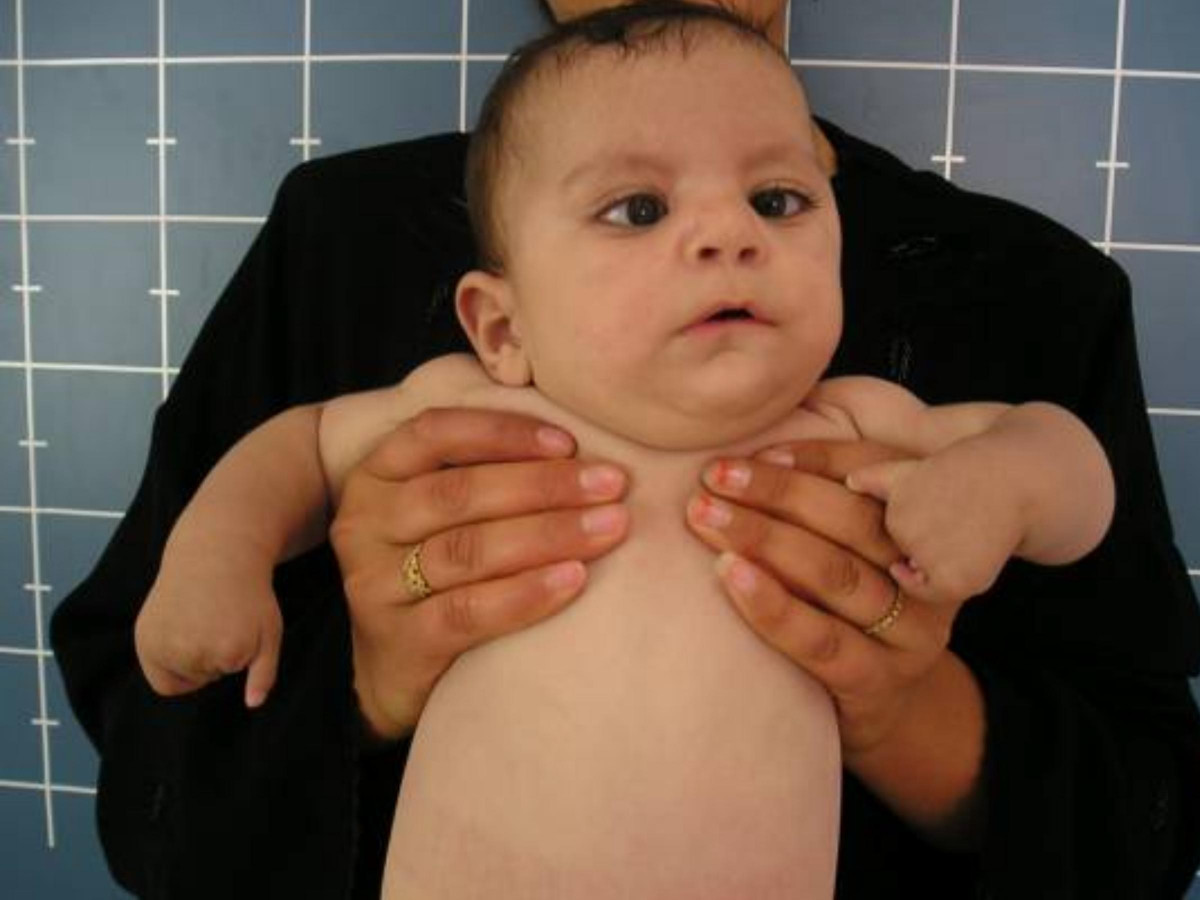
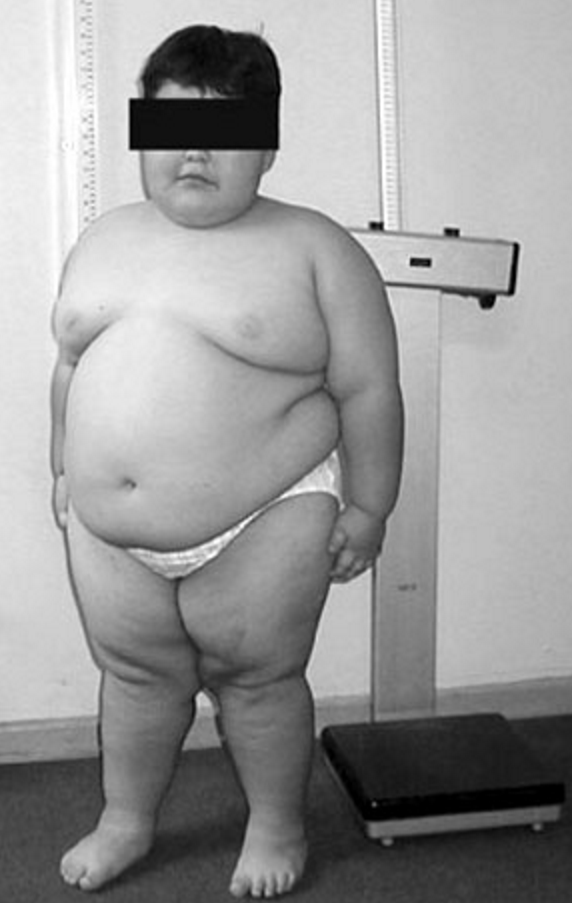
-
Runner's Diarrhea
Wikipedia
Methods to prevent runner's diarrhea will vary between individuals, although it is advisable to consider examining the pre-running diet to determine potential trigger foods. [1] Notable cases [ edit ] At the 1998 London Marathon , winner Catherina McKiernan suffered from recurrent diarrhea during the race. [4] At the 2005 London Marathon, winner Paula Radcliffe , in desperate need for a toilet break during the race, stopped by the road in full view of the crowd and live TV cameras and defecated. She later blamed a surfeit of pasta and grilled salmon from the previous night for the incident. [5] At the 2008 Göteborgsvarvet half marathon, David Bailey finished the race in 21st place in spite of being stained with his own excrement.
-
Visual Snow
Wikipedia
Medications that may be used to treat the condition include lamotrigine , acetazolamide , or verapamil . [4] These do not always result in benefits, however. [3] [2] Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Comorbidities 2 Causes 3 Diagnosis 4 Treatments 5 References 6 External links Signs and symptoms [ edit ] Clear vision versus disturbed vision People report seeing "snow", much like the visual noise or "static" on a TV screen after transmission ends. In a 2010 