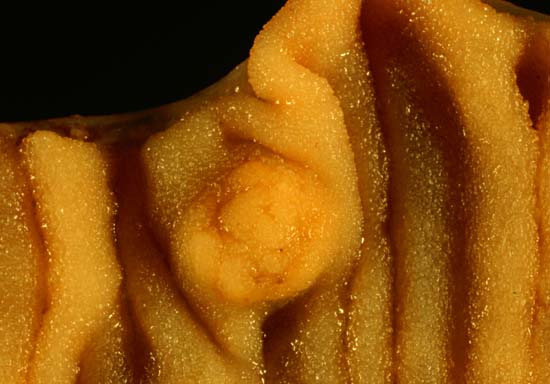
-
Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Wikipedia
PMID 31867475 . ^ a b c Couvidat C, Eiss D, Verkarre V, Merran S, Corréas JM, Méjean A, Hélénon O (November 2014). ... PMID 19448113 . ^ a b c d e Bourlon MT, Meneses-Medina M, Vázquez-Manjarrez S, Bustamante-Romero FM, Gallegos-Garza AC, Lam ET (November 2015). ... PMID 26185343 . ^ Weidner N, Cote RJ, Suster S, Weiss LM (2009-07-08). Modern Surgical Pathology E-Book . ... PMID 28153029 . ^ Ravaud, A.; Oudard, S.; De Fromont, M.; Chevreau, C.; Gravis, G.; Zanetta, S.; Theodore, C.; Jimenez, M.; Sevin, E.; Laguerre, B.; Rolland, F.; Ouali, M.; Culine, S.; Escudier, B. (2015-06-01). ... S2CID 205659715 . ^ Kamai T, Abe H, Arai K, Murakami S, Sakamoto S, Kaji Y, Yoshida KI (March 2016).MET, MITF, PRCC, VHL, TFE3, KRT7, ERBB2, GSTP1, SLC2A1, ELOC, POMC, PIK3CA, ADIPOQ, RPL14, INPP4B, FPGT, TNFSF10, CRADD, UNC5C, TAGLN2, BAP1, KDM5C, PEBP1, MLLT10, PAK1, TSC1, TP53, TGM2, PDHB, HNF1B, HNF1A, NF2, SOD2, SLC5A3, PGK1, ACY1, RYR1, RELA, PVALB, PTGS2, PTEN, ZNF536, ACHE, KEAP1, AHNAK, LMAN2L, CARD11, SLC49A4, NAV3, ZNF765, NLRP12, ZNF804A, CSMD3, LRRK2, ASB15, DNHD1, FAAH2, FLCN, OR4C13, VMO1, MSGN1, FAM111B, BIRC7, SPTBN4, CUL7, FMN2, NDRG1, CPQ, BTG3, AKAP13, RNF139, PDXDC1, SYNE2, PRAME, YIPF3, PNKD, SETD2, SHANK1, LRP1B, TET2, PBRM1, PIDD1, AP5M1, OGG1, SFRP2, APRT, MUC4, IL6, ALDH1A1, ALK, ALOX5, IFNA2, HSPD1, HSPB1, HSPA9, ALOX12B, ANXA4, APAF1, BIRC5, HARS1, EEF2, BCHE, GSTT1, GSTM1, GRB7, GJB1, EPAS1, MTOR, IL6R, IL4R, IL13, KRT32, CNN2, SCARB1, CASP2, CAPG, M6PR, ALAD, LDHB, L1CAM, CRABP1, KRT8, KCNMA1, DAPK1, CTSD, CTSB, CRYAB, FLT1, CDC73, HABP2, LMNA, FOXE1, MINPP1, VEGFA, AMACR, KDR, CD38, FH, MME, RASSF1, CA9, MYC, KIT, SNORD14D, SNORD14C, CD47, MIR1180, TWSG1, MIR1293, MIR379, KMT2C, ACE2, FBXO47, EIF2AK4, MIR34A, MIR200C, MIR181C, MIR134, MIR127, FBXO11, AKT1, DDR1, RAB37, APC, CDC34, SETDB2, BRAF, SNORD35B, RIOX2, BSG, BUB1, SNORD14E, SNORD14B, MEG3, DHCR24, LARP6, CDH1, HIF1A, TOP2A, TIMP3, TIMP1, UBE2K, SYP, IGFBP7, SLC16A1, SFPQ, RRM2, SNORD15A, CD82, PYCR1, PTK7, CFP, PAX2, MUC1, TBC1D25, OAT, NONO, NFE2L2, XRCC1, PAX8, FZD1, KDM4C, CDR2, CMA1, APH1A, CD274, CLDN7, MCTS1, MCAT, UBE2S, HAVCR1, ACE, CUL3, RALBP1, EGF, EGFR, ELAVL2, ETFA, NAPSA, FGFR2, FOLH1, GABPA, MIR3199-2
-
Thiopurine S Methyltranferase Deficiency
GARD
Thiopurine S-methyltransferase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder that affects the body's ability to metabolize thiopurine drugs. Thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) is an enzyme that the body uses to break down thiopurine drugs. Thiopurine S-methyltransferase deficiency patients have a mutation in either one or both copies of the TPMT gene that causes reduced enzyme activity and difficulties breaking down thiopurine drugs.
