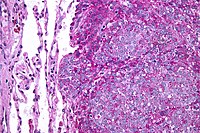
-
Ewing's Sarcoma
Wikipedia
PMID 29431183 . ^ Lahl M, Fisher VL, Laschinger K (February 2008). "Ewing's sarcoma family of tumors: an overview from diagnosis to survivorship".EWSR1, FLI1, EGR2, ERG, ETV1, ETV4, STAG2, CIZ1, NF1, BRD4, DUX4, FLII, NUTM1, TP53, CXCR4, BAP1, RB1, C1orf127, PARP1, RPL24P2, CCND1, SRP14-AS1, FUS, IGF1R, CDKN2A, CD99, CIC, IGF1, BCOR, VEGFA, PIK3CA, PIK3CD, CDK4, PIK3CB, EZH2, PIK3CG, NR0B1, CCNB3, FEV, ATF1, FOXO1, SMUG1, TNFSF10, NFATC2, HLA-A, MYC, TAF15, HIF1A, COL11A2, CAV1, KDM1A, BMI1, CNMD, AKT1, WT1, CCK, PAX3, TNF, KDM3A, STEAP1, MBD2, MDM2, BCL2, COMMD3-BMI1, EWSAT1, ERBB2, ELAVL2, EPHA2, PTEN, ABCB1, ROCK1, DNER, IFNB1, XAGE1A, TNC, FGF2, SH2D1B, HOXD@, XAGE1B, CASP8, LIF, ALK, TGFBR2, STAT3, CTLA4, VIM, SOX2, DDIT3, PAX7, MMP1, MAPK1, MEN1, NKX2-2, NGF, BCL11B, HLA-DOA, MMP9, MET, HGF, RASSF2, NAMPT, TARDBP, NOTCH1, KMT2A, HES1, GLI1, EMG1, DTL, IL2, PDCD1, PDGFRB, PAPPA, IGFBP3, NES, TWIST1, NTRK1, PLK1, RASSF1, CCN3, HTC2, LDHA, NPY, IGF2BP3, PHGDH, MAML3, PTPRC, FAS, ETV5, BCR, FOXM1, TERT, RHD, SMARCB1, S100A1, BRCA1, CSF3, ETS1, EGFR, S100B, CHEK1, ERBB4, ZYX, ENG, TGFB1, E2F3, AURKB, MIR34A, MALAT1, EZR, PTPN13, CBL, CD38, ROCK2, CCND2, FOLH1, CD34, TNFRSF10A, SCG2, HMGA2, REEP5, STRAP, ARID1A, MLXIP, ZBTB16, ZAP70, CHP1, EBNA1BP2, MMRN1, YWHAE, XBP1, WNT5A, MIR708, H3P28, PPRC1, SMARCA5, BCAR1, JTB, YAP1, NR1I3, TMX2-CTNND1, TRIM13, TRIB1, ADAMTS4, RABEPK, SPRY1, RAMP1, ARHGEF2, USP6, STAG1, LANCL1, OLFM1, PIK3R3, HSPB3, SNURF, NR1I2, PROM1, HDAC3, BANF1, TNFRSF10B, TP53I3, ABCC3, BECN1, TP63, USP19, EED, CDK12, TBC1D9, GSTK1, ARMH1, DLX6-AS1, CAVIN1, PGP, MIR20B, MIR193B, FNDC5, CTAG1A, POU5F1P3, LRWD1, POU5F1P4, KDM1B, MARCHF8, RHOV, ASXL1, PRIMA1, CACUL1, CXADRP1, SLCO6A1, IL31RA, BORCS5, FOXP4, PRRT2, SOX2-OT, SH2D4B, ATG4B, ERVFRD-1, MIR34B, MIR31, MIR30D, MIR30A, MIR301A, MIR29B2, MIR29B1, MIR22, MIR21, MIR199B, MIR199A2, MIR335, MIR199A1, MIR186, MIR185, MIR181C, MIR15A, MIR145, MIR139, MIR130B, MIR10B, MIR107, MIRLET7G, CEP41, FOXQ1, SLFN11, FATE1, NME1-NME2, TET2, KRT20, MIR17HG, GDE1, PHF11, PSAT1, CD274, MYLIP, SETD2, IGHV1-12, AGO2, DKK2, PHF19, MIR584, PLA2G15, SUZ12, MIR638, HEY1, SF3B1, KTWS, SATB2, FBXW11, HEATR3, ZNF331, PBK, MRPL41, DCLK3, RITA1, LINGO1, ACCS, AKT1S1, ZNF93, CD276, DHDDS, LIN28A, NKAP, SOX17, LMO3, XYLT2, ZBTB4, KIDINS220, ABHD6, CD248, CCNL1, ACKR3, CHPT1, PRMT8, ACSS2, ACTB, PTK2, TRIP6, FOXC1, GCY, GATA3, GAS6, GAB1, MTOR, FOSB, FOS, FN1, FLT4, FLT3, FHIT, GHRH, FGFR1, FGF4, FCGRT, FAP, EYA3, ERN1, ERF, EPHB2, EPHA3, EMD, GDNF, GJA1, TNNT1, HOXD11, IGF2, IFNG, IFNA13, IFNA1, HSP90AA1, HSPB2, HSPB1, HSPA4, HPRT1, HOXD13, HLA-G, GLG1, HLA-C, HLA-B, NRG1, HDGF, H2AX, GZMB, MSH6, GSTM4, NR3C1, GRB10, EGR1, EGF, EDNRB, AXL, RUNX3, RUNX2, CASR, CASP9, CASP3, CALCB, CALCA, BTK, BID, BDNF, ATR, EDNRA, SERPINC1, ARR3, ARHGAP1, ABCC6, KLK3, APOC3, XIAP, ALDH1A1, ALCAM, ADRB3, CD6, MS4A1, CD86, CD79A, E2F4, DSPP, DPP4, DDX3X, DCC, CYP2C8, CXADR, CTNND1, CTNNB1, CTAG1B, CSF1R, CSE1L, MAPK14, CRP, CEBPB, CDKN2B, CDK6, CDK2, CDH11, CDH2, CDC42, IGL, IHH, IL6, PTPN11, CCL21, S100A12, BRD2, RNF2, RET, REST, RAG2, RAC1, NECTIN2, PTPRD, PTGS2, POU5F1, PTCH1, PSPH, PSMD7, RELN, MAP2K7, MAPK8, PRKCB, PRKCA, PRKAR1A, PRF1, CXCL12, SET, SFRP5, SLC1A5, TMPRSS2, TSPAN7, TLE1, TIE1, THY1, TRBV20OR9-2, TCF4, TBX5, TARBP2, SYP, SYK, SSX1, SST, SRC, SPN, SPG7, SP1, SNRPN, SMN2, SMN1, SLC2A1, PPP1R1A, PMS2, IL9, KIT, MCF2, MCAM, LRP1, LPP, LOX, LGALS3BP, STMN1, RPSA, KRT17, KRAS, KCNA5, PMAIP1, CD82, JUND, JUNB, JUN, JAK1, INSRR, INSR, INSM1, ILK, IL15, MCL1, MDK, MEIS1, MAP3K3, PCNA, PAK3, PAK1, PAFAH1B1, OSM, ROR1, NTRK3, NPTX2, NPM1, NME2, NME1, NNAT, NF2, NCAM1, MYCN, MUC5AC, MSH2, MMP11, MME, MLH1, MGST1, H3P10
- Abortion In Colombia Wikipedia
-
Opioid Use Disorder
Wikipedia
Retrieved 16 July 2018 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z American Psychiatric Association (2013), Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.) , Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing, pp. 540–546 , ISBN 978-0890425558 ^ a b c d e f g h Substance Use and Mental Health Services Administration (30 September 2014). ... Retrieved 16 July 2018 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, Indave BI, Degenhardt L, Wiessing L, Ferri M, Pastor-Barriuso R (April 2017). ... ISBN 9780890425541 . ^ a b Shah, Mansi; Huecker, Martin R. (2019), "Opioid Withdrawal" , StatPearls , StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30252268 , retrieved 21 October 2019 ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Ries RK, Miller SC, Fiellin DA (2009). ... PMID 25083822 . S2CID 19157711 . ^ Blum K, Werner T, Carnes S, Carnes P, Bowirrat A, Giordano J, Oscar-Berman M, Gold M (2012). ... ADDICT DISORD THEIR TREAT. 2019;18(4):246-248. doi:10.1097/ADT.0000000000000175. ^ Bruneau J, Ahamad K, Goyer MÈ, Poulin G, Selby P, Fischer B, Wild TC, Wood E (March 2018).