study Raghaven et al. hypothesize that what the patients see as "snow" is their own intrinsic eigengrau . [7] Many report more visual snow in low light conditions. ... PMID 12609692 . ^ Schankin, Christoph J.; Maniyar, Farooq H.; Digre, Kathleen B.; Goadsby, Peter J. (2014-03-18). " ' Visual snow' – a disorder distinct from persistent migraine aura" .
-
Gelotophobia
Wikipedia
Paul Lewis (Boston College, US) speculated whether political gelotophobia might affect elections in the US ("The twin fears of being effectively mocked or ineffective in mocking others [too harsh, blunt, tasteless] led candidates to aggressive and proactive strategies [going on TV to show they can take a joke, be funny—anything to avoid being rendered pathetically ridiculous or inappropriately derisive]") [p. 42, conference abstract from the 2009 conference of the International Society for Humor Studies ISHS in Long Beach, California]; [17] Sociologist Christie Davies , who is also president of the ISHS, comments satirically on the results of recent elections in the UK. ... Humor . 22 (1–2). doi : 10.1515/humr.2009.003 . ^ Weiss, Elisabeth M.; Schulter, Günter; Freudenthaler, H. Harald; Hofer, Ellen; Pichler, Natascha; Papousek, Ilona (2012-05-31). ... Humor , 22 , 91-110. ^ Papousek, I., Ruch, W., Freudenthaler, H. H., Kogler, E., Lang, B., & Schulter, G. (2009).