-
Carcinoid
Wikipedia
Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Gastrointestinal 1.2 Lung 1.3 Other sites and metastases 1.4 Goblet cell carcinoid 2 Cause 3 Treatment 4 History 5 See also 6 References 7 External links Signs and symptoms [ edit ] Primary site of a carcinoid cancer of gut While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural lifetime and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called coincidental carcinoids ), all carcinoids are considered to have malignant potential. ... Occasionally, haemorrhage or the effects of tumor bulk are the presenting symptoms. The most common originating sites of carcinoid is the small bowel, particularly the ileum; carcinoid tumors are the most common malignancy of the appendix. ... The next most common affected area is the respiratory tract , with 28% of all cases—per PAN-SEER data (1973–1999). The rectum is also a common site. Gastrointestinal [ edit ] Main article: Small intestine neuroendocrine tumor Carcinoid tumors are apudomas that arise from the enterochromaffin cells throughout the gut. ... Main article: Typical lung carcinoid tumor Carcinoid tumors are also found in the lungs . Other sites and metastases [ edit ] Metastasis of carcinoid can lead to carcinoid syndrome .MIR409, MIR155, MIR222, MIR369, MIR154, MIR193A, MIR127, MIR224, MIR30A, MIR34B, MIR34C, MIR302D, MIR136, MIR370, MIR10A, MIR146A, MIR410, MIR432, MIR487B, MIR494, MIR938, MIR511, MEN1, CDKN1B, CDKN1A, BRCA2, CHGA, SST, CDKN2C, CDKN2B, POMC, TP53, KIF16B, GAST, SCLC1, SYP, ASCL1, MTA1, CTNNB1, EGFR, SLC6A2, BCL2, OTP, TGFB1, ELK3, TTF1, RAF1, EPHB1, CD44, PIK3CA, IGF1, INSM1, RASSF1, PAX5, MGMT, NKX2-1, CD274, DLL3, PYY, SSTR2, RET, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, KRT19, KIT, SMUG1, VEGFA, PDGFRA, SDHD, SIM2, NOTCH1, NME1, MYC, APC, TTR, SCTR, AKT1, TERT, CDKN2A, CCN2, MAP2K1, MTOR, MAPK3, GRP, CCKBR, SSTR1, HDC, DAD1, SOX2, TAC1, SSTR5, HMGA2, KMT2D, FZD7, SPHK1, VIM, CXCR4, WT1, TGFA, STC1, TGFB2, TGFB3, TIMP3, UVRAG, UCHL1, TP63, ACTB, GPRC5A, TMED7, RTN4, INTS2, MARCKSL1, WLS, TMPRSS13, LMLN, CDHR1, SPECC1, PIK3IP1, OR51E1, IPMK, NUTM1, TICAM2, MIR100, MIR21, MIR431, MIR497, MIR885, TMED7-TICAM2, LOC105373985, H3P23, BCOR, HPGDS, CLDN2, MYCBP, CLDN1, ATG12, ZFYVE9, NAPSA, CARTPT, KEAP1, BCL2L11, PRMT5, CIB1, ZNRD2, IGF2BP3, DCTN6, POLQ, MAGED2, CKAP4, NLRP1, TBC1D9, SMS, CRTC1, RAB38, PRKD2, SATB2, POU4F1, SLC18A1, FGF3, CPE, CLDN4, CLDN3, DDC, DES, DIO3, EGF, EPHB2, ERBB2, ERBB4, ETS1, FHIT, HES1, FOS, FOSB, GABPA, GCG, GHRH, GIP, GLI1, GNAS, GSK3B, GSTP1, HIF1A, CLU, CHRNA7, CFTR, CDX2, AMY1A, AMY1B, AMY1C, AMY2A, AMY2B, APLP1, APP, AQP4, STS, ATP1A2, ATP4A, BAAT, CEACAM1, BRAF, CA2, CALCA, CASP8, CCNA2, CCNE1, CDH1, CDH13, CDK6, CDKN2D, HOXC6, HSP90AA1, SLC3A2, PRKD1, PAK3, PCNA, PDGFA, PDGFRB, ABCB1, PIP, PITX1, PLAU, PLCB3, PLG, POU3F2, PSMD9, HTR2B, PTEN, PTH, PTHLH, PTPRN, RAD51C, RARB, RNASE3, RPE65, RTN1, SCT, SLC2A1, SERPINE1, NTS, NMB, NGF, IFI27, IL12A, ISL1, JUN, JUNB, JUND, LUM, SMAD4, MAP2, MCAM, CD99, MKI67, MLH1, MMP2, CD200, ABCC1, MSH2, MSMB, MST1, NEUROD1, NF1, NFE2L2, NFKB1, H3P10
