIR505, GGT2, ERVK-8, MIR483, GGTLC5P, H3P38, MIR449B, MUC5B, GGTLC3, IL22RA2, SLC46A1, GEMIN4, SMU1, UGT1A4, UGT1A1, UGT1A3, OTUD4, CASZ1, MARCHF1, NUDT11, PACC1, UGT1A5, ENAH, DEFB103B, LANCL2, CCL28, SPHK2, PNO1, SH3GLB2, UGT1A9, UGT1A6, CD177, BPIFA1, MBL3P, TMED5, TMED7, DYNC1LI1, LINC00328, VPS28, HSPA14, TLR8, UGT1A7, CRLF3, DDX41, ISYNA1, IL23A, DDIT4, UGT1A10, UGT1A8, CHPT1, AICDA, SCGB3A1, NLRC5, NDFIP1, NPL, ZBP1, UNC93B1, TLR10, TRIM56, PARP9, CHD6, DHDDS, GINS4, HOPX, MAK16, WNT3A, FRMD7, MCU, TRIM41, TARS2, NLRX1, GATAD2B, KLRG1, SEMA6A, ARHGAP21, SUGP1, HAMP, C6orf47, NLRC4, PRM3, HEATR6, DHX58, DMRTA1, TNMD, NOD2, CLEC7A, GORASP1, WNK1, WNK4, CALCOCO2, TARS1, DHRS2, ALYREF, GPT, CXCL1, CXCL2, GRP, PDIA3, GRSF1, GZMA, H1-2, HLA-DPB1, HMGCR, NR4A1, HNRNPK, HP, HPD, PRMT1, HES1, HSPA8, GPS1, CXCR3, GLRX, FUT2, EIF4E, EIF4G2, ENO1, ESR1, F2R, FCN2, FLT3LG, FYB1, GLDC, GAD1, GATA2, GATA3, GGT1, GH1, GLA, GLB1, HSPD1, TNC, IFNA6, EPCAM, KRT10, LAG3, LGALS9, LIF, LPO, BCAM, SH2D1A, SMAD3, KPNA4, MATN1, MAX, MBD1, MBP, MEFV, MAP3K5, MIF, KRT5, KPNA3, IFNGR1, ITGB2, IGHM, IL3, IL4R, CXCR1, IL13, INSR, IRF4, ITGB7, KPNA1, JAK3, KEL, KIR2DL1, KLK1, KLRB1, KLRC2, KLRD1, EIF4A1, S1PR1, DPEP1, CASP10, C3, C5, C5AR1, C6, CALCR, CAMK2B, CASP8, CAV1, BDNF, RUNX1T1, SERPINH1, CCK, CCND3, CCNT1, CD1A, CD2, CXCR5, BCR, CD14, ALK, ABL1, ACP3, AGA, JAG1, AHR, AKT1, ALDH2, ANXA2, BCL6, ANXA6, ANXA13, APC, BIRC3, XIAP, ARSF, BAG1, CD9, CD19, DYNC1LI2, CD55, CR2, CREB1, CREM, CSF3, CSF3R, CTNNB1, CYLD, DAP, CCR7, DDOST, DDX3X, DDX5, DEFA1, DEFB1, DLAT, DNM1, KLF6, CLCN7, CD27, CDK9, TNFRSF8, CD38, CD44, CD48, CD69, CD81, CDK1, CDKN1B, AP2M1, CDR1, CDSN, CEL, CENPF, CES1, AKR1C4, CISH, CXCL9, MIP, MPL, UGT1A, TIMP1, TNNI3, TOP1, TP53, HSP90B2P, TNFRSF4, TYR, KDM6A, TERT, UVRAG, VASP, VCP, VEGFA, VIM, BEST1, WAS, THBS1, TMBIM6, DNALI1, SNAI1, SRSF2, SRSF3, SFTPB, SGTA, ST3GAL3, SLC5A5, SLC20A1, SON, TCF7, SPR, ST13, STAT2, SYT1, TAP1, ABCA3, HNF1A, ZBTB25, CXCR4, SELL, CCL4L2, NTN1, GSTO1, AIM2, EIF2AK3, GAL3ST1, TECR, GOSR1, IKBKE, MAPKAPK2, SOCS5, NUP93, SPOCK2, TRIM14, SETDB1, BCAP31, TRIM28, TMPRSS11D, AURKB, RAB7A, PRPF18, DDX39B, PABPN1, IV, GATD3A, USP11, EPX, IFITM1, TP63, MYOM2, SOCS1, IL1RL2, SPHK1, HSPB3, CLDN2, P2RX6, PCSK7, SRSF1, SDC1, MSR1, PDR, PRDX1, SERPINE1, PAK1, PAX5, PDE7A, PDGFRB, PDPK1, PECAM1, PA2G4, PF4, ABCB1, PHB, PITX1, PKM, PKP2, PLS1, FURIN, P2RY2, POLR2A, CNOT4, COX1, MMUT, PPP1R12A, NAGA, NEU1, NFKBIB, NFKBIL1, NPY, P2RY1, NT5E, OSM, P2RX1, P2RX3, P2RX4, P2RX5, P2RX7, POLD1, POLR2B, CCL11, RPE65, PTK2, RAB5A, RAG1, RARA, RARB, DPF2, RNASE1, S100A8, PTEN, S100A11, SAA3P, SAFB, SAG, SATB1, CCL3, CCL4, PTGS1, PTBP1, POU1F1, MAP2K6, PPARA, PRD, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, PRKCD, MAPK8, MAP2K7, PTAFR, PROC, PRSS8, PRTN3, PSMB8, PSMD2, PSMD4, PSMD10, H3P19
-
Health Effects Of Wine
Wikipedia
Catholic monasteries during the Middle Ages also regularly used wine for medical treatments. [13] : 433 So closely tied was the role of wine and medicine, that the first printed book on wine was written in the 14th century by a physician, Arnaldus de Villa Nova , with lengthy essays on wine's suitability for treatment of a variety of medical ailments such dementia and sinus problems. [46] Risks of consumption [ edit ] The lack of safe drinking water may have been one reason for wine's popularity in medicine.
-
Spinocerebellar Ataxia
Wikipedia
In GeneReviews Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): Spinocerebellar Ataxia, Autosomal Recessive 1; SCAR1 - 606002 Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): Senataxin; SETX - 608465 External links [ edit ] ataxia at NINDS msa at NINDS opca_doc at NINDS MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : Olivopontocerebellar atrophy Spinocerebellar ataxia 27 at NIH 's Office of Rare Diseases Spinocerebellar ataxia dysmorphism at NIH 's Office of Rare Diseases Classification D ICD - 10 : G11.1 ICD - 9-CM : 334 OMIM : 164400 MeSH : D020754 DiseasesDB : 12339 v t e Diseases of the nervous system , primarily CNS Inflammation Brain Encephalitis Viral encephalitis Herpesviral encephalitis Limbic encephalitis Encephalitis lethargica Cavernous sinus thrombosis Brain abscess Amoebic Brain and spinal cord Encephalomyelitis Acute disseminated Meningitis Meningoencephalitis Brain / encephalopathy Degenerative Extrapyramidal and movement disorders Basal ganglia disease Parkinsonism PD Postencephalitic NMS PKAN Tauopathy PSP Striatonigral degeneration Hemiballismus HD OA Dyskinesia Dystonia Status dystonicus Spasmodic torticollis Meige's Blepharospasm Athetosis Chorea Choreoathetosis Myoclonus Myoclonic epilepsy Akathisia Tremor Essential tremor Intention tremor Restless legs Stiff-person Dementia Tauopathy Alzheimer's Early-onset Primary progressive aphasia Frontotemporal dementia / Frontotemporal lobar degeneration Pick's Dementia with Lewy bodies Posterior cortical atrophy Vascular dementia Mitochondrial disease Leigh syndrome Demyelinating Autoimmune Inflammatory Multiple sclerosis For more detailed coverage, see Template:Demyelinating diseases of CNS Episodic/ paroxysmal Seizures and epilepsy Focal Generalised Status epilepticus For more detailed coverage, see Template:Epilepsy Headache Migraine Cluster Tension For more detailed coverage, see Template:Headache Cerebrovascular TIA Stroke For more detailed coverage, see Template:Cerebrovascular diseases Other Sleep disorders For more detailed coverage, see Template:Sleep CSF Intracranial hypertension Hydrocephalus Normal pressure hydrocephalus Choroid plexus papilloma Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Cerebral edema Intracranial hypotension Other Brain herniation Reye syndrome Hepatic encephalopathy Toxic encephalopathy Hashimoto's encephalopathy Both/either Degenerative SA Friedreich's ataxia Ataxia–telangiectasia MND UMN only: Primary lateral sclerosis Pseudobulbar palsy Hereditary spastic paraplegia LMN only: Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies Spinal muscular atrophies SMA SMAX1 SMAX2 DSMA1 Congenital DSMA Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance (SMALED) SMALED1 SMALED2A SMALED2B SMA-PCH SMA-PME Progressive muscular atrophy Progressive bulbar palsy Fazio–Londe Infantile progressive bulbar palsy both: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis v t e Non-Mendelian inheritance : anticipation Trinucleotide Polyglutamine (PolyQ), CAG Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy Huntington's disease Kennedy disease Spinocerebellar ataxia 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 17 ( Machado-Joseph disease ) Non-polyglutamine CGG ( Fragile X syndrome ) GAA ( Friedreich's ataxia ) CTG ( Myotonic dystrophy type 1 ) CTG ( Spinocerebellar ataxia 8 ) CAG ( Spinocerebellar ataxia 12 ) Tetranucleotide CCTG ( Myotonic dystrophy type 2 ) Pentanucleotide ATTCT ( Spinocerebellar ataxia 10 ) v t e Inherited disorders of trafficking / vesicular transport proteins Vesicle formation Lysosome / Melanosome : HPS1 – HPS7 Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome LYST Chédiak–Higashi syndrome COPII : SEC23A Cranio-lenticulo-sutural dysplasia COG7 CDOG IIE APC: AP1S2 X-linked intellectual disability AP3B1 Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome 2 AP4M1 CPSQ3 Rab ARL6 BBS3 RAB27A Griscelli syndrome 2 CHM Choroideremia MLPH Griscelli syndrome 3 Cytoskeleton Myosin : MYO5A Griscelli syndrome 1 Microtubule : SPG4 Hereditary spastic paraplegia 4 Kinesin : KIF5A Hereditary spastic paraplegia 10 Spectrin : SPTBN2 Spinocerebellar ataxia 5 Vesicle fusion Synaptic vesicle : SNAP29 CEDNIK syndrome STX11 Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 4 Caveolae : CAV1 Congenital generalized lipodystrophy 3 CAV3 Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2B , Long QT syndrome 9 Vacuolar protein sorting : VPS33B ARC syndrome VPS13B Cohen syndrome DYSF Distal muscular dystrophy See also vesicular transport proteins Authority control NDL : 01033493