- Dentin Hypersensitivity Wikipedia
-
Disorders Of Sex Development
Wikipedia
. ^ Jordan-Young RM , Sönksen PH, Karkazis K (April 2014). "Sex, health, and athletes" . ... ISBN 978-0-306-46759-2 . [ page needed ] ^ Röttger, S., K. Schiebel, G. Singer, S. Ebner, W. Schempp, and G. Scherer. Röttger, S., K. Schiebel, G. Singer, S. Ebner, W.
-
Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Wikipedia
. ^ a b Antshel KM, Hargrave TM, Simonescu M, Kaul P, Hendricks K, Faraone SV (June 2011). "Advances in understanding and treating ADHD" . ... PMID 22976615 . ^ Fayyad J, De Graaf R, Kessler R, Alonso J, Angermeyer M, Demyttenaere K, et al. (May 2007). "Cross-national prevalence and correlates of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder" .
-
Gender Dysphoria In Children
Wikipedia
ISBN 978-0323221528 . ^ a b Marcdante K, Kliegman RM (2014). Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics E-Book . ... Retrieved August 28, 2018 . ^ Alderson K (2012). Counseling LGBTI Clients . ... Journal of Sex and Marital Therapy , Volume 31, Number 1, January–February 2005, pp. 31-42(12) ^ Wilson K (1998). The Disparate Classification of Gender and Sexual Orientation in American Psychiatry 1998 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, Workshop IW57, Transgender Issues, Toronto Canada, June. ^ Wilson, I; Griffith, C; Wren, B (2002). ... Retrieved 2008-06-14 . ^ a b c d Bryant, K (2006). "Making gender identity disorder of childhood: Historical lessons for contemporary debates". Sexuality Research & Social Policy . 3 (3): 23–39. doi : 10.1525/srsp.2006.3.3.23 . S2CID 144613679 . ^ Winters, K. (2008). "Gender Madness in American Psychiatry: Essays from the struggle for dignity".
-
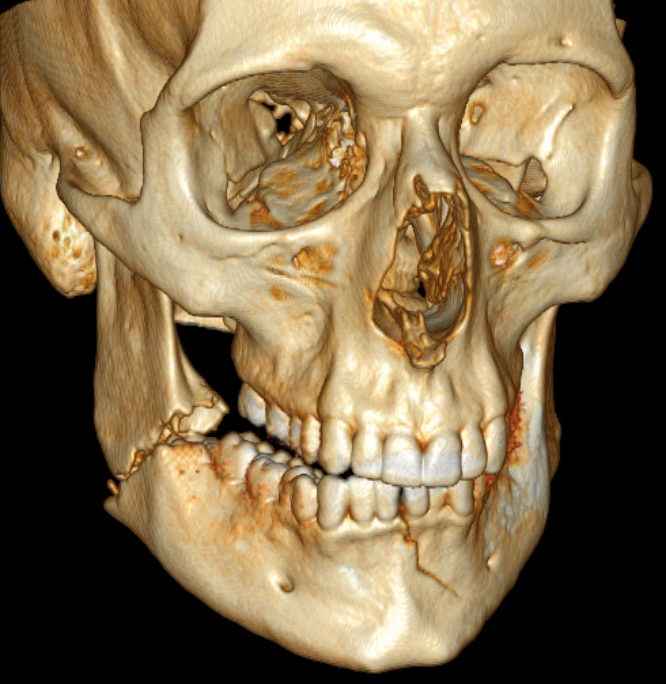
Mandibular Fracture
Wikipedia
Open reduction was described as early as 1869. [40] Since the late 19th century, modern techniques including MMF (see above) have been described with titanium based rigid internal fixation becoming commonplace since the 1970s and biodegradable plates and screws being available since the 1980s. [ citation needed ] References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Murray, JM (May 2013). ... ISBN 978-0-323-02001-5 . ^ Nair, M. K.; Nair, U. P. (2001). "Imaging of mandibular trauma: ROC analysis" . ... PMID 15915103 . S2CID 11089616 . ^ Abdel-Galil, K.; Loukota, R. (2010). "Fractures of the mandibular condyle: Evidence base and current concepts of management". ... PMID 7999738 . ^ Kyrgidis, A.; Koloutsos, G.; Kommata, A.; Lazarides, N.; Antoniades, K. (2013). "Incidence, aetiology, treatment outcome and complications of maxillofacial fractures.