-
Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin-Dependent, 2
OMIM
They found that HLA-DR4-positive diabetics showed an increased risk associated with common variants at polymorphic sites in a 19-kb segment spanned by the 5-prime INS VNTR and the third intron of the gene for insulinlike growth factor II (IGF2; 147470). ... By 'cross-match' haplotype analysis and linkage disequilibrium mapping, Bennett et al. (1995) mapped the IDDM2 mutation to a site within the VNTR locus itself. Other polymorphisms were systematically excluded as primary disease determinants. ... The ILPR is located in the proximal promoter of the insulin gene, 365 bp from the transcription start site. From this location, it was initially thought that the ILPR might be an important transcriptional regulatory region. ... The ILPR contains numerous high-affinity binding sites for the transcription factor Pur-1 (PUR1; 600473), and transcriptional activation of Pur-1 is modulated by naturally occurring sequences in the ILPR. ... In search of a more plausible mechanism for the dominant effect of class III alleles, Vafiadis et al. (1997) analyzed expression of insulin in human fetal thymus, a critical site for tolerance induction to self proteins.
-
Plasma Cell Leukemia
Orphanet
Neoplastic plasma cells may also be found in extramedullary sites, such as the liver or spleen, among others.IL6, CDKN2A, MYC, TP53, CCND1, IGH, FGFR3, RASSF1, RB1, HLA-A, H3P10, CDKN2B, CD40, CKS1B, SOCS3, TMSB4X, BCR, VEGFA, NSD2, CXCR4, BCL10, PKD2L1, SFRP5, MAFB, NES, BCL2, PHF19, MUC16, RBM45, TIMP3, SFRP1, FLT4, SAT1, BRAF, PTEN, PSMB5, NCAM1, MLH1, MGMT, MDM2, KRAS, CD40LG, IL3, CD79A, ICAM1, FRZB, PLIN2
-
Acute Myeloid Leukemia With T(6;9)(P23;q34)
Orphanet
Frequently associated with multilineage bone marrow dysplasia, it usually presents with anemia, thrombocytopenia (often pancytopenia), and other nonspecific symptoms related to ineffective hematopoesis (fatigue, bleeding and bruising, recurrent infections, bone pain) and/or extramedullary site involvement (gingivitis, splenomegaly).
-
Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Of The Elderly
Orphanet
Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly is a rare form of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma occurring most commonly in patients over the age of 50 (usually between 70-75 years of age), without overt immunodeficiency, and presenting with nodal and extranodal involvement (in sites such as the stomach, lung, skin and pancreas) and B symptoms (fever, night sweats, weight loss).
- Poliomyelitis GARD
-
Gross Pathology
Wikipedia
It is vital to systematically explain the gross appearance of a pathological state, for example, a malignant tumor, noting the site, size, shape, consistency, presence of a capsule and appearance on cut section whether well circumscribed or diffusely infiltrating, homogeneous or variegated, cystic, necrotic, hemorrhagic areas, as well as papillary projections.