- Body Inflation Wikipedia
-
Trypophobia
Wikipedia
A significant minority of those with trypophobia meet the DSM-5 criteria for obsessive–compulsive disorder. [3] Martínez-Aguayo et al. stated that other findings refer to trypophobia having common comorbid psychiatric diagnosis, such as major depressive disorder or generalized anxiety disorder , although Le et al. felt that general anxiety does not cause trypophobia. [3] Treatment [ edit ] There are no known treatments for trypophobia, but exposure therapy , which has been used to treat phobias, is likely to be effective for treating trypophobia. [1] Epidemiology [ edit ] The extent to which trypophobia exists is unknown, [1] but the available data suggests that having an aversion to trypophobic imagery is relatively common. [1] [2] [3] 16% of a sample of 286 participants in a 2013 study reported discomfort or repulsion when presented with an image of a lotus seed pod and its authors found that non-trypophobic individuals also experienced more discomfort when viewing trypophobic imagery than when viewing neutral images. [1] Trypophobia appears to be more prevalent in women. [3] Society and culture [ edit ] The term trypophobia is believed to have been coined by a participant in an online forum in 2005. [5] The word is from the Greek : τρῦπα , trŷpa , meaning "hole" and φόβος , phóbos , meaning "fear". [5] Groups on social media sites such as Facebook and Instagram exist for self-identified trypophobics to share and discuss images that they say induce the reaction. [5] [11] Because trypophobia is not well known to the general public, many people with the condition do not know the name for it and believe that they are alone in their trypophobic reactions and thoughts until they find an online community to share them with. [12] This has led to an increase in trypophobic images on social media; in some cases, people seek to intentionally induce trypophobia in those who have it by showing them trypophobic images, with the most trypophobic-inducing images being holes and clusters (especially the lotus seedhead) photoshopped onto human skin. [12] Cole and Wilkins also stated that the level of disgust with trypophobia increases if the holes are on human skin. [12] Writing in Popular Science , Jennifer Abbasi argues that emotional contagion within such social media groups may be responsible for some of the aversive reactions to such images. [5] In 2017, trypophobia received media attention when American Horror Story featured a trypophobic character [13] and trypophobia-inducing advertisements promoting the storyline; some people were disturbed by the imagery, [12] [14] and criticized the show for "insensitivity towards sufferers of trypophobia". [14] Although there was sentiment that the increased media attention could lead to people trying to induce trypophobia, there were also opinions that it might help people understand trypophobia and encourage more research on the matter. [12] Some users responded to the September 2019 release of Apple's iPhone 11 Pro , which features three closely spaced camera lenses, with comments that it triggered their trypophobia. [15] Writer and editor Kathleen McAuliffe suggested that trypophobia is yet to be extensively studied because researchers have not given as much attention to topics of disgust as they have to other areas of research, and because of the revulsion viewing the images could incite in researchers. [16] See also [ edit ] List of phobias References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Milosevic, Irena; McCabe, Randi E. (2015). ... Retrieved October 25, 2017 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Martínez-Aguayo, Juan Carlos; Lanfranco, Renzo C.; Arancibia, Marcelo; Sepúlveda, Elisa; Madrid, Eva (2018). ... Retrieved 10 Apr 2016 . ^ a b c d e LaMottef, Sandee (September 14, 2017). "TV show triggers little-known phobia" .
-
Ruminal Tympany
Wikipedia
This same accident was portrayed in the TV Series of the same name , but with Farmer Skerry striking a match to light his cigarette as James' colleague Tristan releases the gas.
- Ortner's Syndrome Wikipedia
-
Möbius Syndrome
Wikipedia
In the first season of American medical drama The Good Doctor , a teenage patient is depicted with Möbius syndrome. In the BBC TV series Face , Loraine Deveney, a Möbius syndrome patient, was portrayed as a successful example of "smile surgery" performed by R. M. Zuker, M.D. The German TV series Dr. Stefan Frank episode "Ein himmlisches Lächeln" (season 4, episode 4) is about a young boy living with Möbius syndrome. ... Münchener Medizinische Wochenschrift . 35 : 91–4. ^ Al Kaissi A, Grill F, Safi H, Ben Ghachem M, Ben Chehida F, Klaushofer K (2007).
