-
Fowler's Syndrome
Wikipedia
The usual findings are complex repetitive discharges without and with deceleration (decelerating bursts), suggesting an impairment in sphincter muscle relaxation. [7] [4] Treatment [ edit ] Sacral neuro modulation is the commonly practiced treatment for restoration of normal micturition. This technique involves modulation of micturition reflex by stimulating S3 nerve root. [8] [9] History [ edit ] This disease was described first by Fowler et al in 1985. [10] References [ edit ] ^ Wein, Alan J. (2012), "Pathophysiology and Classification of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction", Campbell-Walsh Urology , Elsevier, pp. 1834–1846.e1, doi : 10.1016/b978-1-4160-6911-9.00061-x , ISBN 978-1-4160-6911-9 ^ a b Panicker, Jalesh N; Pakzad, Mahreen; Fowler, Clare J (April 2018). ... Videosurgery and Other Miniinvasive Techniques . 14 (4): 476–485. doi : 10.5114/wiitm.2019.85352 . ... "Abnormal Electromyographic Activity of the Urethral Sphincter, Voiding Dysfunction, and Polycystic Ovaries: A New Syndrome?" . BMJ . 297 (6661): 1436–1438. doi : 10.1136/bmj.297.6661.1436 .
-
Silent Stroke
Wikipedia
Sickle cell anemia [ edit ] Transfusion therapy lowers the risk for a new silent stroke in children who have both abnormal cerebral artery blood flow velocity , as detected by transcranial Doppler, and previous silent infarct, even when the initial MRI showed no abnormality. A finding of elevated TCD ultrasonographic velocity warrants MRI of the brain, as those with both abnormalities who are not provided transfusion therapy are at higher risk for developing a new silent infarct or stroke than are those whose initial MRI showed no abnormality. [50] [51] See also [ edit ] Stroke Hypertension Cerebral hypoxia DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) References [ edit ] ^ Miwa, K; Hoshi, T; Hougaku, H; Tanaka, Makiko; Furukado, Shigetaka; Abe, Yuko; Okazaki, Shuhei; Sakaguchi, Manabu; et al. (2010). ... Clinical and Experimental Hypertension (New York, N.Y. : 1993) . 24 (7–8): 669–76. doi : 10.1081/CEH-120015343 . ... "Silent brain infarcts in 755 consecutive patients with a first-ever supratentorial ischemic stroke. Relationship with index-stroke subtype, vascular risk factors, and mortality" . ... "The use of transcranial ultrasonography to predict stroke in sickle cell disease". The New England Journal of Medicine . 326 (9): 605–10. doi : 10.1056/NEJM199202273260905 .
-
Hemochromatosis
Mayo_clinic
These blood tests for iron are best performed after you have been fasting. Elevations in one or all of these tests can be found in other disorders. ... These tests can help identify liver damage. MRI . An MRI is a fast and noninvasive way to measure the degree of iron overload in your liver. ... Are there any brochures or other printed material that I can take with me? What websites do you recommend? Don't hesitate to ask other questions during your appointment.HFE, HAMP, TFR2, HJV, SLC40A1, SLC11A2, TNF, BMP6, CP, HP, BMP2, AKR1D1, B2M, HMOX1, ALAD, HLA-A, TFRC, HLA-H, CYBRD1, FTL, HLA-B, TMPRSS6, APOE, TF, UBE2D1, TIMP1, GNPAT, TLR4, ACO1, MMP2, HEPH, FTH1, EPO, SUCNR1, COX8A, F5, PPP1R11, SOD2, SOD1, SHBG, ADIPOQ, TP53, UROD, ZKSCAN8, PCSK7, S100A9, GDF15, PIEZO1, TRIM31, NUP42, TNMD, SLC46A1, BTBD9, MCIDAS, LINC01194, CCL2, MDM2, UBL3, SERPINA1, GABPA, GAST, FXN, FOXC2, ELANE, CYLD, CTNNB1, CFTR, CELP, CD68, CALR, ARNTL, ALDH2, ALB, ALAS2, GAPDH, GNRH1, GPT, SMAD1, PGF, NMBR, NFE2L2, MPO, MMP3, SMAD7, IREB2, GSTP1, IL10, IL6, IGHG3, IGFALS, IFNG, HLA-F, MFT2
-
Vulvodynia
Mayo_clinic
Although there's little evidence that alternative techniques work, some women get some relief from yoga, meditation, massage and other stress reducers. ... Do you have brochures or other printed material I can have? What websites do you recommend? Don't hesitate to ask other questions.
-
Ectropion
Mayo_clinic
Understanding how other conditions cause ectropion is important in choosing the correct treatment or surgical technique. Treatment If your ectropion is mild, your doctor might recommend artificial tears and ointments to ease the symptoms. ... Do you have any brochures or other printed material that I can take with me? What websites do you recommend? What to expect from your doctor Your doctor is likely to ask you a number of questions, such as: When did you begin experiencing symptoms?TGM1, ABCA12, ABCA1, PLEC, SULT2B1, TNFRSF1B, UROS, XPA, XPC, RNF113A, POLR3A, ABHD5, MBTPS2, FERMT1, ALOXE3, TWIST2, SDR9C7, CYP4F22, MPLKIP, CERS3, PNPLA1, NIPAL4, GTF2H5, ALOX12B, POLH, ERCC6, MMP1, APC, CD28, COL7A1, CTLA4, DDB2, DHODH, ERCC2, ERCC3, ERCC4, ERCC5, LIPN, FOXC2, FLI1, GATA1, GBA, GTF2E2, ITGA6, ITGB4, LRP4, VEGFA, CYP1B1, TIMP2, NF1
-
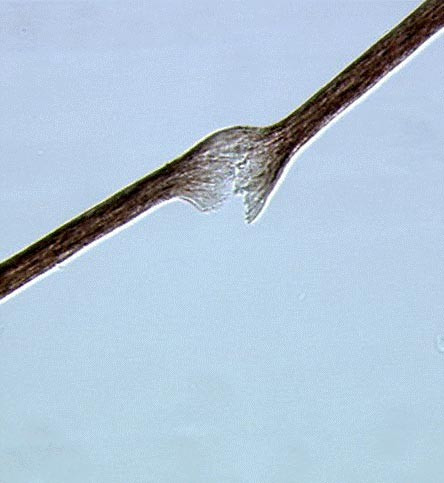
Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Wikipedia
Hair conditioners should be used. [ citation needed ] Prognosis [ edit ] This condition is self-limiting. Improvements in grooming techniques and in environmental conditions will correct the abnormality. ... References [ edit ] MedlinePlus Encyclopedia : Trichorrhexis nodosa External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : L67.0 ICD - 9-CM : 704.2 DiseasesDB : 29680 External resources MedlinePlus : 001449 v t e Disorders of skin appendages Nail thickness: Onychogryphosis Onychauxis color: Beau's lines Yellow nail syndrome Leukonychia Azure lunula shape: Koilonychia Nail clubbing behavior: Onychotillomania Onychophagia other: Ingrown nail Anonychia ungrouped: Paronychia Acute Chronic Chevron nail Congenital onychodysplasia of the index fingers Green nails Half and half nails Hangnail Hapalonychia Hook nail Ingrown nail Lichen planus of the nails Longitudinal erythronychia Malalignment of the nail plate Median nail dystrophy Mees' lines Melanonychia Muehrcke's lines Nail–patella syndrome Onychoatrophy Onycholysis Onychomadesis Onychomatricoma Onychomycosis Onychophosis Onychoptosis defluvium Onychorrhexis Onychoschizia Platonychia Pincer nails Plummer's nail Psoriatic nails Pterygium inversum unguis Pterygium unguis Purpura of the nail bed Racquet nail Red lunulae Shell nail syndrome Splinter hemorrhage Spotted lunulae Staining of the nail plate Stippled nails Subungual hematoma Terry's nails Twenty-nail dystrophy Hair Hair loss / Baldness noncicatricial alopecia : Alopecia areata totalis universalis Ophiasis Androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness) Hypotrichosis Telogen effluvium Traction alopecia Lichen planopilaris Trichorrhexis nodosa Alopecia neoplastica Anagen effluvium Alopecia mucinosa cicatricial alopecia : Pseudopelade of Brocq Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia Pressure alopecia Traumatic alopecia Tumor alopecia Hot comb alopecia Perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens Graham-Little syndrome Folliculitis decalvans ungrouped: Triangular alopecia Frontal fibrosing alopecia Marie Unna hereditary hypotrichosis Hypertrichosis Hirsutism Acquired localised generalised patterned Congenital generalised localised X-linked Prepubertal Acneiform eruption Acne Acne vulgaris Acne conglobata Acne miliaris necrotica Tropical acne Infantile acne / Neonatal acne Excoriated acne Acne fulminans Acne medicamentosa (e.g., steroid acne ) Halogen acne Iododerma Bromoderma Chloracne Oil acne Tar acne Acne cosmetica Occupational acne Acne aestivalis Acne keloidalis nuchae Acne mechanica Acne with facial edema Pomade acne Acne necrotica Blackhead Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei Rosacea Perioral dermatitis Granulomatous perioral dermatitis Phymatous rosacea Rhinophyma Blepharophyma Gnathophyma Metophyma Otophyma Papulopustular rosacea Lupoid rosacea Erythrotelangiectatic rosacea Glandular rosacea Gram-negative rosacea Steroid rosacea Ocular rosacea Persistent edema of rosacea Rosacea conglobata variants Periorificial dermatitis Pyoderma faciale Ungrouped Granulomatous facial dermatitis Idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma Periorbital dermatitis SAPHO syndrome Follicular cysts " Sebaceous cyst " Epidermoid cyst Trichilemmal cyst Steatocystoma simplex multiplex Milia Inflammation Folliculitis Folliculitis nares perforans Tufted folliculitis Pseudofolliculitis barbae Hidradenitis Hidradenitis suppurativa Recurrent palmoplantar hidradenitis Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis Ungrouped Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex Acroosteolysis Bubble hair deformity Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis Erosive pustular dermatitis of the scalp Erythromelanosis follicularis faciei et colli Hair casts Hair follicle nevus Intermittent hair–follicle dystrophy Keratosis pilaris atropicans Kinking hair Koenen's tumor Lichen planopilaris Lichen spinulosus Loose anagen syndrome Menkes kinky hair syndrome Monilethrix Parakeratosis pustulosa Pili ( Pili annulati Pili bifurcati Pili multigemini Pili pseudoannulati Pili torti ) Pityriasis amiantacea Plica neuropathica Poliosis Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome Setleis syndrome Traumatic anserine folliculosis Trichomegaly Trichomycosis axillaris Trichorrhexis ( Trichorrhexis invaginata Trichorrhexis nodosa ) Trichostasis spinulosa Uncombable hair syndrome Wooly hair nevus Sweat glands Eccrine Miliaria Colloid milium Miliaria crystalline Miliaria profunda Miliaria pustulosa Miliaria rubra Occlusion miliaria Postmiliarial hypohidrosis Granulosis rubra nasi Ross’ syndrome Anhidrosis Hyperhidrosis Generalized Gustatory Palmoplantar Apocrine Body odor Chromhidrosis Fox–Fordyce disease Sebaceous Sebaceous hyperplasia