- Visual Impairment Due To Intracranial Pressure Wikipedia
-
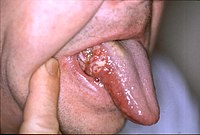
Angular Cheilitis
Wikipedia
External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : K13.0 ICD - 9-CM : 528.5 , 686.8 MeSH : D002613 Wikimedia Commons has media related to Angular cheilitis . v t e Oral and maxillofacial pathology Lips Cheilitis Actinic Angular Plasma cell Cleft lip Congenital lip pit Eclabium Herpes labialis Macrocheilia Microcheilia Nasolabial cyst Sun poisoning Trumpeter's wart Tongue Ankyloglossia Black hairy tongue Caviar tongue Crenated tongue Cunnilingus tongue Fissured tongue Foliate papillitis Glossitis Geographic tongue Median rhomboid glossitis Transient lingual papillitis Glossoptosis Hypoglossia Lingual thyroid Macroglossia Microglossia Rhabdomyoma Palate Bednar's aphthae Cleft palate High-arched palate Palatal cysts of the newborn Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia Stomatitis nicotina Torus palatinus Oral mucosa – Lining of mouth Amalgam tattoo Angina bullosa haemorrhagica Behçet's disease Bohn's nodules Burning mouth syndrome Candidiasis Condyloma acuminatum Darier's disease Epulis fissuratum Erythema multiforme Erythroplakia Fibroma Giant-cell Focal epithelial hyperplasia Fordyce spots Hairy leukoplakia Hand, foot and mouth disease Hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis Herpangina Herpes zoster Intraoral dental sinus Leukoedema Leukoplakia Lichen planus Linea alba Lupus erythematosus Melanocytic nevus Melanocytic oral lesion Molluscum contagiosum Morsicatio buccarum Oral cancer Benign: Squamous cell papilloma Keratoacanthoma Malignant: Adenosquamous carcinoma Basaloid squamous carcinoma Mucosal melanoma Spindle cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Verrucous carcinoma Oral florid papillomatosis Oral melanosis Smoker's melanosis Pemphigoid Benign mucous membrane Pemphigus Plasmoacanthoma Stomatitis Aphthous Denture-related Herpetic Smokeless tobacco keratosis Submucous fibrosis Ulceration Riga–Fede disease Verruca vulgaris Verruciform xanthoma White sponge nevus Teeth ( pulp , dentin , enamel ) Amelogenesis imperfecta Ankylosis Anodontia Caries Early childhood caries Concrescence Failure of eruption of teeth Dens evaginatus Talon cusp Dentin dysplasia Dentin hypersensitivity Dentinogenesis imperfecta Dilaceration Discoloration Ectopic enamel Enamel hypocalcification Enamel hypoplasia Turner's hypoplasia Enamel pearl Fluorosis Fusion Gemination Hyperdontia Hypodontia Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis Impaction Wisdom tooth impaction Macrodontia Meth mouth Microdontia Odontogenic tumors Keratocystic odontogenic tumour Odontoma Dens in dente Open contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia Resorption Shovel-shaped incisors Supernumerary root Taurodontism Trauma Avulsion Cracked tooth syndrome Vertical root fracture Occlusal Tooth loss Edentulism Tooth wear Abrasion Abfraction Acid erosion Attrition Periodontium ( gingiva , periodontal ligament , cementum , alveolus ) – Gums and tooth-supporting structures Cementicle Cementoblastoma Gigantiform Cementoma Eruption cyst Epulis Pyogenic granuloma Congenital epulis Gingival enlargement Gingival cyst of the adult Gingival cyst of the newborn Gingivitis Desquamative Granulomatous Plasma cell Hereditary gingival fibromatosis Hypercementosis Hypocementosis Linear gingival erythema Necrotizing periodontal diseases Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis Pericoronitis Peri-implantitis Periodontal abscess Periodontal trauma Periodontitis Aggressive As a manifestation of systemic disease Chronic Perio-endo lesion Teething Periapical, mandibular and maxillary hard tissues – Bones of jaws Agnathia Alveolar osteitis Buccal exostosis Cherubism Idiopathic osteosclerosis Mandibular fracture Microgenia Micrognathia Intraosseous cysts Odontogenic : periapical Dentigerous Buccal bifurcation Lateral periodontal Globulomaxillary Calcifying odontogenic Glandular odontogenic Non-odontogenic: Nasopalatine duct Median mandibular Median palatal Traumatic bone Osteoma Osteomyelitis Osteonecrosis Bisphosphonate-associated Neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis Osteoradionecrosis Osteoporotic bone marrow defect Paget's disease of bone Periapical abscess Phoenix abscess Periapical periodontitis Stafne defect Torus mandibularis Temporomandibular joints , muscles of mastication and malocclusions – Jaw joints, chewing muscles and bite abnormalities Bruxism Condylar resorption Mandibular dislocation Malocclusion Crossbite Open bite Overbite Overeruption Overjet Prognathia Retrognathia Scissor bite Maxillary hypoplasia Temporomandibular joint dysfunction Salivary glands Benign lymphoepithelial lesion Ectopic salivary gland tissue Frey's syndrome HIV salivary gland disease Necrotizing sialometaplasia Mucocele Ranula Pneumoparotitis Salivary duct stricture Salivary gland aplasia Salivary gland atresia Salivary gland diverticulum Salivary gland fistula Salivary gland hyperplasia Salivary gland hypoplasia Salivary gland neoplasms Benign: Basal cell adenoma Canalicular adenoma Ductal papilloma Monomorphic adenoma Myoepithelioma Oncocytoma Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum Pleomorphic adenoma Sebaceous adenoma Malignant: Acinic cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenoid cystic carcinoma Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma Lymphoma Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Sclerosing polycystic adenosis Sialadenitis Parotitis Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis Sialectasis Sialocele Sialodochitis Sialosis Sialolithiasis Sjögren's syndrome Orofacial soft tissues – Soft tissues around the mouth Actinomycosis Angioedema Basal cell carcinoma Cutaneous sinus of dental origin Cystic hygroma Gnathophyma Ludwig's angina Macrostomia Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome Microstomia Noma Oral Crohn's disease Orofacial granulomatosis Perioral dermatitis Pyostomatitis vegetans Other Eagle syndrome Hemifacial hypertrophy Facial hemiatrophy Oral manifestations of systemic disease
-
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
Wikipedia