-
Werner Syndrome
Wikipedia
PMID 3909762 . ^ a b Hasty P, Campisi J, Hoeijmakers J, van Steeg H, Vijg J (2003). "Aging and genome maintenance: lessons from the mouse?". ... Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1514/ ^ Goto M, Miller RW, Ishikawa Y, Sugano H (1996). "Excess of rare cancers in Werner syndrome (adult progeria)". ... PMC 3040982 . PMID 20934517 . ^ a b c d e f g h Goto, Makoto (2004). Clinical Aspects of Werner's Syndrome: Its Natural History and the Genetics of the Disease . ... PMID 5431223 . ^ Salk D, Au K, Hoehn H, Martin GM (1981). "Cytogenetics of Werner's syndrome cultured skin fibroblasts: variegated translocation mosaicism". ... PMID 2762303 . ^ a b Crabbe L, Jauch A, Naeger CM, Holtgreve-Grez H, Karlseder J (2007). "Telomere dysfunction as a cause of genomic instability in Werner syndrome" .WRN, BLM, HFM1, TP53, PARP1, RECQL4, LMNA, SERPINE1, FEN1, RAD51, POLB, XRCC6, IGFBP3, FN1, AHSA1, PRKAR1A, H2AX, GRAP2, PCNA, RECQL5, MRE11, XRCC5, EFEMP1, TGFB1, RECQL, MLH1, AIMP2, GYPA, MAPK1, ATR, WRNIP1, RNF19A, CRK, MAPK14, POLDIP2, SLC35G1, TAGLN, RAC1, MIR200C, CHD9, TFRC, APLF, BRIP1, TERT, GTF2IRD2, RPS3, PIWIL4, SSRP1, TOP3A, SLC20A1, SLC2A1, RPS6KA3, TIMP1, MON2, NEIL1, SIRT6, MMRN1, SAMHD1, RBPMS, PRPF19, DDX46, POLL, DESI1, EXD3, ENOSF1, ADIPOQ, PIWIL1, EXO1, CES2, DHX16, RAD54L, DDX19A, SUMO1, ABL1, PPP2CB, PPARG, GOLGA3, GCK, MTOR, FGFR1, FANCD2, EWSR1, ERCC4, ERCC1, DNA2, DKC1, DHX9, ACE, DCN, COL3A1, CKMT2, CDKN2A, CDC42, CAT, CASP1, CALCA, BRCA1, ATM, APOA1, APEX1, ANK1, HOXA@, HOXA1, HOXA3, KDR, POU1F1, POLD1, PLIN1, PLG, ACTB, OGG1, NBN, MYC, MECP2, MBNL1, LIG4, INSR, HOXA4, IL1B, IL1A, IGF2, ICAM1, HOXA13, HOXA11, HOXA10, HOXA9, HOXA7, HOXA6, HOXA5, H3P10
-
Survivor Guilt
Wikipedia
Fox ) goes to a therapist to deal with his own survivor's guilt after a friend is killed in a car crash while running an errand that Alex refused to help with. The TV series Rescue Me follows the lives of firefighters post 9/11 in New York City , focusing on Tommy Gavin , a 9/11 first responder experiencing severe survivor guilt over the civilians he was unable to save and the other firefighters who died in the attack, many of whom he personally knew. ... Spooner has survivor's guilt. In the TV show Arrow , the main character, Oliver Queen, has survivor's guilt in the episode "Three Ghost". ... The light novel sequel to the 5th part of the long-running manga series JoJo's Bizarre Adventure called Purple Haze Feedback has Pannacotta Fugo, a character from the beginning of the part who left the main cast in the main part when they went to fight the main villain, become distraught after learning of the deaths of three of his old comrades who joined the main fight and wonders why he didn't join them. In an episode of TV show " Hawaii Five-0 ", Danny Williams mentions that his life since the September 11 attacks is all "borrowed time", when he and his then-partner Grace Tillwell raided a gang warehouse (without having told anyone about it) in the early morning hours of September 11, 2001, and were tortured by the gang members, who then killed his partner, and were about to proceed on him before being distracted by the sound of sirens outside, allowing Danny to break free and kill the gang members, before running outside to try and flag down a police car, only to see them speeding towards a huge billow of dark smoke.
-
Fear Of Bees
Wikipedia
Archived 2007-07-02 at the Wayback Machine a transcript from Impact Television, a weekly TV series by University of Florida ^ Bee or Yellow Jacket Stings Archived 2006-12-13 at the Wayback Machine , a hospital advise ^ "The Birds, the Bees, and the Flying Foxes: Pollinators in Jeopardy" (PDF) .
-
Haemolacria
Wikipedia
Contents 1 History 2 See also 3 References History [ edit ] Twinkle Dwivedi From Lucknow , India , Dwivedi presented a rare condition that appeared to cause her to spontaneously bleed from her eyes and other parts of her body without presenting any visible wounds. [3] Dwivedi was the subject of numerous medical research studies and TV shows including Body Shock [4] and a National Geographic documentary. [5] In the absence of a medical explanation for her condition, some religious explanations have been posed.