-
Eruptive Vellus Hair Cyst
Wikipedia
The cysts appear similar clinically to steatocystoma multiplex , as well as acneiform eruptions and milia . Therapeutic techniques that are safe and effective are rare, with incision and drainage being the primary form of treatment when sporadic regression does not occur. [3] It was first described in 1977. [4] Contents 1 Signs/symptoms 2 Cause 3 Diagnosis 3.1 Associations 4 Treatment 5 See also 6 References 7 Further reading Signs/symptoms [ edit ] This section is empty. ... PMID 21958358 . v t e Disorders of skin appendages Nail thickness: Onychogryphosis Onychauxis color: Beau's lines Yellow nail syndrome Leukonychia Azure lunula shape: Koilonychia Nail clubbing behavior: Onychotillomania Onychophagia other: Ingrown nail Anonychia ungrouped: Paronychia Acute Chronic Chevron nail Congenital onychodysplasia of the index fingers Green nails Half and half nails Hangnail Hapalonychia Hook nail Ingrown nail Lichen planus of the nails Longitudinal erythronychia Malalignment of the nail plate Median nail dystrophy Mees' lines Melanonychia Muehrcke's lines Nail–patella syndrome Onychoatrophy Onycholysis Onychomadesis Onychomatricoma Onychomycosis Onychophosis Onychoptosis defluvium Onychorrhexis Onychoschizia Platonychia Pincer nails Plummer's nail Psoriatic nails Pterygium inversum unguis Pterygium unguis Purpura of the nail bed Racquet nail Red lunulae Shell nail syndrome Splinter hemorrhage Spotted lunulae Staining of the nail plate Stippled nails Subungual hematoma Terry's nails Twenty-nail dystrophy Hair Hair loss / Baldness noncicatricial alopecia : Alopecia areata totalis universalis Ophiasis Androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness) Hypotrichosis Telogen effluvium Traction alopecia Lichen planopilaris Trichorrhexis nodosa Alopecia neoplastica Anagen effluvium Alopecia mucinosa cicatricial alopecia : Pseudopelade of Brocq Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia Pressure alopecia Traumatic alopecia Tumor alopecia Hot comb alopecia Perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens Graham-Little syndrome Folliculitis decalvans ungrouped: Triangular alopecia Frontal fibrosing alopecia Marie Unna hereditary hypotrichosis Hypertrichosis Hirsutism Acquired localised generalised patterned Congenital generalised localised X-linked Prepubertal Acneiform eruption Acne Acne vulgaris Acne conglobata Acne miliaris necrotica Tropical acne Infantile acne / Neonatal acne Excoriated acne Acne fulminans Acne medicamentosa (e.g., steroid acne ) Halogen acne Iododerma Bromoderma Chloracne Oil acne Tar acne Acne cosmetica Occupational acne Acne aestivalis Acne keloidalis nuchae Acne mechanica Acne with facial edema Pomade acne Acne necrotica Blackhead Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei Rosacea Perioral dermatitis Granulomatous perioral dermatitis Phymatous rosacea Rhinophyma Blepharophyma Gnathophyma Metophyma Otophyma Papulopustular rosacea Lupoid rosacea Erythrotelangiectatic rosacea Glandular rosacea Gram-negative rosacea Steroid rosacea Ocular rosacea Persistent edema of rosacea Rosacea conglobata variants Periorificial dermatitis Pyoderma faciale Ungrouped Granulomatous facial dermatitis Idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma Periorbital dermatitis SAPHO syndrome Follicular cysts " Sebaceous cyst " Epidermoid cyst Trichilemmal cyst Steatocystoma simplex multiplex Milia Inflammation Folliculitis Folliculitis nares perforans Tufted folliculitis Pseudofolliculitis barbae Hidradenitis Hidradenitis suppurativa Recurrent palmoplantar hidradenitis Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis Ungrouped Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex Acroosteolysis Bubble hair deformity Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis Erosive pustular dermatitis of the scalp Erythromelanosis follicularis faciei et colli Hair casts Hair follicle nevus Intermittent hair–follicle dystrophy Keratosis pilaris atropicans Kinking hair Koenen's tumor Lichen planopilaris Lichen spinulosus Loose anagen syndrome Menkes kinky hair syndrome Monilethrix Parakeratosis pustulosa Pili ( Pili annulati Pili bifurcati Pili multigemini Pili pseudoannulati Pili torti ) Pityriasis amiantacea Plica neuropathica Poliosis Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome Setleis syndrome Traumatic anserine folliculosis Trichomegaly Trichomycosis axillaris Trichorrhexis ( Trichorrhexis invaginata Trichorrhexis nodosa ) Trichostasis spinulosa Uncombable hair syndrome Wooly hair nevus Sweat glands Eccrine Miliaria Colloid milium Miliaria crystalline Miliaria profunda Miliaria pustulosa Miliaria rubra Occlusion miliaria Postmiliarial hypohidrosis Granulosis rubra nasi Ross’ syndrome Anhidrosis Hyperhidrosis Generalized Gustatory Palmoplantar Apocrine Body odor Chromhidrosis Fox–Fordyce disease Sebaceous Sebaceous hyperplasia