-
Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease
Orphanet
Patients may have more than one type of PTLD in a single or in different locations. The most commonly involved sites are lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and liver, although the disease may occur almost anywhere in the body.
-
Ascariasis
Wikipedia
References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u Dold C, Holland CV (July 2011). ... PMID 22291577 . ^ a b Fung IC, Cairncross S (March 2009). "Ascariasis and handwashing". ... PMID 18789465 . ^ Jia TW, Melville S, Utzinger J, King CH, Zhou XN (2012). ... PMID 22325616 . ^ a b Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. (December 2012). ... Image (warning, very graphic): Image 1 CDC DPDx Parasitology Diagnostic Web Site Classification D ICD - 10 : B77 ICD - 9-CM : 127.0 OMIM : 604291 MeSH : D001196 DiseasesDB : 934 External resources MedlinePlus : 000628 eMedicine : article/212510 v t e Parasitic disease caused by helminthiases Flatworm/ platyhelminth infection Fluke/trematode ( Trematode infection ) Blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni / S. japonicum / S. mekongi / S. haematobium / S. intercalatum Schistosomiasis Trichobilharzia regenti Swimmer's itch Liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis Clonorchiasis Dicrocoelium dendriticum / D. hospes Dicrocoeliasis Fasciola hepatica / F. gigantica Fasciolosis Opisthorchis viverrini / O. felineus Opisthorchiasis Lung fluke Paragonimus westermani / P. kellicotti Paragonimiasis Intestinal fluke Fasciolopsis buski Fasciolopsiasis Metagonimus yokogawai Metagonimiasis Heterophyes heterophyes Heterophyiasis Cestoda ( Tapeworm infection ) Cyclophyllidea Echinococcus granulosus / E. multilocularis Echinococcosis Taenia saginata / T. asiatica / T. solium (pork) Taeniasis / Cysticercosis Hymenolepis nana / H. diminuta Hymenolepiasis Pseudophyllidea Diphyllobothrium latum Diphyllobothriasis Spirometra erinaceieuropaei Sparganosis Diphyllobothrium mansonoides Sparganosis Roundworm/ Nematode infection Secernentea Spiruria Camallanida Dracunculus medinensis Dracunculiasis Spirurida Filarioidea ( Filariasis ) Onchocerca volvulus Onchocerciasis Loa loa Loa loa filariasis Mansonella Mansonelliasis Dirofilaria repens D. immitis Dirofilariasis Wuchereria bancrofti / Brugia malayi / | B. timori Lymphatic filariasis Thelazioidea Gnathostoma spinigerum / G. hispidum Gnathostomiasis Thelazia Thelaziasis Spiruroidea Gongylonema Strongylida ( hookworm ) Hookworm infection Ancylostoma duodenale / A. braziliense Ancylostomiasis / Cutaneous larva migrans Necator americanus Necatoriasis Angiostrongylus cantonensis Angiostrongyliasis Metastrongylus Metastrongylosis Ascaridida Ascaris lumbricoides Ascariasis Anisakis Anisakiasis Toxocara canis / T. cati Visceral larva migrans / Toxocariasis Baylisascaris Dioctophyme renale Dioctophymosis Parascaris equorum Rhabditida Strongyloides stercoralis Strongyloidiasis Trichostrongylus spp.
-
Oral And Maxillofacial Pathology
Wikipedia
Atlas of oral & maxillofacial surgery . Tiwana, Paul S. St. Louis, Mo. ISBN 9781455753284 . OCLC 912233495 . ^ a b c M., Balaji, S. (2007). Textbook of oral and maxillofacial surgery . ... ISBN 9780198564898 . OCLC 61756542 . ^ Elad S, Zadik Y, Hewson I, et al. (August 2010). ... Retrieved on 2010-02-01 ^ Women's Oral Health and Overall ^ Elad S, Zadik Y, Zeevi I, et al. (December 2010). ... Retrieved on 2010-02-01 ^ Zadik Y, Drucker S, Pallmon S (Aug 2011). "Migratory stomatitis (ectopic geographic tongue) on the floor of the mouth".