-
Ronnie And Donnie Galyon
Wikipedia
Oldest conjoined twins Ronnie and Donnie Galyon Born Ronald Galyon Donald Galyon ( 1951-10-28 ) October 28, 1951 Dayton, Ohio Died July 4, 2020 (2020-07-04) (aged 68) Dayton, Ohio Occupation Sideshow attractions, reality TV personalities Known for Oldest living set of conjoined twins Ronnie and Donnie Galyon (October 28, 1951 – July 4, 2020) [1] were American conjoined twins .
-
Party And Play
Wikipedia
In an article published by The Guardian , it has been argued that an exaggerated reporting might give the public a distorted impression of the magnitude of this phenomenon – and that can only increase the level of collective anxiety. [25] See also [ edit ] LGBT portal Human sexuality portal Bugchasing Group sex HIV superinfection LGBT slang Sex and drugs Chemsex (documentary film) References [ edit ] ^ a b "PSA tackles PNP : TV ad warns against crystal meth usage in the gay male community" . metroweekly.com . 2007-09-21. ... Retrieved 2018-06-11 . ^ a b c d e f g h San Francisco Meth Zombies (TV documentary).
-
Gnathostomiasis
Wikipedia
ISBN 0-7216-2921-0 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j David T. John; William A. Petri (2006). ... PMID 11023048 . ^ Setasuban P; Nuamtanong S; Rojanakittikoon V; Yaemput S; Dekumyoy P; Akahane H; Kojima S. (1991). "Gnathostomiasis in Thailand: a survey on intermediate hosts of Gnathostoma spp. with special reference to a new type of larvae found in Fluta alba ". Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health . 22 Suppl: 220–4. PMID 1822890 . ^ Akahane H, Setasuban P, Nuamtanong S, Horiuchi S, Koga M, Kojima S (1995). ... S2CID 24447639 . ^ Sieu TP, Dung TT, Nga NT, Hien TV, Dalsgaard A, Waikagul J, Murrell KD (Feb 2009). ... Cockman-Thomas; Curtis A. Colleton; Chris H. Gardiner; Wayne M. Meyers (1993).
-
Prader–willi Syndrome
Wikipedia
Revista Médica de Chile . 133 (1): 33–41. doi : 10.4067/s0034-98872005000100005 . PMID 15768148 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Prader-Willi syndrome" . ... PMID 12091883 . S2CID 5253679 . ^ Clark DJ, Boer H, Webb T (1995). "General and behavioural aspects of PWS: a review". ... Archived from the original on June 29, 2014. ^ Davies PS, Evans S, Broomhead S, Clough H, Day JM, Laidlaw A, Barnes ND (May 1998). ... PMID 11932286 . ^ Höybye C, Hilding A, Jacobsson H, Thorén M (May 2003). "Growth hormone treatment improves body composition in adults with Prader-Willi syndrome". ... Retrieved June 12, 2009 . ^ "Extreme Makeover: Home Edition Articles on AOL TV" . Aoltv.com. Archived from the original on September 23, 2015 .MAGEL2, SNRPN, NDN, MKRN3, NPAP1, IPW, PWAR1, SNORD116-1, MKRN3-AS1, PWRN1, SNORD115-1, MRAP2, HERC2, HTR2C, CEP63, CENPJ, SOS1, PTPN11, RIT1, KRAS, RAF1, LZTR1, ATR, GH1, UBE3A, GABRB3, SNORD116@, UROD, SNURF, LEP, SNORD14D, SNORD14B, SNORD35B, SNORD14E, SNORD14C, GHRL, SNORD15A, IGF1, HCRT, GHR, SLC52A2, OCA2, F2R, NR1I2, ADIPOQ, PCSK1, ATP10A, POMC, SETDB1, IL6, GHRH, SNHG14, MAGED1, PWAR5, DMD, BEST1, ZNF274, FMR1, GNAQ, GLP1R, EHMT1, STOML3, HSPG2, STS, RASA1, TNFSF11, CRP, SLC6A4, LEPR, MARK2, TNFRSF11B, EHMT2, METAP2, NHLH2, GHSR, GABRA5, SOST, SIM1, PIK3CA, DKK1, PROCR, PADI4, EID1, RNF13, CIT, ABCB6, GREM1, CYFIP1, ACADS, ADIPOR1, RCBTB1, ZGLP1, MIR23A, MIR122, GOLGA8EP, RBMY1D, ENHO, PWARSN, RBMY2DP, GOLGA6A, WHAMMP3, SNORD109