-
Maladaptive Daydreaming
Wikipedia
Find sources: "Maladaptive daydreaming" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR ( December 2020 ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message ) Maladaptive daydreaming , also called excessive daydreaming, is a proposed diagnosis of a disordered form of dissociative absorption associated with excessive fantasy that is not recognized by any major medical or psychological criteria. ... "Maladaptive daydreaming as a new form of behavioral addiction" . Journal of Behavioral Addictions. doi : 10.1556/2006.7.2018.95 . ... Retrieved 2020-07-17 . ^ Singer, J. L. (1966) Daydreaming . New York, NY: Random House ^ Somer, E.; Somer, L.; Jopp, S.D. (9 June 2016). ... (August 2018). "Maladaptive daydreaming as a new form of behavioral addiction" . Journal of Behavioral Addictions . 7 (3): 838–843. doi : 10.1556/2006.7.2018.95 . ... PMID 29867613 . ^ Bershtling, O., & Somer, E. (27 August 2018). "The Micro-Politics of a New Mental Condition: Legitimization in Maladaptive Daydreamers' Discourse" .
-
Parkinson's Disease
Mayo_clinic
Clinical trials Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition. ... An occupational therapist can show you techniques that make daily life easier. If you are having trouble talking, a speech therapist may be able to help. ... You may modify most poses to fit your physical abilities. Alexander technique. This technique — which focuses on muscle posture, balance and thinking about how you use muscles — may reduce muscle tension and pain. ... Having a dog or cat may increase your flexibility and movement and improve your emotional health. Relaxation techniques. These practices help lower your blood pressure, reduce your heart rate and improve muscle tone. ... Are there any brochures or other printed material that I can take home with me? What websites do you recommend? In addition to the questions that you've prepared to ask your care team, don't hesitate to ask questions that occur to you during your appointment.SNCA, PINK1, DRD2, TH, DDC, MAOB, ATP13A2, PRKN, SLC18A2, PARK7, DRD1, IGF1R, LRRK2, BST1, MAPT, GBA, GAK, HLA-DRA, CYP2D6, CP, PPARGC1A, TNF, SOD2, SOD1, BDNF, ABCB1, VPS35, IL6, NOS1, PARK16, MTHFR, GDNF, GFAP, TMEM230, MAOA, DNM1L, GSTM1, HFE, HMOX1, HSPA9, SLC6A3, DDIT4, GSTP1, CYP2E1, MAP3K5, NGF, AIF1, NQO1, IGF2, GSTA4, TRPM2, IGF2R, INS, HLA-DRB5, GPX1, TCL1B, MIR181C, MTA1, ENO2, BAG5, MAG, FCER2, HGF, HSPA1A, FBP1, INSR, HSPA8, NCAPG2, HBG1, RPL23A, GSK3B, HSPA4, NR4A2, RPS8, COL19A1, TALDO1, SLC30A10, DRAXIN, PITX3, CNTNAP2, NECTIN2, IL1B, ADARB2, CEACAM6, TFAM, MAP2, EDN1, FGB, KCNJ4, RPL6, RPL14, SLC2A14, OPTN, SPR, TWNK, ATG7, GRK5, HTR1A, PENK, GDF5, PPP1R9B, ADH7, DLG4, ABL1, HSF1, LEP, PTN, HSPD1, ND3, GRK6, DLG1, DBN1, ADCY5, HCN3, CCN2, FEZ1, APOE, FASLG, COX10, GJC2, RRN3, RIT2, GCH1, ARPC3, GRK3, GRK2, STK39, LAMP3, SLC41A1, CCDC62, MCCC1, GPNMB, DGKQ, TMEM175, VPS13C, STH, HLA-DRB1, SIPA1L2, CTSB, SREBF1, HIP1R, NUCKS1, MAPT-AS1, RAI1, BCKDK, BIN3, RREB1, TCEANC2, TPM1, PAM, DLG2, ITPKB, MMRN1, KANSL1, FAM47E, ITGA8, LHFPL2, SH3GL2, LMNA, FAM47E-STBD1, NSF, INPP5F, TMC3-AS1, CCDC82, DRD3, SLC50A1, DSCAS, MUL1, RABEP2, NOS2, MANF, ADORA2A, WBP1L, AIMP2, PLPPR1, PTEN, GBF1, EEF1A2, DNAJC1, BAP1, NEFL, SQSTM1, PIP4P2, EIF4G1, PLA2G6, GPR65, MX2, ESR1, PDSS2, NFE2L2, TBC1D5, LINC02224, SMUG1, HTT, SIRT1, TARDBP, SF3B1, GSTT1, LAMC2, GRM5, LRRK2-DT, FRY, FBXO7, GRIN2B, RNF19A, GRN, LINC02451, ACHE, SYNM, RAB29, AHSA1, IL1A, IL10, IGFALS, IGF1, CIT, ITIH1, SIRT2, MCF2L, RET, LOC107987479, TBC1D9, MPHOSPH6, SYT11, TNK2, GPR37, GIGYF2, POLDIP2, MAP4K4, SNCAIP, IP6K2, FYN, MTOR, ATXN3, SYT17, FMR1, FGF20, DCUN1D1, GRAP2, TREM2, MPZ, TET2, CNNM2, GABPA, CHCHD2, GAPDH, ZNF646, GBAP1, GCG, LINC02210-CRHR1, LINC02471, CTNNA3, REM1, HTRA2, HPGDS, GLP1R, CTIF, LY6E, PLEKHM1, LRP2, KCNIP4, ATXN2, ZP3, PARK3, TPTE2P6, PM20D1, LINC02210, MAPK1, TP53, TPO, LINC01121, SLCO6A1, DPY19L2P3, CA8, CDNF, TYW1B, APP, POLG, CNTN1, COL5A2, COL13A1, KLHDC1, COMT, BORCS7, AGAP1, CRHR1, CRK, PIK3CD, CRP, RAB39B, GSTK1, TLR4, CHM, CASP3, PIK3CG, PRSS53, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, TMC3, ALDH1A1, C9orf72, NAT2, ASXL1, PARK10, SPTSSB, SPPL2C, CDH8, CDK5, PRNP, MCIDAS, MDGA2, TMEM229B, PTGS2, CBLL2, THY1, CNKSR3, CASC16, TMPRSS9, SNCA-AS1, NLRP3, RPA2P1, MAPK14, NDUFAF2, UCHL1, SMPD1, YWHAE, BCHE, ALDH2, BCL2, SCN2A, CCL2, AKT1, LINGO1, WNT3, VDR, SLC45A3, CYP17A1, MAPT-IT1, UNC13C, SNCG, CCNT2-AS1, ADAMTSL1, CTSD, TPTE2, BORCS7-ASMT, ZNF165, PREP, SLC2A13, PON1, SNCB, BRINP1, CSF2, ACE, PAFAH1B1, ZSCAN16-AS1, NRTN, CAB39L, DBH, VEGFA, HCRT, GAD1, FUS, SLC11A2, CXCL8, SLC6A4, PARP1, CRMP1, DENR, PPARG, ULK1, DNAJC13, P2RX7, REG1A, IFNG, UTRN, MIR133B, DAPK2, LAMP2, APLN, CTNNB1, TYR, HIF1A, ESR2, PAEP, HNMT, CYP1A2, MC1R, EHMT1, LRRK1, ACMSD, CALB1, USP24, NUP62, CASP9, GRIN2A, TSPO, S100B, CAT, LMX1A, TAC1, GTF2H1, UBE2K, SIRT3, TLR2, LINC01672, DYRK1A, CNR2, ADRB2, CNR1, PDE10A, SYNJ1, HSP90AA1, KHDRBS1, SLC1A2, TPPP, ANG, DNAJB1, ZGLP1, CHRNA4, RMDN3, SCARB2, GIP, LILRB1, DCTN4, PSPN, ROS1, TGFB1, ACTB, SERPINA3, DECR1, IL17A, GRM4, PSPH, CRYZ, STX1B, HTR2A, SLC6A2, BPIFA2, STXBP3, MSMB, MPO, AGER, MAPK8, MEF2D, LMX1B, RIDA, HMGB1, CAV1, CXCR4, CYBB, TOMM40, POTEKP, CCR2, REST, MIR433, AQP4, AGFG1, POTEM, SIGMAR1, ACOT7, ACTG1, MIR34B, ZFPM1, RPS27A, RMDN2, CLOCK, FHL5, NMS, COX2, GSTO2, SUCLA2, SYBU, UBC, BECN1, CST3, CYP1A1, NTS, NNMT, NTF3, DRD4, TFEB, PPP1R2C, RMDN1, MMP9, NQO2, MIR221, TBP, ACTG2, ACTBL2, STAT3, CHMP2B, MFN2, CHCHD10, GSTM2, DNAJC6, GLA, CCK, PLK2, NEDD4, NPC1, VCP, PICALM, NGFR, SYP, SEPTIN4, TRPV1, PTPA, NPY, XBP1, LCN2, TFRC, MAPK3, SKP1, AKR1A1, PRDX2, GDF15, GSTO1, MMP3, LAG3, KLK6, OGA, PSEN1, DNAJB6, PHOX2B, CDK5R1, CXCL12, TCF3, CX3CL1, A2M, REN, CREB1, SNHG1, MIR34A, MIR205, DNM3, MALAT1, NEAT1, GLRX, RLS1, DNAJB1P1, LINGO2, ZNF746, CUX1, SV2C, CYP2D7, DMRT1, NIF3L1, ELAVL4, FKBP1A, ELK3, EPHB1, SLC2A9, FGF2, PTK2B, FABP3, ATF4, RHOT1, MIR4697, HP, HSPA5, ADCYAP1, ICAM1, APOA1, IAPP, CX3CR1, MAP1LC3B, WNT1, AGT, CYP2B6, VIPR2, OGDH, OGG1, VDAC1, APRT, NRGN, P2RX3, VCAM1, AGTR1, UCP2, CTSL, PEBP1, UBB, PINK1-AS, PROKR2, TMEM163, RAB10, NRF1, ADH1B, MOK, RAC1, NR1I2, PARL, F2, ACP3, RAB1A, EPHB2, MARK2, NDUFV2, TRPC1, NEDD9, PVALB, RTN4R, RIC3, HSD3B7, DNMT1, ADH1C, DNAJC5, YWHAZ, TSC2, CLU, PCNA, PACRG, PSMC4, PON2, PPARA, PPARD, MIR29C, PRKAA1, HOTAIR, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, AVP, SMN2, SMN1, PRKAR2A, PRKD1, SGCA, MIR135B, ASAH1, ARNTL, WASH6P, FAS, SKIL, APEX1, MIR200A, SEPTIN5, ATXN8OS, SIAH1, PDE4A, CHRM3, PDYN, TIMP2, ALB, CFP, CDKN2D, CDKN2A, CD38, MIR19B1, WASHC1, USP40, APAF1, PIN1, CASP1, CALCA, SST, PNOC, MIR195, TFR2, IL4, DCTN1, DCDC2, FKBP1AP2, FOXA2, TRAP1, ATG12, GAP43, GRIA2, FKBP1AP3, FKBP1AP4, PRRX2, HMOX2, FTL, MSC, MEFV, FKBP4, ISYNA1, GPX4, NCS1, PPIG, FOXO1, LSAMP, TLR9, LGALS4, MACF1, LAMP1, LRPPRC, ATG5, GRIN2D, MFAP1, BAG3, LDLR, LRP10, GRM2, IREB2, KEAP1, COQ2, FAF1, SBNO2, VPS41, SGSM3, NOX1, SEMA5A, IL1RN, PSIP1, FKBP1AP1, TOMM20, CYP4F3, SLC40A1, PTPN22, GLUD2, SBNO1, IL18, MIR27A, MIR185, MIR137, SNAP25, MIR132, MIR126, TAL1, MIR29A, SP1, SRY, PPIF, MIR204, SPG7, SPP1, FBXO8, MIR21, HDAC6, MIR212, MIR223, USP15, MIR22, RNF11, SOAT1, SNRPF, SNRNP70, SOD3, BDNF-AS, BACE1, FST, ARL6IP5, NLRP1, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, SCD, TXNIP, MGLL, CHP1, MIR4519, HRH3, NES, OPN1MW3, RIPK3, RAB32, TMED10, RNASE4, RNASE1, MTCO2P12, PRSS21, TRIM27, RFC1, LINC02605, H3P13, RENBP, CCL5, P2RX2, ATP6AP2, ABCA7, SMARCA1, CD2AP, SLC22A1, SLC18A3, SRRM2, MIR326, SLC16A1, SLC8A1, MIR494, MIR505, ARC, UCA1, RNF41, MPRIP, HMGXB3, ST3GAL2, MIR563, SI, SHMT2, TRIM32, SHMT1, OPN1MW2, SGTA, SIGLEC7, SPHK1, ERCC6L2, TET1, P2RX6, AXIN2, NEUROG2, NOD2, FBRS, HS1BP3, DDRGK1, SLC52A2, PANK2, MAP3K13, NELFE, H3C1, RAB7A, XPR1, COASY, ZNF184, NDFIP1, EGLN1, MFHAS1, GPR55, KLF4, RNF146, HIVEP3, H3C4, XIST, TMED9, TRPM7, CISD1, RIPK1, DNAJC12, B3GALT4, H3C7, PDE8B, KHSRP, SLC17A6, MGAM, STBD1, H3C3, NOL3, SEMA6A, H3C2, H3C10, H3C12, TMEM106B, H3C8, H3C11, H3C6, TRIB3, C19orf12, SESN2, TCOF1, TIMP3, TRAF2, MZB1, SESN3, GAL, TNFRSF1B, PWAR1, TRAT1, PLB1, TLN1, HDAC4, ATG13, CD200R1, TAS2R13, BMS1, RMC1, EIF2B3, MCAT, MTIF3, ANKK1, PGP, RAB7B, HCAR2, TRH, TTR, PPP1R1B, IL23A, SYVN1, GPR88, HOMER1, SHC3, VIM, ATAD1, MIDN, SELENOT, ROCK2, SLC25A27, DNER, TPH2, USP1, SCLY, UCHL3, FTMT, OPN4, UBE2L3, TXNRD3, VPS26A, CARD16, TXN, TGM2, TGFB2, IDUA, CHRNA5, HK2, LGALS1, BAG1, PLA2G1B, F9, HLA-C, LBP, E2F1, BAX, CLK1, NCL, HCN2, F2R, NR4A1, FOXA1, NDUFA1, NDUFA2, NDUFS3, PLD2, HK1, HOXD13, TOR1A, COL17A1, COL11A2, PPID, FCGR3A, POU2F1, POMC, POLB, ARSA, ASCL1, LGALS3, HCLS1, PLXNA2, LIFR, FAAH, ATM, ATOX1, NRG1, ATP1A3, BNIP3L, NDUFS4, PDIA3, CBS, P2RY2, IL7, KCNJ6, P2RY1, P2RX5, P2RX4, P2RX1, OPRL1, CCKAR, KDR, GPR143, NUCB2, IL13RA1, ISG20, ITGAM, NTRK2, NT5E, CD19, IL2RB, IL2RA, EGF, PCP4, HRES1, NEFM, CHAT, CTSC, ERG, CEBPB, PDC, NFKB1, EGR1, CAST, HTC2, CACNA1A, NHS, HTR1B, KRT7, IDE, CAPN1, NOS3, COX8A, ELAVL2, FRAXE, CBLIF, RBM3, PSMB8, DDIT3, CD200, DAPK1, CSF3, PSEN2, APOD, PSAP, CYTB, GPX7, APOB, DNMT3B, MFGE8, ADCYAP1R1, FXN, GLB1, PTBP1, GLUL, GRP, FTH1, PTPRC, ALOX5, AKR1B1, MSRA, ADH4, MEF2C, GAD2, AHR, GALC, MS, DPEP1, FOSL2, ND1, ATF2, CYP3A4, DRD5, MIF, ACACA, MTRR, NR3C1, MTR, DPYSL2, MAPK10, DPP4, KLK3, ND5, MRC1, FOXO3, OPN1MW, GC, CD55, ND2, CRY1, SLC39A8, FSD1L, SNX6, CYP27