External links [ edit ] PXE international Classification D ICD - 10 : Q82.8 ( ILDS Q82.81) ICD - 9-CM : 757.39 OMIM : 264800 MeSH : D011561 DiseasesDB : 10876 External resources eMedicine : derm/359 oph/475 Patient UK : Pseudoxanthoma elasticum pxe at NIH / UW GeneTests Pseudoxanthoma elasticum at NLM Genetics Home Reference v t e Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis / erythrokeratodermia AD Ichthyosis vulgaris AR Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma : Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis Lamellar ichthyosis Harlequin-type ichthyosis Netherton syndrome Zunich–Kaye syndrome Sjögren–Larsson syndrome XR X-linked ichthyosis Ungrouped Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens Ichthyosis follicularis Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa Ichthyosis hystrix EB and related EBS EBS-K EBS-WC EBS-DM EBS-OG EBS-MD EBS-MP JEB JEB-H Mitis Generalized atrophic JEB-PA DEB DDEB RDEB related: Costello syndrome Kindler syndrome Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome Skin fragility syndrome Ectodermal dysplasia Naegeli syndrome / Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis Hay–Wells syndrome Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Focal dermal hypoplasia Ellis–van Creveld syndrome Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome / Hay–Wells syndrome Elastic / Connective Ehlers–Danlos syndromes Cutis laxa ( Gerodermia osteodysplastica ) Popliteal pterygium syndrome Pseudoxanthoma elasticum Van der Woude syndrome Hyperkeratosis / keratinopathy PPK diffuse : Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert Meleda disease syndromic connexin Bart–Pumphrey syndrome Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Vohwinkel syndrome Corneodermatoosseous syndrome plakoglobin Naxos syndrome Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez Olmsted syndrome Cathepsin C Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome Haim–Munk syndrome Camisa disease focal : Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis Howel–Evans syndrome Pachyonychia congenita Pachyonychia congenita type I Pachyonychia congenita type II Striate palmoplantar keratoderma Tyrosinemia type II punctate : Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa Focal acral hyperkeratosis Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome Porokeratosis plantaris discreta Spiny keratoderma ungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia desmoplakin Carvajal syndrome connexin Erythrokeratodermia variabilis HID / KID Other Meleda disease Keratosis pilaris ATP2A2 Darier's disease Dyskeratosis congenita Lelis syndrome Dyskeratosis congenita Keratolytic winter erythema Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenita and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei Keratosis pilaris Other cadherin EEM syndrome immune system Hereditary lymphedema Mastocytosis / Urticaria pigmentosa Hailey–Hailey see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages , Template:Phakomatoses , Template:Pigmentation disorders , Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorder Developmental anomalies Midline Dermoid cyst Encephalocele Nasal glioma PHACE association Sinus pericranii Nevus Capillary hemangioma Port-wine stain Nevus flammeus nuchae Other/ungrouped Aplasia cutis congenita Amniotic band syndrome Branchial cyst Cavernous venous malformation Accessory nail of the fifth toe Bronchogenic cyst Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux Congenital lip pit Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs Congenital preauricular fistula Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma Cystic lymphatic malformation Median raphe cyst Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy Mongolian spot Nasolacrimal duct cyst Omphalomesenteric duct cyst Poland anomaly Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome Skin dimple Superficial lymphatic malformation Thyroglossal duct cyst Verrucous vascular malformation Birthmark v t e Genetic disorder , membrane: ABC-transporter disorders ABCA ABCA1 ( Tangier disease ) ABCA3 ( Surfactant metabolism dysfunction 3 ) ABCA4 ( Stargardt disease 1 , Retinitis pigmentosa 19 ) ABCA12 ( Harlequin-type ichthyosis , Lamellar ichthyosis 2 ) ABCB ABCB4 ( Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 3 ) ABCB7 ( ASAT ) ABCB11 ( Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 2 ) ABCC ABCC2 ( Dubin–Johnson syndrome ) ABCC6 ( Pseudoxanthoma elasticum ) ABCC7 ( Cystic fibrosis ) ABCC8 ( HHF1 , TNDM2 ) ABCC9 ( Dilated cardiomyopathy 1O ) ABCD ABCD1 ( Adrenoleukodystrophy , Adrenomyeloneuropathy ) ABCG ABCG5 ( Sitosterolemia ) ABCG8 ( Gallbladder disease 4, Sitosterolemia ) see also ABC transporters
-
Oral Pigmentation
Wikipedia
Disorders of oral pigmentation:Medscape v t e Oral and maxillofacial pathology Lips Cheilitis Actinic Angular Plasma cell Cleft lip Congenital lip pit Eclabium Herpes labialis Macrocheilia Microcheilia Nasolabial cyst Sun poisoning Trumpeter's wart Tongue Ankyloglossia Black hairy tongue Caviar tongue Crenated tongue Cunnilingus tongue Fissured tongue Foliate papillitis Glossitis Geographic tongue Median rhomboid glossitis Transient lingual papillitis Glossoptosis Hypoglossia Lingual thyroid Macroglossia Microglossia Rhabdomyoma Palate Bednar's aphthae Cleft palate High-arched palate Palatal cysts of the newborn Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia Stomatitis nicotina Torus palatinus Oral mucosa – Lining of mouth Amalgam tattoo Angina bullosa haemorrhagica Behçet's disease Bohn's nodules Burning mouth syndrome Candidiasis Condyloma acuminatum Darier's disease Epulis fissuratum Erythema multiforme Erythroplakia Fibroma Giant-cell Focal epithelial hyperplasia Fordyce spots Hairy leukoplakia Hand, foot and mouth disease Hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis Herpangina Herpes zoster Intraoral dental sinus Leukoedema Leukoplakia Lichen planus Linea alba Lupus erythematosus Melanocytic nevus Melanocytic oral lesion Molluscum contagiosum Morsicatio buccarum Oral cancer Benign: Squamous cell papilloma Keratoacanthoma Malignant: Adenosquamous carcinoma Basaloid squamous carcinoma Mucosal melanoma Spindle cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Verrucous carcinoma Oral florid papillomatosis Oral melanosis Smoker's melanosis Pemphigoid Benign mucous membrane Pemphigus Plasmoacanthoma Stomatitis Aphthous Denture-related Herpetic Smokeless tobacco keratosis Submucous fibrosis Ulceration Riga–Fede disease Verruca vulgaris Verruciform xanthoma White sponge nevus Teeth ( pulp , dentin , enamel ) Amelogenesis imperfecta Ankylosis Anodontia Caries Early childhood caries Concrescence Failure of eruption of teeth Dens evaginatus Talon cusp Dentin dysplasia Dentin hypersensitivity Dentinogenesis imperfecta Dilaceration Discoloration Ectopic enamel Enamel hypocalcification Enamel hypoplasia Turner's hypoplasia Enamel pearl Fluorosis Fusion Gemination Hyperdontia Hypodontia Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis Impaction Wisdom tooth impaction Macrodontia Meth mouth Microdontia Odontogenic tumors Keratocystic odontogenic tumour Odontoma Dens in dente Open contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia Resorption Shovel-shaped incisors Supernumerary root Taurodontism Trauma Avulsion Cracked tooth syndrome Vertical root fracture Occlusal Tooth loss Edentulism Tooth wear Abrasion Abfraction Acid erosion Attrition Periodontium ( gingiva , periodontal ligament , cementum , alveolus ) – Gums and tooth-supporting structures Cementicle Cementoblastoma Gigantiform Cementoma Eruption cyst Epulis Pyogenic granuloma Congenital epulis Gingival enlargement Gingival cyst of the adult Gingival cyst of the newborn Gingivitis Desquamative Granulomatous Plasma cell Hereditary gingival fibromatosis Hypercementosis Hypocementosis Linear gingival erythema Necrotizing periodontal diseases Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis Pericoronitis Peri-implantitis Periodontal abscess Periodontal trauma Periodontitis Aggressive As a manifestation of systemic disease Chronic Perio-endo lesion Teething