B, SNORD109A, NIPA1, TUBGCP5, LMLN, TMPRSS13, NIPA2, DHDDS, POM121, ADIPOR2, ANKRD36B, CHPT1, PRDM9, RETN, NSMCE3, ANGPTL8, ZNF654, DHX40, SMN2, PREPL, MSMB, MECP2, STMN1, HTR2B, HTC2, NR4A1, HDC, GCG, GAPDH, GABRG3, FRAXA, FMO2, EPHB1, EFNB2, DIO3, DAZ1, DAG1, CNR1, CD36, BTF3P11, BRAF, BGLAP, BDNF, BCR, AVP, ARSD, ARSA, AR, APOC3, ALCAM, MEN1, MST1, DLK1, CYTB, SCG2, VEGFA, TYR, TWIST1, TSPY1, TNF, THAS, STATH, STAR, AGRP, SMN1, SLC5A2, CCL5, SAG, RBMY1A1, PYY, PRNP, PRL, PRKCA, PTPA, PML, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PGC, PDPK1, NPY2R, NPY, HNRNPM, FMR1-IT1
-
Colitis-X
Wikipedia
The probiotics most often used for this purpose contain Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium . [2] See also [ edit ] Horse colic References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Colitis-X" . Merck Veterinary Manual . ... Retrieved 2008-11-17 . ^ Thomas C, Stevenson M, Riley TV (June 2003). "Antibiotics and hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea: a systematic review" .
- Leucism Wikipedia
-
Pinworm Infection
Wikipedia
Archived from the original on 5 November 2017. ^ a b c d e f g h i j Burkhart & burkhart 2005 , p. 838 ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Cook et al. 2009 , p. 1516 ^ a b c d e f g h i Gutiérrez 2005 , p. 355. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Caldwell 1982 , p. 307. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Cook 1994 , p. 1159 ^ a b c d e f g h Cook 1994 , p. 1160 ^ a b c d Gutiérrez 2005 , p. 356. ^ a b Gutiérrez 2005 , p. 363. ^ Gutiérrez 2005 , p. 354. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Burkhart & burkhart 2005 , p. 837 ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Garcia 1999 , p. 246 ^ Cook, G C (1994). ... PMC 1375686 . PMID 7959218 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j Caldwell 1982 , p. 308. ^ dpdx 2009 ^ Garcia 1999 , p. 247 ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Cook 1994 , p. 1161 ^ a b c d e Caldwell 1982 , p. 309. ^ "Fact sheets: neglected tropical diseases" . ... S2CID 21775189 . References Hasegawa H, Ikeda Y, Fujisaki A, et al. (December 2005). ... Nakano T, Okamoto M, Ikeda Y, Hasegawa H (December 2006). "Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene and nuclear rDNA regions of Enterobius vermicularis parasitic in captive chimpanzees with special reference to its relationship with pinworms in humans". ... Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée (in French). 58 (4): 403–4. doi : 10.1051/parasite/1983584403 . PMID 6416131 . Hasegawa H, Takao Y, Nakao M, Fukuma T, Tsuruta O, Ide K (February 1998).
-
Abortion In Croatia
Wikipedia
That was increased opposition compared to the same poll from 1999 when only 40% opposed. [15] However, this poll was criticized by some for being suggestive. [16] In 2011, Catholic bishop Valter Župan publicly called for abortion to be banned. In response, Nova TV had an opinion poll conducted, in which 67% of respondents in Croatia said they believe that the current abortion law should not be changed, while 23% supported a ban on abortions. ... Retrieved 2015-05-04 . ^ "Ekskluzivno istraživanje: Zabranu pobačaja podupiru najviše žene" (in Croatian). Nova TV . 2011-06-09 . Retrieved 2013-10-08 . ^ Vlasta Ilišin; Dejana Bouillet; Anja Gvozdanović; Dunja Potočnik (2013).