B1, KREMEN1, TNMD, DLGAP3, EHHADH, ANO3, GBA2, CYP3A5, TINAGL1, MAK16, DTNBP1, EIF2B1, NEUROD6, LSM2, ATP13A4, MINDY4, DAPK3, TLCD3B, FKBP10, EIF4E, PROK2, EIF4EBP1, HAPLN2, HAMP, LGR6, ACE2, EIF4A2, LIN28A, APH1B, PAGR1, DOCK3, SLC8B1, ASPSCR1, ELOVL7, FA2H, DHRS11, BRCC3, FSD1, CWC22, DHDDS, XYLT2, DVL1, DUSP8, TNFAIP8L2, MCPH1, PEAK1, NEIL1, RTL10, ATN1, DUSP2, DUSP26, DMPK, DLD, TIMM8A, SLC25A28, TFB2M, MS4A6A, EGFR, MEGF8, HIF3A, RAB1B, CSMD1, DAXX, DBI, DCC, DCN, TAS1R2, ZNF436, PDIA2, EEF2, RAPH1, TNKS2, EEF1A1, FYCO1, REL, USP37, FBXO42, FPR2, WWOX, INPP5K, IL17D, PANK1, FN1, PPIL3, IMMTP1, AFF2, FLNB, H2BS1, FKBP5, TREM1, WNT4, FKBP3, ATG16L1, FKBP2, UGT1A9, FKBP1B, FGG, MARCHF5, FGF13, FGF9, FGF8, NDE1, FGF1, GPC4, FDXR, ANKHD1, FCGR3B, VPS29, TRAPPC2L, NUB1, FKBP7, GDF1, DPP7, PSAT1, UBQLN2, UBQLN1, SLC39A2, OBP2A, VSX1, NOX4, ASAP1, GATA2, SOST, TMED7, ST8SIA3, NMD3, POLR1D, GALNS, TFB1M, B4GALNT1, TRIM17, GABBR1, TRAPPC4, G6PD, GAST, HSD17B7, FRAXA, SIRT7, RAB6B, PPIL1, HEATR3, OXR1, SH3RF1, PELI1, EPRS1, NPDC1, TCIM, PNO1, EPO, PAK6, ARNTL2, ZGPAT, RGMA, EPHX2, CASS4, TIGAR, EPHX1, PGLYRP4, ENDOG, THAP1, ANKRD50, VN1R1, MCOLN1, CYP20A1, NDRG2, PPM1H, ZNF512B, NLN, XPO5, GPR158, NUFIP2, NCEH1, ELF4, ELAVL1, ERBB2, ERBB3, CTNNBL1, ZNF253, MTPAP, FCGR2B, MAP1S, FASN, RCBTB1, ADI1, QRSL1, F12, FBXW7, CHDH, YOD1, TRPV6, GPRC5D, SAGE1, SMPD3, F2RL1, SOX6, AMBRA1, EZH2, MECOM, ARFGAP1, MBD5, VPS11, ESRRG, PSENEN, GPRC5C, ERN1, MYO5C, MYDGF, MAP1LC3A, CRY2, EBPL, GET3, MIR342, MIR335, MIR331, ASIP, MIR324, MIR148B, GPR166P, SPAG11A, VN1R17P, ATP5F1B, ATP7A, ATR, MIR96, MIR34C, PLF, MIR425, FBXO48, MIR410, ARRB1, MIR520D, ARR3, MIR486-1, ARG1, POU5F1P3, ARF3, AR, POU5F1P4, CCDC154, NORAD, LINC00273, AQP9, ADGRB1, MIR320A, MIR30E, MIR19A, MIR107, CA12, CA2, MIR134, C4B, MIR142, MIR144, MIR15B, MIR181A2, C4A, MIR183, C1R, MIR190A, KLF9, BRAF, MIR30C2, DST, BMX, BMP2, BMI1, MIR214, MIR217, BGLAP, CFB, MIR222, BCR, MIR27B, BCL2L1, MIR30A, MIR30C1, CXADRP1, AQP1, MIRLET7D, PGR-AS1, LOC102724334, MIR8061, LOC101928100, ADORA1, UCHL1-AS1, TLE5, APLNR, OCM, ERVW-4, MIR4639, ALAD, MICOS10-NBL1, AMFR, BIN1, CBSL, HAGLROS, TP53COR1, APOA1-AS, SNHG14, ADAM10, ADA, ACO2, SIRT1-AS, BUB1B-PAK6, ACO1, ASIC2, LOC110366354, LOC110806262, AOC1, ABCA1, H3P17, MIR3143, ANGPT1, TMED7-TICAM2, PLIN4, MIR545, MIR542, PARK12, MIR561, MIR579, MIR590, MIR599, MIR613, MIR625, MIR626, MIR634, ATXN8, POTEF, APOC3, MIR671, C4B_2, XIAP, VTRNA2-1, MIR543, APC, MUPP, APBB1, ANXA5, ANK2, ANK1, CD24, MIR1224, MFT2, ANGPT2, TIMM23, MIR100, CALB2, SPZ1, KLF6, CCR7, ABCC2, CNGA1, CNTF, GPR139, MTFMT, CPOX, CHI3L1, CRAT, EXOSC6, MRGPRX4, MRGPRX3, RAB3IP, NUS1, GNPDA2, CCR5, GPR151, CCR3, PXDNL, CMA1, SIRPA, STK35, CACUL1, CLN3, CHRNB4, ZFP90, CHRNB3, ZNF569, GLIS1, PDIK1L, FBXO41, PGLYRP3, PGLYRP2, EEF2K, PLXNA4, CYP2C9, USP30, PTPN5, ORAI1, CYP2C19, CYP1B1, PPIL4, DNAJC14, CYLD, CHRFAM7A, CYC1, MCU, IL33, TRIM41, DEPDC7, CRYAB, CXADR, MTDH, CTSZ, CTSK, PRDM6, CTRL, CADPS2, CTNS, CSNK1D, TGS1, NACC1, TRIM9, CSF1R, CSF1, CHIT1, CEL, HSP90AB2P, TMED10P1, CASR, GOLGA6A, CPP, RSPO2, CAV2, RUNX1, PPIL6, SHOC1, FBXW12, ZNF763, LYPD5, CCKBR, CCND3, OR10A4, NANOS3, HSD17B13, PFN3, CASP8, CASP7, SEPTIN14, AMIGO2, HCN1, TICAM2, CASP6, NDUFS7, CALR, CALD1, CALCR, TMEM189, TMEM189-UBE2V1, UOX, CD14, SELENOH, MRGPRX1, ARID2, CDKN1B, CDKN1A, FSIP1, CDK6, CDC42, TMPRSS6, OXER1, CDK1, DDX53, CDA, CD69, RHOV, CD59, CD47, MLKL, GPX6, CDCP2, PRSS55, CD44, CD36, TPCN2, ZUP1, GPRC6A, CD34, IL27, LCLAT1, EBF3, PHYHD1, CD28, GK5, HOOK2, GPR3, USP25, UMOD, VHL, VGF, OPA1, OPRM1, UQCRH, UQCRFS1, UCP1, NPPC, UCN, P2RY6, P4HB, UBTF, UBE3A, UBE2V1, OMP, VIP, VIPR1, VSNL1, WAS, WFS1, NUCB1, WNT5A, NTRK1, NTF4, XK, XRCC1, XRCC3, YWHAG, YWHAH, NPTX2, CNBP, PRDX1, PAH, SERPINE1, TRAF6, PECAM1, TKT, PDR, PDPK1, PDHA1, TM7SF2, PDE1B, PDE7A, PDCD2, PDB1, TPT1, CRISP2, NR2C1, HSP90B1, PCNT, TYROBP, PCMT1, TRPC6, SERPINA5, PAX4, PHLDA2, TST, PAWR, TUBA4A, TUFM, TNFRSF4, REG3A, TXNRD1, TYMS, PAK1, ZSCAN21, NPPB, EIF2S2, MYOC, PEA15, MYL4, EIF3A, HSD17B6, TP63, PSMG1, USO1, NPPA, PRKRA, CASK, NAGLU, PDXK, NBL1, LGR5, MYD88, SNX3, MYCN, MYC, TNFRSF14, FADD, SNAP23, RGS9, MTX1, FGF18, CCN6, TRNL1, ASAP2, MTTP, MTNR1B, FUBP1, EIF2B4, CHST1, DGKD, NUBP1, SLC14A2, MAP3K12, PRDM2, LRP8, TUBA1A, NPM1, NPAS2, NOTCH4, ST8SIA4, NOTCH2, LAP, NKTR, CSRP3, FGF23, SLC7A5, MLRL, CUL1, SYN3, GTPBP6, NFKBIA, AXIN1, NFKB2, FZD4, NFE2L1, NFE2, NEK1, NEFH, NEDD8, NDN, NR0B2, NCK2, SERPINF1, TIMP1, TIAL1, PSMC1, PSMA2, SGK1, SELENOP, SELE, SEL1L, PSMB9, PSMD11, PER1, CCL3, SCN9A, SCN8A, TAS2R38, SCN1A, PTGER2, PSG5, SHH, HTRA1, KLK7, PRSS2, LGMN, PROS1, SLC1A1, PROP1, SLC1A6, SLC2A1, SLC2A4, PROC, PRL, MAP2K7, SLC6A8, SLC6A11, PTGER4, PTH, SATB1, ROCK1, RB1, RAP2B, RAP1B, RAN, RGS2, RGS4, RGS10, RHEB, RAD51