Periapical, mandibular and maxillary hard tissues – Bones of jaws Agnathia Alveolar osteitis Buccal exostosis Cherubism Idiopathic osteosclerosis Mandibular fracture Microgenia Micrognathia Intraosseous cysts Odontogenic : periapical Dentigerous Buccal bifurcation Lateral periodontal Globulomaxillary Calcifying odontogenic Glandular odontogenic Non-odontogenic: Nasopalatine duct Median mandibular Median palatal Traumatic bone Osteoma Osteomyelitis Osteonecrosis Bisphosphonate-associated Neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis Osteoradionecrosis Osteoporotic bone marrow defect Paget's disease of bone Periapical abscess Phoenix abscess Periapical periodontitis Stafne defect Torus mandibularis Temporomandibular joints , muscles of mastication and malocclusions – Jaw joints, chewing muscles and bite abnormalities Bruxism Condylar resorption Mandibular dislocation Malocclusion Crossbite Open bite Overbite Overeruption Overjet Prognathia Retrognathia Scissor bite Maxillary hypoplasia Temporomandibular joint dysfunction Salivary glands Benign lymphoepithelial lesion Ectopic salivary gland tissue Frey's syndrome HIV salivary gland disease Necrotizing sialometaplasia Mucocele Ranula Pneumoparotitis Salivary duct stricture Salivary gland aplasia Salivary gland atresia Salivary gland diverticulum Salivary gland fistula Salivary gland hyperplasia Salivary gland hypoplasia Salivary gland neoplasms Benign: Basal cell adenoma Canalicular adenoma Ductal papilloma Monomorphic adenoma Myoepithelioma Oncocytoma Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum Pleomorphic adenoma Sebaceous adenoma Malignant: Acinic cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenoid cystic carcinoma Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma Lymphoma Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Sclerosing polycystic adenosis Sialadenitis Parotitis Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis Sialectasis Sialocele Sialodochitis Sialosis Sialolithiasis Sjögren's syndrome Orofacial soft tissues – Soft tissues around the mouth Actinomycosis Angioedema Basal cell carcinoma Cutaneous sinus of dental origin Cystic hygroma Gnathophyma Ludwig's angina Macrostomia Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome Microstomia Noma Oral Crohn's disease Orofacial granulomatosis Perioral dermatitis Pyostomatitis vegetans Other Eagle syndrome Hemifacial hypertrophy Facial hemiatrophy Oral manifestations of systemic disease
-
Chronic Kidney Disease
Wikipedia
Measurement of kidney length on the US image is illustrated by '+' and a dashed line. [44] End-stage chronic kidney disease with increased echogenicity, homogenous architecture without visible differentiation between parenchyma and renal sinus and reduced kidney size. Measurement of kidney length on the US image is illustrated by '+' and a dashed line. [44] Additional imaging [ edit ] Additional tests may include nuclear medicine MAG3 scan to confirm blood flow and establish the differential function between the two kidneys.TGFB1, ADIPOQ, CCL2, ACE, HAMP, CYBA, ADIPOR1, SERPINE1, CYBB, RELA, HMGCR, ACAT1, CBR1, CAT, SREBF2, TNF, ALB, EPO, IL6, MYH9, CRP, IGF1, NOX4, RETN, PTGS2, PPARA, PAX2, CYP2B6, HMOX1, NFKB1, NGF, APRT, GUCA2B, LRP2, CYP2C19, CPT1A, DNAJB11, CD68, FABP1, ABCG1, GTPBP4, MLXIPL, MSR1, NOS3, HBEGF, FASN, SREBF1, SLC22A2, AGTR1, SLC34A1, FGF23, SCARB1, NCF1, ABCA1, KL, PTGS1, PTH, IL1B, CCR5, EDN1, HAVCR1, NFE2L2, MTOR, NOS1, HP, EPOR, BCL2, LCAT, CCL5, ICAM1, ADIPOR2, OPA1, RNLS, PLAU, NR3C1, ABCB1, CLU, MFN1, BGLAP, SLC19A3, PCSK2, NR4A1, PGF, OLR1, CYP1A1, INSR, IRS1, LPIN1, POSTN, LPL, APOL1, PTGER4, SLC19A2, DNM1L, BECN1, DGAT1, ABCC3, F2, XDH, VCAM1, DRD1, UMOD, TERT, NQO1, SLC19A1, LIPC, SHH, KEAP1, SOAT2, NAT2, DDC, IL20, ABCC2, FIS1, ARG2, SLC46A1, C6, AGTR2, DGAT2, BNIP3, CST3, NPHS1, AFF3, SDCCAG8, RREB1, GCKR, RPN1, REN, CFH, ALMS1P1, TMEM229B, SLC30A8, SLC16A9, PTPRN2, PDILT, ATXN2, THEM4, AQP4-AS1, SLC6A13, NTAN1, PRODH, GATM, SLC25A26, ZNF618, UBE2Q2, IDI2, TFDP2, TLL1, LRSAM1, SLC22A16, PLXDC2, THSD7A, PKD2, WDR72, LINC01723, LPA, AOC1, LPP, LINC02188, LINC02284, ACADL, MTHFR, ACADS, KCNQ1, NFATC1, LINC01804, NFIC, HOXD-AS2, LINC01006, ADCY8, TRIM49B, INHBC, MIR1908, IL10, LINC00624, ZAR1L, CCSER1, LINC01721, IGF2R, C12orf75, AGT, ASPG, PKD1, VEGFA, OTOGL, VDR, SLC22A1, FADS1, SIPA1L3, PDZRN3, WDR37, SLC7A9, MMP20, MYO19, DSCAM, NFAT5, CERS4, DPEP1, PRKAG2, FTO, SFMBT1, LUC7L3, FADS2, ABCG2, SPATA5L1, SLC13A3, BCAS3, ELOVL2, RGS14, SLC47A1, SLC2A9, IGAN1, SHROOM3, DAB2, DACH1, PDXDC1, TMEM258, LARP4B, GJA10, NPHS2, PIP5K1B, LRIG1, L3MBTL3, DIANPH, KIRREL2, C9, MYRF, DNAH17, RAPGEF5, CDON, CALM2, DLGAP2, CPS1, SYNE2, PKD2L1, NAT8, CRH, MPO, GLA, COL4A3, ESR1, IL4, IL1RN, B2M, IL1A, MMP9, HLA-DRB1, SELE, CXCL8, GSTT1, KLK1, APOE, IFNG, ACTN4, ENPP1, GSTM1, HGF, LCN2, HLA-A, ERAL1, GLP1R, PPARG, SLC17A5, COPD, GCG, RBM45, SOST, SLC5A2, PON1, MUC1, EGFR, SLCO6A1, FN1, MMP2, CD46, FGF21, COL4A4, SPP1, CASR, CNDP1, AGER, EHMT1, OR10A4, DPP4, CX3CR1, GSTK1, HIF1A, CCN2, PTHLH, VWF, MAPK1, MCTP2, TRPC6, TLR4, PRTN3, NOS2, INF2, CD2AP, PVT1, ZGLP1, CABIN1, CFHR5, SLC12A3, NPHP1, NPY, MIR499A, LINC02210-CRHR1, APOB, APOA1, AVP, CD40, FCGR3A, DECR1, ADD1, FCGR3B, BMP7, F3, COL4A5, KNG1, CYP3A4, ABO, GSTP1, LEP, AHSG, CRHR1, GIP, BTBD9, NLRP3, SLC9A3, SOD2, APOL3, BMP2, NT5C1A, CAPG, GABPA, BDKRB2, ARSA, SLC4A1, SLC3A1, SELP, CXCL12, TFPI, GNB3, S100A10, CLDN19, GPT, GPX1, KLK3, GSTM2, PTX3, GUCA2A, PCSK9, HNF1B, UCP2, CD14, NPHP3, FOXP3, COL1A1, DIO1, MTRF1, KLK4, INVS, COX8A, TLR2, CYP2D6, CTNNB1, C1QL1, SMUG1, ADAMTS13, CRHR2, EXOSC3, EFNB2, EPHB2, WNT4, ETF1, HBHR, CUBN, CHGA, CHDH, XRCC1, RGMA, PDXP, HLA-B, CXCL16, TP53, TNNI3, CD28, FRMD3, CSF2, PAPPA, PIK3CA, HNP1, MBL2, IL2RA, KLKB1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, ADA, ADM, IL17A, MEN1, CCR2, IFNA1, IFNA13, MIR122, IL2, MGP, TNFRSF11B, CXCR2, MIR146A, LDLR, LGALS3, AGXT, MIR29B2, ISG20, MIR29B1, HLA-G, KIR3DL1, MIR133B, MIR302B, PARP1, CLCNKB, SIRT6, CHPT1, CD40LG, DCDC2, GHRL, ARID4B, CLTC, CLCN5, TLR9, VUR, KTWS, CDH13, ANKH, CCR1, PLF, RCBTB1, MOCOS, CD151, ADRA1A, CHI3L1, ADRA1B, WDR11, ZC4H2, EPB41L4B, ADRA1D, MIR4453HG, CCHCR1, ATF7IP, CD59, PPP6R3, ERCC8, SLC9C1, TRPV2, PLCE1, CPD, RNF19A, MGAT4C, POU2F3, PRDX5, MICA, KLRC4-KLRK1, CPOX, IL17RA, MIR499B, TMEM245, CPT2, PGR-AS1, CR1, CREB1, MCF2L, ACHE, ACACA, CRK, TBC1D9, MAPK14, POLDIP2, COL11A2, ACP5, SMARCAL1, CCR3, CCR4, CCR6, CCR7, ZMIZ1, MIR885, ACKR2, KIR2DS2, COL4A1, CD24, COL4A2, NXPH1, HILPDA, KLF15, HPGDS, TINAG, LINC00963, B3GAT1, ACTB, FOXD3, MDD1, TNFRSF8, KIDINS220, ARNT, CREBRF, ERFE, SKOR1, PTX4, PLB1, SIK1, AFP, PTPRVP, LYPD4, NRG4, C1QL3, STS, ASS1, MTFMT, ADRB2, ATM, ATP12A, ATP4A, FBXO32, MIRLET7B, AQP2, RHOV, DBA2, MCIDAS, NEK8, SLC24A5, ALDH2, LINC00667, ALK, ALOX5, AMBP, GOLGA6A, ANXA5, CASC2, RLS1, FNDC5, SPESP1, APC, ENHO, MALAT1, PRSS54, APEX1, IL31, JAG1, MIRLET7C, ATP5PF, MIR30C2, P2RY12, RUNX3, MIR214, CORO7, CD19, CD27, VKORC1, GRAMD2B, WNK1, IL25, MIR29A, RUNX2, GORASP1, CD80, ABCG8, BTBD8, ACE2, ZNF410, CD36, MIR30C1, ENTPD1, TTC21B, COQ8B, HOGA1, BRCA2, ATR, MIR142, BDKRB1, KNSTRN, CSH1, BDNF, BMP4, MIR149, MIR192, SARNP, SEMA6D, C3, ESPN, MIR196A2, MIR19B1, APOL4, CASP3, MIR21, PPP1R2C, CAV1, LIMK2, CYP24A1, KLRK1, PRKAA1, RNASE3, RNASE2, RET, GRN, GSN, GSTA1, RBBP4, RARRES2, MOK, RAC1, PTPRF, PTH1R, GYPA, HDAC1, HDAC2, HFE, PTGDS, PSMA6, PSEN1, CFHR1, MAP2K5, HLA-DQA1, PRKD1, PRKCB, PRKAB1, RTN1, S100A4, S100A9, CBLIF, SOD1, SMARCB1, SMARCA4, SMARCA2, GALNT3, GEM, GFRA3, GGT1, GH1, SLC9A5, SLC9A1, SLC6A3, SAA1, GLB1, SHC1, SHBG, SGK1, SELL, GNAO1, CCL15, CCL14, GNG7, SCT, GOT2, PRKAA2, HLA-DQB1, GAD1, HLA-DQB2, MUTYH, MTR, MTM1, KIR3DL2, KIR3DS1, KTN1, MMP1, NR3C2, MIF, MFAP1, MET, MEST, MEIS1, MEFV, DNAJB9, SMCP, LBP, MCAM, SMAD3, EPCAM, LUM, LTB, LHCGR, LMX1B, LMNA, KIR2DS1, KCNMA1, KCNJ1, ID2, POR, POMC, PLP1, PLCL1, HNF4A, PLA2G2A, PLA2G1B, HSD11B1, HSD11B2, SERPINA1, HSPA9, IGFBP1, ITGA2B, CNTN3, IGFBP3, P2RX7, IGHA1, OGG1, ODC1, NPPB, IL4R, IL18, INS, INSRR, SOX2, FOLH1, CSH2, ERBB4, HDAC9, RBM39, PTGES, DMD, GRAP2, GRHPR, COX5A, DNASE1, ATN1, PPIG, CD163, PTER, ECE1, MSC, EDN3, SLC33A1, PCSK7, SLC7A7, EDNRA, SELENBP1, SOCS2, SCEL, EGF, ELANE, EPAS1, DBP, BMS1, SFI1, CLDN16, SLCO2B1, CHP1, WDHD1, CTLA4, NUP42, DIDO1, UTS2, MMP24, CFHR3, HPSE, CTSS, SLCO1B1, LIG4, AHSA1, CYP3A5, SLC9A6, TNIP1, ZMPSTE24, ATP6AP2, CEBPZ, OPTN, CYP11B2, MAMLD1, ELMO1, RFXANK, DHX16, STAT1, PLA2G10, TRAF6, TPD52, TNFRSF1B, TNFRSF1A, FGB, FGF2, TLR3, FGF13, TIMP3, TIMP2, TIMP1, TGFB2, FOXO3, TGFA, FLOT2, FLT1, TEAD1, TCF21, TCF7L2, HNF1A, TAP2, TAC1, SYT1, STAT6, STAT4, HSP90B2P, FCN1, TRPS1, WNT1, WT3, F5, TFPI2, AIMP2, ST8SIA4, F10, BSND, YWHAZ, FABP4, WT1, WNT7B, WIPF1, TTR, FANCD2, TRPV1, BEST1, VIPR1, VIL1, VHL, FBN2, FCAR, UROD, UGT1A, SCGB1A1, RBP4
-
Angina
Wikipedia
"Ivabradine – the first selective sinus node if channel inhibitor in the treatment of stable angina" . ... External links [ edit ] Treatment of stable angina recommendations for patients in layman terms British Heart Foundation - Angina Angina Pectoris Animation Video 3D Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris - European Society of Cardiology Heart Attack and Angina Statistics by American Heart Association : Final 2006 statistics for the United States Classification D ICD - 10 : I20 ICD - 9-CM : 413 MeSH : D000787 DiseasesDB : 8695 External resources MedlinePlus : 000198 eMedicine : med/133 v t e Symptoms and signs relating to the circulatory system Chest pain Referred pain Angina Levine's sign Auscultation Heart sounds Split S2 S3 S4 Gallop rhythm Heart murmur Systolic Functional murmur Still's murmur Diastolic Pulmonary insufficiency Graham Steell murmur Continuous Carey Coombs murmur Mitral insufficiency Presystolic murmur Pericardial friction rub Heart click Bruit carotid Pulse Tachycardia Bradycardia Pulsus paradoxus doubled Pulsus bisferiens Pulsus bigeminus Pulsus alternans Other Palpitations Apex beat Cœur en sabot Jugular venous pressure Cannon A waves Hyperaemia Shock Cardiogenic Obstructive Hypovolemic Distributive See further Template:Shock Cardiovascular disease Aortic insufficiency Collapsing pulse De Musset's sign Duroziez's sign Müller's sign Austin Flint murmur Mayne's sign Other endocardium endocarditis : Roth's spot Janeway lesion / Osler's node Bracht–Wachter bodies Pericardium Cardiac tamponade / Pericardial effusion : Beck's triad Ewart's sign Other rheumatic fever : Anitschkow cell Aschoff body EKG J wave Gallavardin phenomenon Vascular disease Arterial aortic aneurysm Cardarelli's sign Oliver's sign pulmonary embolism Right heart strain radial artery sufficiency Allen's test pseudohypertension thrombus Lines of Zahn Adson's sign arteriovenous fistula Nicoladoni sign Venous Friedreich's sign Caput medusae Kussmaul's sign Trendelenburg test superior vena cava syndrome Pemberton's sign v t e Cardiovascular disease (heart) Ischaemic Coronary disease Coronary artery disease (CAD) Coronary artery aneurysm Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) Coronary thrombosis Coronary vasospasm Myocardial bridge Active ischemia Angina pectoris Prinzmetal's angina Stable angina Acute coronary syndrome Myocardial infarction Unstable angina Sequelae hours Hibernating myocardium Myocardial stunning days Myocardial rupture weeks Aneurysm of heart / Ventricular aneurysm Dressler syndrome Layers Pericardium Pericarditis Acute Chronic / Constrictive Pericardial effusion Cardiac tamponade Hemopericardium Myocardium Myocarditis Chagas disease Cardiomyopathy Dilated Alcoholic Hypertrophic Tachycardia-induced Restrictive Loeffler endocarditis Cardiac amyloidosis Endocardial fibroelastosis Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia Endocardium / valves Endocarditis infective endocarditis Subacute bacterial endocarditis non-infective endocarditis Libman–Sacks endocarditis Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis Valves mitral regurgitation prolapse stenosis aortic stenosis insufficiency tricuspid stenosis insufficiency pulmonary stenosis insufficiency Conduction / arrhythmia Bradycardia Sinus bradycardia Sick sinus syndrome Heart block : Sinoatrial AV 1° 2° 3° Intraventricular Bundle branch block Right Left Left anterior fascicle Left posterior fascicle Bifascicular Trifascicular Adams–Stokes syndrome Tachycardia ( paroxysmal and sinus ) Supraventricular Atrial Multifocal Junctional AV nodal reentrant Junctional ectopic Ventricular Accelerated idioventricular rhythm Catecholaminergic polymorphic Torsades de pointes Premature contraction Atrial Junctional Ventricular Pre-excitation syndrome Lown–Ganong–Levine Wolff–Parkinson–White Flutter / fibrillation Atrial flutter Ventricular flutter Atrial fibrillation Familial Ventricular fibrillation Pacemaker Ectopic pacemaker / Ectopic beat Multifocal atrial tachycardia Pacemaker syndrome Parasystole Wandering atrial pacemaker Long QT syndrome Andersen–Tawil Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Romano–Ward Cardiac arrest Sudden cardiac death Asystole Pulseless electrical activity Sinoatrial arrest Other / ungrouped hexaxial reference system Right axis deviation Left axis deviation QT Short QT syndrome T T wave alternans ST Osborn wave ST elevation ST depression Strain pattern Cardiomegaly Ventricular hypertrophy Left Right / Cor pulmonale Atrial enlargement Left Right Athletic heart syndrome Other Cardiac fibrosis Heart failure Diastolic heart failure Cardiac asthma Rheumatic fever Authority control NDL : 00567282AVP, PLAU, APOE, LDLR, GLA, CRELD1, ABCG8, ABCG5, GATA4, GATA6, XYLT2, XYLT1, NR2F2, LMNA, LCAT, JAK2, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, LDLRAP1, IDUA, LIPC, CYP27A1, TET2, PRTN3, ZMPSTE24, CTLA4, SCN5A, PTEN, MPL, ENPP1, PIGA, PCSK9, PTPN22, ABCC6, VEGFA, PMM2, APOB, ACE, CRP, CAD, CCS, IL6, SERPINE1, ITGB2, TNNI3, DLD, CXCL16, OXCT1, LAD1, SERPINA5, PLA2G1B, APOA1, TNF, NOS3, PLB1, KLF14, PLA2G7, PLA2G6, YWHAZ, IL37, NEAT1, VIP, MIR208A, MIR34A, MIR499A, TNFRSF1B, ZGLP1, CYP4F2, PROM1, TNFSF10, CPSF4, HDL3, MOCOS, QRSL1, POC1A, TBC1D9, JTB, ZC4H2, CMAS, SELL, EHMT1, PPP1R2C, FERMT3, ADIPOQ, WASF1, NLRP3, NR1I2, FGF21, ADAM10, CCL2, EDN1, ICAM1, HSPA5, GNB3, GLP1R, GLB1, GDF10, GCG, FGF4, F5, F3, CYP19A1, RENBP, CPB2, CLCN1, CETP, CD34, CD14, VPS51, KLK3, APOC3, ALB, AGTR1, IFNG, IGF2R, IL1A, IL1B, PYGM, PRKCD, PLXNA2, PLA2G2A, ABCB1, PAPPA, CNTN3, ADRB1, OPA1, NOS2, NOS1, MPI, MMP3, SMCP, LPA, KDR, ITGA2B, IL10, CXCL8, IL7, IL1RN, LINC02605
-
Oral Cancer
Wikipedia