-
Berylliosis
Wikipedia
PMID 25398119 . ^ Frome, Edward L; Newman, Lee S; Cragle, Donna L; Colyer, Shirley P; Wambach, Paul F (2003-02-01). ... I.; Latza, U.; Groneberg, D.; Letzel, S. (2012-10-01). "Systematic review: progression of beryllium sensitization to chronic beryllium disease" . ... M.; Zhen, B.; Martyny, J. W.; Newman, L. S. (1993-10-01). "Epidemiology of beryllium sensitization and disease in nuclear workers". ... ISSN 0003-0805 . PMID 8214955 . ^ Newman, Lee S.; Mroz, Margaret M.; Balkissoon, Ronald; Maier, Lisa A. (2005-01-01). ... K.; Cumro, D.; Deubner, D. D.; Kent, M. S.; McCawley, M.; Kreiss, K. (2001-04-01).
-
Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Inv(3)(Q21q26.2) Or T(3;3)(Q21;q26.2)
Orphanet
Patients typically present with leukocytosis, anemia, variable platelet counts and a variety of nonspecific symptoms related to ineffective hematopoesis (fatigue, bleeding, bruising, recurrent infections, bone pain) and/or extramedullary site involvement (gingivitis, splenomegaly).
-
Acute Myeloid Leukemia And Myelodysplastic Syndromes Related To Topoisomerase Type 2 Inhibitor
Orphanet
This subgroup of t-MN is typically associated with overt leukemia, without preceding myelodysplastic syndrome, developing 2-3 years after exposure, presenting with non-specific symptoms related to ineffective hematopoesis (fatigue, bleeding and bruising, recurrent infections, bone pain) and/or extramedullary site involvement.
-
Clear Cell Sarcoma Of Kidney
Orphanet
Metastatic spread to lymph nodes, bones, lungs, retroperitoneum, brain and liver is common at time of diagnosis and therefore bone pain, cough or neurological compromise may be associated. Metastasis to unusual sites, such as the scalp, neck, nasopharynx, axilla, orbits and epidural space, have been reported.
- Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid GARD
-
Scorpion Envenomation
Orphanet
Scorpion envenomation is a rare intoxication caused by a scorpion sting which typically manifests with localized pain, edema, erythema, and paresthesias at the site of the sting and, when severe, progresses to produce systemic symptoms of variable severity that include respiratory difficulties, abnormal systemic blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmia, and a combination of parasympathetic (i.e. excessive salivation and lacrimation, diaphoresis, miosis, frequent urination, diarrhea, vomiting, priapism) and sympathetic (e.g. hyperthermia, hyperglycemia, mydriasis) manifestations.
-
Rhabdoid Tumor Predisposition Syndrome
GeneReviews
If ultrasound is not sufficient consider MRI at least every two to three months for affected site and ultrasound for all other sites. ... Variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. ... The absence of a clinical and family history of rhabdoid tumor(s) distinguishes these individuals from those with RTPS. ... If ultrasound is not sufficient consider MRI at least every two to three months for affected site and ultrasound for all other sites.
-
Autosomal Dominant Nocturnal Frontal Lobe Epilepsy
Wikipedia
PMID 7550350 . ^ a b Matsushima N, Hirose S, Iwata H, Fukuma G, Yonetani M, Nagayama C, Hamanaka W, Matsunaka Y, Ito M, Kaneko S, Mitsudome A, Sugiyama H (2002). ... J Neurosci . 17 (23): 9035–47. doi : 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-23-09035.1997 . PMID 9364050 . ^ a b Bertrand S, Weiland S, Berkovic S, Steinlein O, Bertrand D (1998). ... PMID 9831911 . ^ a b c d Bertrand D, Picard F, Le Hellard S, Weiland S, Favre I, Phillips H, Bertrand S, Berkovic S, Malafosse A, Mulley J (2002). ... PMID 12754307 . ^ Steinlein O, Magnusson A, Stoodt J, Bertrand S, Weiland S, Berkovic S, Nakken K, Propping P , Bertrand D (1997). ... PMID 11062464 . ^ Phillips H, Favre I, Kirkpatrick M, Zuberi S, Goudie D, Heron S, Scheffer I, Sutherland G, Berkovic S, Bertrand D, Mulley J (2001).