-
Psychopathy
Wikipedia
Mental disorder characterized by persistent antisocial behavior, impaired empathy and remorse, and bold, disinhibited, and egotistical traits Psychopathy Pronunciation / s aɪ ˈ k ɒ p ə θ i / Specialty Psychiatry , clinical psychology Symptoms Boldness , lack of empathy , inclination to violence and manipulation , impulsivity Causes Genetic and environmental Risk factors Family history , poverty , being neglected by parents Differential diagnosis Sociopathy , Narcissism , Machiavellianism , Sadism , Borderline personality disorder , Bipolar disorder (mania) Prognosis Poor Frequency 1% of general population Personality disorders Cluster A (odd) Paranoid Schizoid Schizotypal Cluster B (dramatic) Antisocial Borderline Histrionic Narcissistic Cluster C (anxious) Avoidant Dependent Obsessive–compulsive Not specified Depressive Haltlose Immature Passive–aggressive Cyclothymic Psychopathy v t e Psychopathy , sometimes considered synonymous with sociopathy , is traditionally a personality disorder characterized by persistent antisocial behavior , impaired empathy and remorse , and bold , disinhibited , and egotistical traits . [1] [2] [3] Different conceptions of psychopathy have been used throughout history that are only partly overlapping and may sometimes be contradictory. [4] Hervey M.MAOA, FLT4, PKD2L1, SLC6A4, DRD2, ANKK1, ALLC, CCHCR1, EIF2AK1, CCRL2, ALDH2, MAOB, MTA2, OXTR, HTR2A, STIN2-VNTR, BDNF, EXT1, TNF, CYP2E1, CRP, HGS, HTR3B, CAT, ADAMTS2, BAG3, SIRT1, AVPR1A, TGFB1, CCAR1, AVP, LRFN2, COL25A1, EBPL, SLC22A12, OR2AG1, ANK3, LINC00951, THAS, SNAP25, FAAH, HTR2B, FGD1, FKBP5, ELK3, GABBR1, GABRA2, GAD1, HARS1, HTR1B, ATN1, IARS1, DBH, IL10, DRD5, DRD4, NTRK2, ACE, POMC, PRL, ROBO2, SRSF5, ADH1B
-
Prelabor Rupture Of Membranes
Wikipedia
ISBN 9780195189384 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v Committee on Practice, Bulletins-Obstetrics. ... The Global Library of Women's Medicine . doi : 10.3843/GLOWM.10120 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Beckmann, Charles (2010). ... ISBN 978-0781788076 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v DeCherney, Alan (2013). ... ISBN 978-0071638562 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Cunningham, F (2014). ... ISBN 978-0071798938 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah "Practice Bulletins No. 139".
-
Polysubstance Dependence
Wikipedia
ISBN 978-0-495-09557-6 . ^ a b c d e Medina, K; Shear, PK; Schafer, J; Armstrong, TG; Dyer, P (2004). ... Archived from the original on November 13, 2011. ^ Agrawal, Arpana; Lynskey, Michael T.; Madden, Pamela A. F.; Bucholz, Kathleen K.; Heath, Andrew C. (2007). "A latent class analysis of illicit drug abuse/dependence: Results from the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions".