This is based on the size of the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis. [38] TNM classification cancer of the oral cavity (does not apply to HPV+ or HPV- oralpharyngeal cancers) [38] T: Primary tumor TX Primary tumor cannot be assessed Tis Carcinoma in situ T1 Tumor ≤ 2 cm with depth of invasion (DOI*) ≤5mm T2 Tumor ≤ 2 cm with DOI* >5mm or tumor >2 cm and ≤ 4 cm with DOI* ≥10mm T3 Tumor > 2 cm and ≤4 cm with DOI* > 10mm or tumor >4 cm with DOI* ≤ 10mm T4 Moderately advanced or very advanced local disease T4a Moderately advanced local disease, tumor >4 cm with DOI* >10mm or tumor invades adjacent structures only (cortical bone of the mandible or maxilla (excluding superficial erosion of tooth socket alone in gingival tumors) or involves the maxillary sinus or skin of the face) T4b Very advanced local disease.TP53, PTGS2, HRAS, CDKN2A, MGMT, SFN, KRAS, SOD2, GAPDH, SERPINB3, HOXD11, MT1A, HOXA5, NAMPT, LAMC3, HOXD10, TPI1, HMGCS2, HSPA8, RACK1, HSPB1, ICAM1, VDAC2, IL18, UMPS, KRT6B, LGALS7, TSC2, ADH1B, TSC1, NDRG1, CCL2, FGA, ANXA5, PTK2, CDKN2B-AS1, PRTFDC1, CRYAB, MRPL13, CYP1B1, PIK3CA, SIRT3, ATP7B, ANXA2, PPIA, ANXA1, GPN1, DSPP, PGAM1, TIAM1, ADH7, ENO1, ADH1C, CLPTM1L, NRAS, ERBB3, ETS1, ERBB2, MYC, LMNA, WRN, MMP9, GSTM1, CCND1, MMP13, EGFR, IL10, XRCC4, SDC1, TLR4, TP73, CXCL12, SNAI1, NAT2, UPP1, HBP1, MIR375, MIR99A, LTO1, C6orf141, GRHL2, NANOG, WWOX, POSTN, VHL, AGR2, DLEU1, IFITM1, RECK, XRCC2, XRCC1, VIM, XRCC3, LOXL2, S100A2, CTNNB1, FOXM1, FHIT, FAT1, ERCC6, TYMP, E2F1, DCN, DAPK1, CYP2A6, CPB2, PTH1R, CDKN2B, CDKN1B, CDKN1A, CDK4, CDC20, CD5, CAV1, BSG, BMI1, FRG1, GP1BA, GSTM3, GSTP1, POU5F1, PLG, PLAU, PCBP2, NFKB1, MRC1, MMP7, MMP3, MAP2, LGALS9, ITGA2, CXCL8, IL4, IL1B, IGF2, IGF1R, TNC, HMOX1, GSTT1, H3P10
-
Varicose Veins
Wikipedia
. ^ Bailey and Love textbook of Surgery [ full citation needed ] External links [ edit ] Media related to Varicose veins at Wikimedia Commons Classification D ICD - 10 : I83 , I85 , I86 , K64 , O22.0 , O22.1 , O22.4 , O87.2 , O43.8 , O87.8 , P02.6 , Q27.8 ICD - 9-CM : 454 - 456 , 671 OMIM : 192200 MeSH : D014648 DiseasesDB : 13734 External resources MedlinePlus : 001109 eMedicine : med/2788 Patient UK : Varicose veins v t e Cardiovascular disease (vessels) Arteries , arterioles and capillaries Inflammation Arteritis Aortitis Buerger's disease Peripheral artery disease Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis Foam cell Fatty streak Atheroma Intermittent claudication Critical limb ischemia Monckeberg's arteriosclerosis Arteriolosclerosis Hyaline Hyperplastic Cholesterol LDL Oxycholesterol Trans fat Stenosis Carotid artery stenosis Renal artery stenosis Other Aortoiliac occlusive disease Degos disease Erythromelalgia Fibromuscular dysplasia Raynaud's phenomenon Aneurysm / dissection / pseudoaneurysm torso : Aortic aneurysm Abdominal aortic aneurysm Thoracic aortic aneurysm Aneurysm of sinus of Valsalva Aortic dissection Aortic rupture Coronary artery aneurysm head / neck Intracranial aneurysm Intracranial berry aneurysm Carotid artery dissection Vertebral artery dissection Familial aortic dissection Vascular malformation Arteriovenous fistula Arteriovenous malformation Telangiectasia Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia Vascular nevus Cherry hemangioma Halo nevus Spider angioma Veins Inflammation Phlebitis Venous thrombosis / Thrombophlebitis primarily lower limb Deep vein thrombosis abdomen Hepatic veno-occlusive disease Budd–Chiari syndrome May–Thurner syndrome Portal vein thrombosis Renal vein thrombosis upper limb / torso Mondor's disease Paget–Schroetter disease head Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Post-thrombotic syndrome Varicose veins Gastric varices Portacaval anastomosis Caput medusae Esophageal varices Hemorrhoid Varicocele Other Chronic venous insufficiency Chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency Superior vena cava syndrome Inferior vena cava syndrome Venous ulcer Arteries or veins Angiopathy Macroangiopathy Microangiopathy Embolism Pulmonary embolism Cholesterol embolism Paradoxical embolism Thrombosis Vasculitis Blood pressure Hypertension Hypertensive heart disease Hypertensive emergency Hypertensive nephropathy Essential hypertension Secondary hypertension Renovascular hypertension Benign hypertension Pulmonary hypertension Systolic hypertension White coat hypertension Hypotension Orthostatic hypotension Authority control GND : 4032758-9 NDL : 00575407VHL, MGP, TIMP1, TNC, DPT, KCNN3, FOXC2, CASZ1, GLG1, GJC2, GP1BB, KIF5A, HLA-A, LBH, FLT4, CNGB3, HIRA, SLC29A3, RREB1, SMAD3, NFATC2, NOTCH3, PIK3CA, PRKAR1B, PIEZO1, SEC24C, RASA1, FIBP, SLC12A2, SLC12A3, TBX1, VEGFC, G6PC3, HDAC7, UFD1, ARVCF, COL3A1, EBF1, CLCNKB, JMJD1C, EPHB4, COMT, LINC02549, LINC01152, ROCR, MMP9, VEGFA, SNCA, BLOC1S2, SYP, SLC17A6, NLRP3, ELN, MMP3, MMP2, MMP1, MTHFR, HIF1A, SLC18A3, TGFB1, STS, CALCA, NPY, GFAP, MCF2L2, TAC1, CALB1, KDR, TIMP2, DBH, ROCK2, CYP4F2, CHST3, CLOCK, HOMER1, RBM14-RBM4, TNFSF11, GNG13, TRPV4, MFAP5, PORCN, VIM, EHMT1, EGLN3, DCLK3, PAPLN, FOXC2-AS1, USH2A, ZGLP1, PPARGC1A, MIR202, AKR1B10, TRPV2, DLL4, SLC17A8, PRLH, EXOSC3, PACSIN1, PYCARD, CBLN4, SLC32A1, TSACC, ADI1, CACYBP, RBM14, KANK2, TP53INP1, BACE2, SLC17A7, HEY2, SYNM, EXOC7, PRRT2, ERC1, PGP, MMRN1, MYOCD, ACHE, TRH, GJA1, F13B, FLT1, FN1, FOS, FOSB, GCG, GJA8, ESR1, GLP1R, GRM1, HCCS, HCRT, HTT, HFE, F2, EPAS1, TIMP3, CALR, ADM, JAG1, AKT1, RHOA, AVP, CALB2, CASP1, DSP, CAV2, CYP4A11, CYP19A1, DES, DLD, DOCK3, ICAM1, ITGB2, ITGB3, CCL2, PRKCA, PRKCB, PTGS2, ACP3, S100A10, S100A12, SELE, JUN, SLC6A3, SLC18A2, SPP1, SST, TH, THBD, PPARG, POU2F1, PLG, PEPD, OPRM1, NOS1, NGFR, NGF, MTR, COX2, MMP13, SMAD2, LIF, LGALS3BP, LAD1, JUND, JUNB, MTCO2P12
-
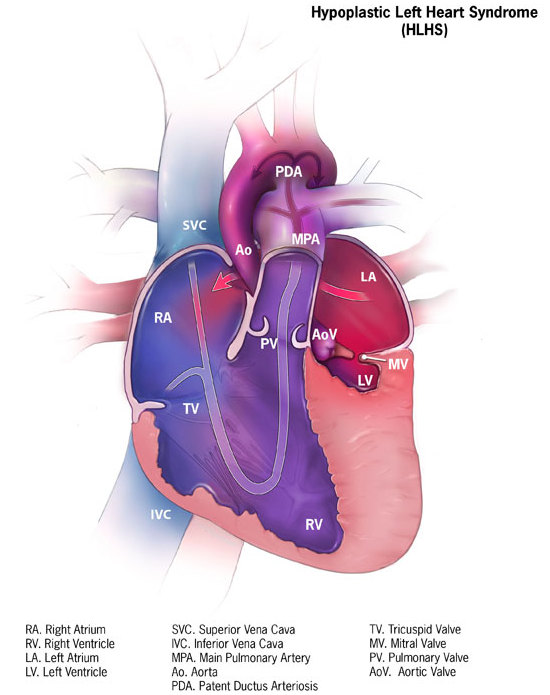
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Wikipedia
Classification D ICD - 10 : Q23.4 ICD - 9-CM : 746.7 OMIM : 241550 MeSH : D018636 DiseasesDB : 31507 External resources MedlinePlus : 001106 eMedicine : ped/1131 Orphanet : 2248 Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hypoplastic left heart syndrome . v t e Congenital heart defects Heart septal defect Aortopulmonary septal defect Double outlet right ventricle Taussig–Bing syndrome Transposition of the great vessels dextro levo Persistent truncus arteriosus Aortopulmonary window Atrial septal defect Sinus venosus atrial septal defect Lutembacher's syndrome Ventricular septal defect Tetralogy of Fallot Atrioventricular septal defect Ostium primum Consequences Cardiac shunt Cyanotic heart disease Eisenmenger syndrome Valvular heart disease Right pulmonary valves stenosis insufficiency absence tricuspid valves stenosis atresia Ebstein's anomaly Left aortic valves stenosis insufficiency bicuspid mitral valves stenosis regurgitation Other Underdeveloped heart chambers right left Uhl anomaly Dextrocardia Levocardia Cor triatriatum Crisscross heart Brugada syndrome Coronary artery anomaly Anomalous aortic origin of a coronary artery Ventricular inversion v t e Diseases of ion channels Calcium channel Voltage-gated CACNA1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 1 Episodic ataxia 2 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-6 CACNA1C Timothy syndrome Brugada syndrome 3 Long QT syndrome 8 CACNA1F Ocular albinism 2 CSNB2A CACNA1S Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 1 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 1 CACNB2 Brugada syndrome 4 Ligand gated RYR1 Malignant hyperthermia Central core disease RYR2 CPVT1 ARVD2 Sodium channel Voltage-gated SCN1A Familial hemiplegic migraine 3 GEFS+ 2 Febrile seizure 3A SCN1B Brugada syndrome 6 GEFS+ 1 SCN4A Hypokalemic periodic paralysis 2 Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis Paramyotonia congenita Potassium-aggravated myotonia SCN4B Long QT syndrome 