B, RING1, RAD51, RAB6A, RNH1, RNY1, RAB3B, SAT1, QDPR, PTX3, RPL32, RPS6, RPS6KB1, PTPRA, RRAS, PTPN6, RTN1, RXRA, S100A9, S100A10, QSOX1, SALL1, SLC6A13, SLC7A1, MAP2K6, DYNLT3, CDKL5, STXBP1, SERPINF2, ABCC8, PLEK, PLG, ADAM17, TACR1, TAF1, PLD1, TAP1, CNTN2, PLAG1, PKD1, PITX2, STAT4, TEF, TMBIM6, TF, PIK3C2B, TFDP2, PIGC, SERPINA1, PHF1, SLC25A3, PHB, PGK1, THAS, THBS1, THOP1, STIM1, PLK1, SLC8A3, PPP3R1, SLC11A1, MAP2K2, PRKCG, SLC19A1, SLC20A2, PRKCD, SLC22A5, PRKAR1B, PRKAR1A, PRKACB, PRKACA, SMPD2, SMS, PPY, PPP4C, STAT1, PPP2R2B, PPP1R1A, PPBP, MED1, POU5F1, SORL1, SOX2, SPN, PODXL, PNMT, SPTBN1, PRRX1, FXYD1, ST13, EIF2B2, ENDOU, GFPT1, SARM1, HLA-A, HLA-B, ACSBG1, HLA-DQB1, KDM6B, CUL9, SMG1, GSR, TNIK, FAIM2, HLF, HNF4A, HNRNPA1, SEPHS1, SATB2, NEDD4L, HEXA, ZNF629, NCSTN, HDAC2, DICER1, SIRT5, HDAC1, HCRTR1, TPSD1, HAS2, ATP1B4, HSD17B10, ABCA5, TRAM1, GTF2H4, TLX2, RPH3A, HPD, RER1, MRPS30, JTB, PNPLA6, SUGT1, PAPOLA, RALBP1, PRDX3, IKBKB, IGHG3, COPS5, IMMT, RAB35, IFNAR1, STMN2, HTR6, DLGAP4, SLC2A6, PTGDR2, HSPB2, HSPB1, COPE, ECD, FKBP9, HSPA1L, PDAP1, TUSC2, GABARAP, HSPA1B, GABARAPL2, RRAS2, ZFYVE26, SEC14L2, MBD2, PDE7B, GLI1, RBMS3, SIT1, GLI2, GPR78, AGO2, CACYBP, LPAR3, CACNG5, B3GAT1, GLS, GLUD1, GNAL, ACAD8, TOX3, GJB2, GJB1, MAT2B, TOR2A, GHSR, GIT1, ACAD9, FLVCR1, MCTS1, DBNL, HIPK2, GHR, SETD2, SCG3, PYCARD, TBK1, ATP2C1, GNAQ, SEC22A, ARIH1, GSPT1, PDSS1, OPN3, MKRN2, GRM8, GRM3, LDOC1, PPP1R15A, SLC7A11, PPIL2, MAFF, GRIN2C, ATXN10, NOCT, TPSG1, CHORDC1, PRDX5, BACE2, PART1, GRIN1, GRIK3, GORASP2, FFAR1, GPER1, MCHR1, GPR17, UTS2R, FBXO2, FBXO9, GPR6, IL9, PPP1R13L, IL13, MICD, MAP3K3, RAB8A, PTGES, MGMT, TMEM59, NPEPPS, TBX4, PPP1R17, MAPK8IP1, MIP, MAP3K11, SH3BP5, KMT2A, AFF1, DNAJB9, ISG15, MCL1, HERPUD1, MBP, SART3, HDAC9, SETD1A, CLSTN3, PHACTR2, MATN3, MAS1, MARK1, PIEZO1, MAP6, MAP1B, CD180, AFDN, NR3C2, MME, MSX1, MTHFD1, NUDT1, USP13, MT3, HSPB3, PGLYRP1, MT2A, SOCS3, MT1E, ERDA1, MT1B, MT1A, PIAS2, USP10, AIFM1, COX5A, OSMR, SLC16A7, SLC33A1, VAPB, MOG, MMP8, GPR37L1, MMP7, MMP2, TAOK2, MMP1, LONP1, KL, ADIPOQ, LTF, LTA, LRPAP1, NXF1, SPRY1, STUB1, DNAJA2, KLC1, DLEU1, KNG1, CCL26, KLK2, NPM3, NDRG1, SPAG11B, UBAC1, KIF2A, KCNMA1, CIB1, CALCOCO2, PROCR, KCNA5, ARFGEF1, NPC2, SCGN, JUP, TRIM3, ITPR3, YKT6, ITPR1, ITGB2, PTGES3, GJB6, CPLX1, KRT10, STX6, HEPH, LPA, PSMD6, SV2B, SRGAP3, RBM19, NCAPD2, SEC16A, LRP6, LRP1, USP3, MVP, NR1I3, SRA1, LPO, BCL2L11, ABCB6, EIF1, LIG4, PTPRU, PQBP1, LIF, TRIM10, LCN1, G3BP1, RPSA, WASF2, LAMB2, LAD1, L1CAM, KRT31, TRIM13, H3P42
-
Fear Of Missing Out
Wikipedia
Grohol, founder and Editor-in-Chief of Psych Central , FOMO may lead to a constant search for new connections with others, abandoning current connections to do so. ... Maybe it's your Facebook wall" . The New York Times . ^ Shea, Michael (27 July 2015). ... "Internet Gratifications and Internet Addiction: On the Uses and Abuses of New Media". CyberPsychology & Behavior . 7 (4): 384–394. doi : 10.1089/cpb.2004.7.384 . PMID 15331025 . ^ Herman, Dan (2000-05-01). "Introducing short-term brands: A new branding tool for a new consumer reality". ... "The Inventor of FOMO is Warning Leaders About a New, More Dangerous Threat" . Inc.com .
-
Lissencephaly Type Iii And Bone Dysplasia
Omim
The fetus had a normal XY karyotype. Like the index case, he had craniofacial edema and arthrogryposis, as well as epiphyseal stippling of cervical vertebrae, feet, and sacrum. ... Attia-Sobol et al. (2001) suggested that the disorder in this family is a new type III lissencephaly syndrome because of epiphyseal calcifications and metacarpal phalangeal bone dysplasia.
-
Wasting
Wikipedia
WFH as % of median reference value is calculated this way: W F H = weight of a given child median weight for a given child of that height × 100 {\displaystyle \mathrm {WFH} ={\frac {\mbox{weight of a given child}}{\mbox{median weight for a given child of that height}}}\times 100} Cutoff points may vary, but <80% (close to −2 Z-score ) is often used. Adults: Body Mass Index (BMI) is the quotient between weight and height squared (kg/m 2 ). ... UNICEFWHO- World Bank Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates. (UNICEF, New York; WHO, Geneva; The World Bank, Washington, DC; 2012) ^ Michael Powers, "Performance-Enhancing Drugs" in Joel Houglum, in Gary L.
-
Cold Urticaria
Mayo_clinic
Do you have any brochures or other printed material I can take with me? What websites do you recommend? What to expect from your doctor Your doctor is likely to ask you questions such as: When did you begin experiencing symptoms? ... Do others in your family have similar symptoms? Have you taken any new medications recently? Have you tried any new foods? Have you traveled to a new place? Does anything seem to improve your symptoms?