10 SCN5A Brugada syndrome 1 Long QT syndrome 3 SCN9A Erythromelalgia Febrile seizure 3B Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder Congenital insensitivity to pain Constitutively active SCNN1B / SCNN1G Liddle's syndrome SCNN1A / SCNN1B / SCNN1G Pseudohypoaldosteronism 1AR Potassium channel Voltage-gated KCNA1 Episodic ataxia 1 KCNA5 Familial atrial fibrillation 7 KCNC3 Spinocerebellar ataxia type-13 KCNE1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Long QT syndrome 5 KCNE2 Long QT syndrome 6 KCNE3 Brugada syndrome 5 KCNH2 Short QT syndrome KCNQ1 Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome Romano–Ward syndrome Short QT syndrome Long QT syndrome 1 Familial atrial fibrillation 3 KCNQ2 BFNS1 Inward-rectifier KCNJ1 Bartter syndrome 2 KCNJ2 Andersen–Tawil syndrome Long QT syndrome 7 Short QT syndrome KCNJ11 TNDM3 KCNJ18 Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis 2 Chloride channel CFTR Cystic fibrosis Congenital absence of the vas deferens CLCN1 Thomsen disease Myotonia congenita CLCN5 Dent's disease CLCN7 Osteopetrosis A2, B4 BEST1 Vitelliform macular dystrophy CLCNKB Bartter syndrome 3 TRP channel TRPC6 FSGS2 TRPML1 Mucolipidosis type IV Connexin GJA1 Oculodentodigital dysplasia Hallermann–Streiff syndrome Hypoplastic left heart syndrome GJB1 Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease X1 GJB2 Keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome Ichthyosis hystrix Bart–Pumphrey syndrome Vohwinkel syndrome ) GJB3 / GJB4 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis Progressive symmetric erythrokeratodermia GJB6 Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Porin AQP2 Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus 2 See also: ion channelsNKX2-5, GJA1, SAP130, PCDHA13, PCDHA9, NOTCH1, FOXF1, MYRF, ARHGAP31, TBX1, TBX5, NR2F2, WT1, ZNF148, TBX20, CRELD1, ARID1A, KYNU, WASHC5, HAAO, MKKS, PAH, CCDC22, SMAD6, GATA6, GATA4, FLI1, TRAF7, GATA5, B3GLCT, DTNA, PKD1L1, TMEM258, MCTP2, HAND1, MYH6, JAM3, C20orf181, APOE, FOXP1, RBFOX2, KMT2D, SMN2, S100B, PROX1, FXN, FOXC2, FOXL1, EDN1, ACE, CBL, RN7SL263P
-
Hypokinesia
Wikipedia
Classification D MeSH : D018476 v t e Diseases of the nervous system , primarily CNS Inflammation Brain Encephalitis Viral encephalitis Herpesviral encephalitis Limbic encephalitis Encephalitis lethargica Cavernous sinus thrombosis Brain abscess Amoebic Brain and spinal cord Encephalomyelitis Acute disseminated Meningitis Meningoencephalitis Brain / encephalopathy Degenerative Extrapyramidal and movement disorders Basal ganglia disease Parkinsonism PD Postencephalitic NMS PKAN Tauopathy PSP Striatonigral degeneration Hemiballismus HD OA Dyskinesia Dystonia Status dystonicus Spasmodic torticollis Meige's Blepharospasm Athetosis Chorea Choreoathetosis Myoclonus Myoclonic epilepsy Akathisia Tremor Essential tremor Intention tremor Restless legs Stiff-person Dementia Tauopathy Alzheimer's Early-onset Primary progressive aphasia Frontotemporal dementia / Frontotemporal lobar degeneration Pick's Dementia with Lewy bodies Posterior cortical atrophy Vascular dementia Mitochondrial disease Leigh syndrome Demyelinating Autoimmune Inflammatory Multiple sclerosis For more detailed coverage, see Template:Demyelinating diseases of CNS Episodic/ paroxysmal Seizures and epilepsy Focal Generalised Status epilepticus For more detailed coverage, see Template:Epilepsy Headache Migraine Cluster Tension For more detailed coverage, see Template:Headache Cerebrovascular TIA Stroke For more detailed coverage, see Template:Cerebrovascular diseases Other Sleep disorders For more detailed coverage, see Template:Sleep CSF Intracranial hypertension Hydrocephalus Normal pressure hydrocephalus Choroid plexus papilloma Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Cerebral edema Intracranial hypotension Other Brain herniation Reye syndrome Hepatic encephalopathy Toxic encephalopathy Hashimoto's encephalopathy Both/either Degenerative SA Friedreich's ataxia Ataxia–telangiectasia MND UMN only: Primary lateral sclerosis Pseudobulbar palsy Hereditary spastic paraplegia LMN only: Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies Spinal muscular atrophies SMA SMAX1 SMAX2 DSMA1 Congenital DSMA Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance (SMALED) SMALED1 SMALED2A SMALED2B SMA-PCH SMA-PME Progressive muscular atrophy Progressive bulbar palsy Fazio–Londe Infantile progressive bulbar palsy both: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis v t e Symptoms and signs relating to movement and gait Gait Gait abnormality CNS Scissor gait Cerebellar ataxia Festinating gait Marche à petit pas Propulsive gait Stomping gait Spastic gait Magnetic gait Truncal ataxia Muscular Myopathic gait Trendelenburg gait Pigeon gait Steppage gait Antalgic gait Coordination Ataxia Cerebellar ataxia Dysmetria Dysdiadochokinesia Pronator drift Dyssynergia Sensory ataxia Asterixis Abnormal movement Athetosis Tremor Fasciculation Fibrillation Posturing Abnormal posturing Opisthotonus Spasm Trismus Cramp Tetany Myokymia Joint locking Paralysis Flaccid paralysis Spastic paraplegia Spastic diplegia Spastic paraplegia Syndromes Monoplegia Diplegia / Paraplegia Hemiplegia Triplegia Tetraplegia / Quadruplegia General causes Upper motor neuron lesion Lower motor neuron lesion Weakness Hemiparesis Other Rachitic rosary Hyperreflexia Clasp-knife responseGCH1, OPRL1, APOD, SLC6A3, TH, LRRK2, MAPT, SNCA, ATXN3, ATXN1, FMR1, GBA, PSEN1, TWNK, PLA2G6, KLHL41, ATP6AP2, DNAJC6, KMT2B, SNCAIP, SYNJ1, PDE8B, PRKRA, UCHL1, XPA, FARS2, TPM3, TPM2, TK2, DHDDS, TBP, ACTA1, SPR, SLC20A2, PINK1, WDR45, AFG3L2, DNAJC12, VPS35, SLC30A10, TTC19, VPS13C, C19orf12, CHCHD2, ATL1, RRM2B, HTRA2, COQ2, JPH3, GIGYF2, FBXO7, MYORG, SLC39A14, ATP13A2, DNAJC13, ADGRV1, PARK7, TUBB6, POLG2, TAF1, SCN2A, SCN9A, NR4A2, MYPN, COASY, STX1B, KCNC3, RAB39B, HTT, EARS2, GLUD2, GABRG2, GABRD, FTL, EIF4G1, HCN1, DCTN1, KBTBD13, CSF1R, LYST, ATP1A3, ATXN8, SLC25A4, ADH1C, NEB, PANK2, PRKAR1B, POLG, ATXN2, ATXN8OS, SCN1A, PRNP, PPP2R2B, PTS, SCN1B, PODXL, PDGFRB, PDGFB, PRKN, SF3B1, YWHAE, ASXL1, TET2, PAFAH1B1, REG1A, STXBP3, PSPH, BPIFA2, RIDA, PSPN, HTR2C, MSMB, CCDC62, TMEM240, PPP1R1B, ACO1, TMEM106B, GRIN2A, APOE, CYP1A2, NQO1, DRD2, DRD4, EEF1A2, GRIN2B, MCF2L, IREB2, LRP2, NBN, RGS2, SLC18A2, SOD2, ECT
-
Xeroderma Pigmentosum
Wikipedia
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on xeroderma pigmentosum Classification D ICD - 10 : Q82.1 ICD - 9-CM : 757.33 OMIM : 278700 MeSH : D014983 DiseasesDB : 14198 External resources MedlinePlus : 001467 eMedicine : derm/462 neuro/399 Patient UK : Xeroderma pigmentosum GeneReviews : Xeroderma Pigmentosum Orphanet : 910 v t e Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis / erythrokeratodermia AD Ichthyosis vulgaris AR Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma : Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis Lamellar ichthyosis Harlequin-type ichthyosis Netherton syndrome Zunich–Kaye syndrome Sjögren–Larsson syndrome XR X-linked ichthyosis Ungrouped Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens Ichthyosis follicularis Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa Ichthyosis hystrix EB and related EBS EBS-K EBS-WC EBS-DM EBS-OG EBS-MD EBS-MP JEB JEB-H Mitis Generalized atrophic JEB-PA DEB DDEB RDEB related: Costello syndrome Kindler syndrome Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome Skin fragility syndrome Ectodermal dysplasia Naegeli syndrome / Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis Hay–Wells syndrome Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Focal dermal hypoplasia Ellis–van Creveld syndrome Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome / Hay–Wells syndrome Elastic / Connective Ehlers–Danlos syndromes Cutis laxa ( Gerodermia osteodysplastica ) Popliteal pterygium syndrome Pseudoxanthoma elasticum Van der Woude syndrome Hyperkeratosis / keratinopathy PPK diffuse : Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert Meleda disease syndromic connexin Bart–Pumphrey syndrome Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Vohwinkel syndrome Corneodermatoosseous syndrome plakoglobin Naxos syndrome Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez Olmsted syndrome Cathepsin C Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome Haim–Munk syndrome Camisa disease focal : Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis Howel–Evans syndrome Pachyonychia congenita Pachyonychia congenita type I Pachyonychia congenita type II Striate palmoplantar keratoderma Tyrosinemia type II punctate : Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa Focal acral hyperkeratosis Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome Porokeratosis plantaris discreta Spiny keratoderma ungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia desmoplakin Carvajal syndrome connexin Erythrokeratodermia variabilis HID / KID Other Meleda disease Keratosis pilaris ATP2A2 Darier's disease Dyskeratosis congenita Lelis syndrome Dyskeratosis congenita Keratolytic winter erythema Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenita and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei Keratosis pilaris Other cadherin EEM syndrome immune system Hereditary lymphedema Mastocytosis / Urticaria pigmentosa Hailey–Hailey see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages , Template:Phakomatoses , Template:Pigmentation disorders , Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorder Developmental anomalies Midline Dermoid cyst Encephalocele Nasal glioma PHACE association Sinus pericranii Nevus Capillary hemangioma Port-wine stain Nevus flammeus nuchae Other/ungrouped Aplasia cutis congenita Amniotic band syndrome Branchial cyst Cavernous venous malformation Accessory nail of the fifth toe Bronchogenic cyst Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux Congenital lip pit Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs Congenital preauricular fistula Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma Cystic lymphatic malformation Median raphe cyst Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy Mongolian spot Nasolacrimal duct cyst Omphalomesenteric duct cyst Poland anomaly Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome Skin dimple Superficial lymphatic malformation Thyroglossal duct cyst Verrucous vascular malformation Birthmark v t e Metabolic disease : DNA replication and DNA repair-deficiency disorder DNA replication Separation/initiation: RNASEH2A Aicardi–Goutières syndrome 4 Termination/ telomerase : DKC1 Dyskeratosis congenita DNA repair Nucleotide excision repair Cockayne syndrome / DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome Thymine dimer Xeroderma pigmentosum IBIDS syndrome MSI / DNA mismatch repair Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer Muir–Torre syndrome Mismatch repair cancer syndrome MRN complex Ataxia telangiectasia Nijmegen breakage syndrome Other RecQ helicase Bloom syndrome Werner syndrome Rothmund–Thomson syndrome / Rapadilino syndrome Fanconi anemia Li-Fraumeni syndrome Severe combined immunodeficiency v t e Progeroid syndromes DNA repair RecQ-associated Werner syndrome Bloom syndrome Rothmund–Thomson syndrome NER protein-associated Cockayne syndrome Xeroderma pigmentosum Trichothiodystrophy Lamin A/C Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome Restrictive dermopathy Other/related disorders Li–Fraumeni syndrome Rapadilino syndrome Baller–Gerold syndrome DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome Nijmegen breakage syndrome Fanconi anemia Dyskeratosis congenita Ataxia telangiectasia De Barsy syndrome PIBI(D)S syndrome BIDS syndrome Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy syndrome See also: DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderXPA, XPC, POLH, ERCC5, ERCC2, ERCC1, DDB2, ERCC4, ERCC3, TERF2, GTF2H1, TP53, NR1H2, BIVM-ERCC5, GTF2H2, GTF2H3, GTF2H5, GTF2H4, POLQ, CAT, XRCC1, CSH2, XRCC6P5, HPRT1, LIG4, ERCC6, CSH1, HRAS, OGG1, HPGDS, PCNA, PTEN, XRCC3, ENDOV, CDKN2A, GSTM1, SIRT1, MC1R, LCE2B, HSPA9, RAD23A, NRAS, FUS, WDR76, ATR, BRIP1, CHEK1, DDB1, BCL2, DECR1, ERCC8, CCNH, ATM, TYMS, BTN2A2, PTF1A, IRF9, EXO1, HERC2, RAD54L, H3P38, PDIK1L, HFM1, UBE3B, USP7, IFI44, XRCC2, CATSPER1, TDG, SLX4, XYLT2, VPS11, RTEL1, CRLF3, DEFB103A, DEFB103B, MEPE, WDR77, LRRC59, RNU1-1, VEPH1, PRDX5, SMUG1, AAGAB, KAT7, ZC3H12D, NAT1, TALDO1, CGA, FEN1, EGFR, NQO1, TIMM8A, DDX11, GADD45A, CYP1B1, CSNK2A1, CRYZ, COMT, CETN2, SYCP1, CDK7, CDK4, DDR1, BRAF, BRCA1, BAX, ATF3, ASIP, FAS, APEX1, GOT1, GSTM2, GSTT1, HGF, SULT1A1, STAT3, ST13, SMO, RNU2-1, RNU1-4, RECQL, RAD23B, PTCH1, PTAFR, MAPK8, PRKDC, POMC, AKT1, ODC1, NPM1, NCAM1, MYC, MPO, LBR, KIT, H3P33
-
Atypical Teratoid Rhabdoid Tumor
Wikipedia
Metastatic dissemination via this mechanism has been reported with other brain tumors, including germinomas , medulloblastomas , astrocytomas , glioblastomas , ependymomas , and endodermal sinus tumors . Guler and Sugita separately reported cases of lung metastasis without a shunt. [47] [48] Epidemiology [ edit ] An estimated 3% of pediatric brain tumors are AT/RTs, although this percentage may increase with better differentiation between PNET/medulloblastoma tumors and AT/RTs. [ citation needed ] As with other CNS tumors, more males are affected than females (ratio 1.6:1).SMARCB1, TP53, LIN28A, MYC, PROM1, CCND1, SMARCA4, BRAF, TSPO, SPP1, NF2, EWSR1, CLDN6, LIN28B, HMGA2, CHRM3, RASSF1, CXCL13, BMS1, ACACA, MLRL, XRS, VIM, TLE1, TEAD4, TBX5, TYR, CD274, FBXW11, MIRLET7B, LINC01672, MIR601, SMIM10L2B, MIR34A, MIR221, MIR155, MIR142, SMIM10L2A, SUN2, CHDM, PHF5A, MAP1LC3B, PRDM16, PID1, TBX1, GPKOW, CNTN2, SMARCA1, TAGLN, ACTB, IGF1, HTC2, H2AX, MTOR, F8, F3, EZH2, EREG, EGFR, TIMM8A, CNN1, BTF3, BCL2, ATM, ADA, IGF1R, CXCL8, INSR, SERPINF2, SHH, RPL10, RPL5, RHD, MAP2K7, PLK1, PIP, CD99, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, NPM1, MYCN, PERCC1
-
Wiskott–aldrich Syndrome
Wikipedia
Similarly, prophylactic antibiotic use may also be considered in patients with recurrent bacterial sinus or lung infections. When there are signs or symptoms of an infection, prompt and thorough evaluation is important including blood cultures to guide therapy (often IV antibiotics).WAS, WIPF1, FOXP3, ACTB, SPN, ACTR2, AICDA, ANGPTL2, FUT1, ADA, TIMP1, CD34, IL2, NOL3, WASF1, CD28, OTC, WASL, DOCK8, G6PD, BTK, TBX21, CDC42, CD19, TBC1D25, USF2, THPO, ZNF182, CXCL12, TFE3, CXCR4, TRBV20OR9-2, UBL4A, ATXN2, SYP, ACTR3, BCAR1, NELFCD, G6PC3, MIB1, VPS35, INTS8, QRSL1, NCKIPSD, ICOS, ARPC1B, CCNDBP1, WASF3, TNFSF13B, CIB1, HAX1, RAC2, RAG1, PFN1, PTK2, FCER2, CTTN, ELANE, CSF2, CSF1, CR2, COX8A, CD69, CD40LG, CD27, CASP3, CAST, SLC25A20, CA2, C4BPA, BCL6, AR, FAS, FBN1, FCGR2B, PSMA7, FLNA, PPARG, PKD2, PGK1, NFATC2, NFATC1, NCK1, LY6E, LIG4, ITGB3, ISG20, IL6, IL4, IL2RG, IL2RA, IGHG3, NCKAP1L, GFI1, WIPF2