-
Bleeding Canker Of Horse Chestnut
Wikipedia
Infections by the gram-negative fluorescent bacterium Pseudomonas syringae pathovar aesculi are a new phenomenon, and have caused most of the bleeding cankers on horse chestnut that are now frequently seen in Britain. [1] Contents 1 Disease cycle 2 Causes 2.1 Pseudomonas syringae pathovar aesculi 3 Management 4 Importance 5 References 6 External links Disease cycle [ edit ] Pseudomonas syringae pv. ... Causes [ edit ] Pseudomonas syringae pathovar aesculi [ edit ] In the past few years, the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. aesculi has emerged as a new and virulent agent for this disease in Western Europe. ... "Isolation and identification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. aesculi causing bleeding canker of horse chestnut in the UK" . New Disease Reports . British Society for Plant Pathology (BSPP) . ... External links [ edit ] UK Forest Research Kew Royal Botanical Gardens- (Aesculus indica) Indian horse chestnut Forestry Commission Website Working group Aesculaap
-
Idiopathic Postprandial Syndrome
Wikipedia
The episodes typically occur a few hours after a meal, rather than after many hours of fasting. The principal treatments recommended are extra small meals or snacks and avoidance of excessive simple sugars . ... Non-disease [ edit ] In October 1974, The New England Journal of Medicine carried an article "Non-hypoglycemia as an epidemic condition" which described the condition as a "non-disease". [4] The authors claim Over the past few years people have appeared in droves with the self-diagnosis of "hypoglycemia" – a term that has become the layman's final common pathway for a variety of conditions, only a few of which are related to endocrinologic abnormalities. ... Young (1974) "Non-hypoglycemia as an epidemic condition", The New England Journal of Medicine 291:907,8 ^ George F. ... Stuart Soeldner (1974) "A non-editorial on non-hypoglycemia", The New England Journal of Medicine 291: 905,6 ^ "postprandiale Hypoglykämie" .
-
Collapsed Vein
Wikipedia
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Collapsed vein" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR ( July 2007 ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message ) Collapsed veins are a common injury that results from repeated use of intravenous injections . ... Contents 1 Causes 2 Mechanism 3 Prognosis 4 See also 5 References Causes [ edit ] Permanent vein collapse occurs as a consequence of: Repeated injections, especially with blunt needles. Poor injection technique. Injection of substances which irritate the veins; in particular, injection of liquid methadone intended for oral use.
-
Angina
Mayo_clinic
It may feel like a heavy weight lying on the chest. Angina may be a new pain that needs to be checked by a health care provider, or recurring pain that goes away with treatment. ... Any new or worsening angina symptoms need to be evaluated immediately by a health care provider who can determine whether you have stable or unstable angina. ... An ECG can show if the heart is beating too fast, too slow or not at all. Your health care provider also can look for patterns in the heart rhythm to see if blood flow through the heart has been slowed or interrupted. ... Clinical trials Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition. ... Are there any brochures or other printed materials that I can take home with me? What websites do you recommend visiting? Don't hesitate to ask any other questions that you may have during your appointment.AVP, PLAU, APOE, LDLR, GLA, CRELD1, ABCG8, ABCG5, GATA4, GATA6, XYLT2, XYLT1, NR2F2, LMNA, LCAT, JAK2, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, LDLRAP1, IDUA, LIPC, CYP27A1, TET2, PRTN3, ZMPSTE24, CTLA4, SCN5A, PTEN, MPL, ENPP1, PIGA, PCSK9, PTPN22, ABCC6, VEGFA, PMM2, APOB, ACE, CRP, CAD, CCS, IL6, SERPINE1, ITGB2, TNNI3, DLD, CXCL16, OXCT1, LAD1, SERPINA5, PLA2G1B, APOA1, TNF, NOS3, PLB1, KLF14, PLA2G7, PLA2G6, YWHAZ, IL37, NEAT1, VIP, MIR208A, MIR34A, MIR499A, TNFRSF1B, ZGLP1, CYP4F2, PROM1, TNFSF10, CPSF4, HDL3, MOCOS, QRSL1, POC1A, TBC1D9, JTB, ZC4H2, CMAS, SELL, EHMT1, PPP1R2C, FERMT3, ADIPOQ, WASF1, NLRP3, NR1I2, FGF21, ADAM10, CCL2, EDN1, ICAM1, HSPA5, GNB3, GLP1R, GLB1, GDF10, GCG, FGF4, F5, F3, CYP19A1, RENBP, CPB2, CLCN1, CETP, CD34, CD14, VPS51, KLK3, APOC3, ALB, AGTR1, IFNG, IGF2R, IL1A, IL1B, PYGM, PRKCD, PLXNA2, PLA2G2A, ABCB1, PAPPA, CNTN3, ADRB1, OPA1, NOS2, NOS1, MPI, MMP3, SMCP, LPA, KDR, ITGA2B, IL10, CXCL8, IL7, IL1RN, LINC02605
-
Antimicrobial Resistance
Wikipedia
Clinical resistance is shown through the failure of many therapeutic techniques where the bacteria that are normally susceptible to a treatment become resistant after surviving the outcome of the treatment. ... Given that lifespans and production of new generations can be on a timescale of mere hours, a new (de novo) mutation in a parent cell can quickly become an inherited mutation of widespread prevalence, resulting in the microevolution of a fully resistant colony. ... In recent years, the emergence and spread of β-lactamases called carbapenemases has become a major health crisis. [100] One such carbapenemase is New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1 (NDM-1), [101] an enzyme that makes bacteria resistant to a broad range of beta-lactam antibiotics . ... Drug resistance has "become a major concern". [116] History [ edit ] The 1950s to 1970s represented the golden age of antibiotic discovery, where countless new classes of antibiotics were discovered to treat previously incurable diseases such as tuberculosis and syphilis. [117] However, since that time the discovery of new classes of antibiotics has been almost nonexistent, and represents a situation that is especially problematic considering the resiliency of bacteria [118] shown over time and the continued misuse and overuse of antibiotics in treatment. [119] The phenomenon of antimicrobial resistance caused by overuse of antibiotics was predicted as early as 1945 by Alexander Fleming who said "The time may come when penicillin can be bought by anyone in the shops. ... Furthermore, if the use of vaccines increases, there is evidence that antibiotic resistant strains of pathogens will decrease; the need for antibiotics will naturally decrease as vaccines prevent infection before it occurs. [132] However, new strains that escape immunity induced by vaccines may evolve ; for example, an updated influenza vaccine is needed each year.
-
Apert Syndrome
Wikipedia
However, the typical hand deformities in patients with Apert syndrome distinguish it from the other syndromes. [8] The hands in patients with Apert syndrome always show four common features: [9] a short thumb with radial deviation complex syndactyly of the index, long and ring finger symbrachyphalangism simple syndactyly of the fourth webspace The deformity of the space between the index finger and the thumb may be variable. ... The thumb shows radial deviation and clinodactyly but is separated from the index finger. The index, long and ring finger are fused together in the distal interphalangeal joints and form a flat palm. ... This is a more serious anomaly since the thumb is fused to the index finger by simple complete or incomplete syndactyly. Only the distal phalanx of the thumb is not joined in the osseous union with the index finger and has a separate nail. ... In both type I and type II, the recurrent syndactyly of the second web space will occur because of a pseudoepiphysis at the base of the index metacarpal. This should be corrected by later revisions.
-
Age Spots (Liver Spots)
Mayo_clinic
Risk factors You might be more likely to develop age spots if you: Have light skin Have a history of frequent or intense sun exposure or sunburn Prevention To help avoid age spots and new spots after treatment, follow these tips for limiting your sun exposure: Avoid the sun between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. ... Dermabrasion sands down the surface layer of skin with a rapidly rotating brush. New skin grows in its place. You may need to undergo the procedure more than once. ... If you have rosacea or tiny red veins on your face, this technique could make the condition worse. ... This method involves applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove the top layers. New, smoother skin forms to take its place. ... Also, make sure your dermatologist is specially trained and experienced in the technique you're considering. Self care Many nonprescription fade creams and lotions for lightening age spots are available for sale.