- Osteonecrosis Of The Jaw Wikipedia
-
Sadomasochism
Wikipedia
Find sources: "Sadomasochism" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR ( August 2014 ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message ) Joe Shuster (1950s), co-creator of Superman , from Nights of Horror A male dominant whipping a female submissive while another woman watches ( Paris , 1930) Sadomasochism ( / ˌ s eɪ d oʊ ˈ m æ s ə k ɪ z əm / SAY -doh- MASS -ə-kiz-əm ) [1] is the giving and receiving of pleasure from acts involving the receipt or infliction of pain or humiliation . [2] Practitioners of sadomasochism may seek sexual gratification from their acts.
-
Grapefruit–drug Interactions
Wikipedia
Retrieved 21 November 2006 . ^ "Synonymy of C. reticulata at The Plant List" . ^ Larry K. Jackson and Stephen H. Futch (10 July 2018). ... ISSN 0269-4727 . PMID 10583697 . ^ Sugimoto K, Araki N, Ohmori M, et al. (March 2006). ... PMID 9264312 . ^ Preissner S, Kroll K, Dunkel M, et al. (January 2010). ... PMID 25547640 . ^ Samojlik, I.; Rasković, A.; Daković-Svajcer, K.; Mikov, M.; Jakovljević, V. (1 July 1999). ... PMID 22286159 . ^ Lilja JJ, Laitinen K, Neuvonen PJ (September 2005). "Effects of grapefruit juice on the absorption of levothyroxine" .
-
Cryptorchidism
Wikipedia
Recent Advances in Small Animal Reproduction . Retrieved 2006-08-10 . ^ Scott K, Levy J, Crawford P (2002). "Characteristics of free-roaming cats evaluated in a trap-neuter-return program".INSL3, RXFP2, CASP3, ATRX, CBL, CHRM3, HSD3B2, STS, PUM1, BCL2L1, GPX4, ESR1, HSF1, GFER, KDM5A, SYNE2, MSX1, HTRA2, ANXA5, FAS, AR, IGF1R, AMH, NR5A1, FGFR1, DAZ1, SRY, CYP19A1, RAF1, PTPN11, AMHR2, HOXD13, WT1, FGF8, OPHN1, TACR3, TAC3, ARNT2, PROKR2, OCRL, STAR, CHD7, CYP17A1, CYP11A1, GNRHR, SOS1, KISS1R, EBP, GATA4, RBMY1A1, FLNA, ANOS1, MECP2, EED, ACTB, NR0B1, PWAR1, SEC24C, OGT, ORC6, PEX3, NPAP1, FLRT3, RAB3GAP2, NIPBL, LMOD1, ATP6V0A2, RTTN, SIN3A, C2CD3, NSMF, CNTNAP2, PIGN, NNT, IFT172, TP63, SZT2, PTCH2, SYNE1, SMCHD1, SPECC1L, MED13L, ADNP, KAT6B, ZFPM2, KCNAB2, GRIP1, GPR161, TGDS, SUZ12, AUTS2, CUL4B, PHGDH, WDPCP, POMT2, SLC25A24, DHH, CDON, TBX22, GMNN, POLR1D, RPGRIP1L, KDM5C, KMT5B, RLIM, CCDC174, TMEM216, DACT1, GMPPB, ANKRD11, UBE2T, SETD2, CCDC22, BBS9, AFF4, ACTA1, B9D1, TBL2, TINF2, NAA10, HIBCH, USP9Y, ARID1A, TRRAP, CDC45, NEDD4L, DDX3Y, SEMA3E, APC2, HUWE1, GPC6, MKRN3-AS1, CD96, IRX5, STAG1, RXYLT1, LARGE1, SMC3, BAZ1B, CITED2, SEMA3A, EMG1, MAD2L2, HACD1, MAMLD1, PACS2, PEX16, GTF2IRD1, TMEM94, PTDSS1, LRIG2, FIG4, POLR1C, MED12, TRIP4, RECQL4, HS6ST1, SRA1, COG1, NRXN1, LONP1, COG5, SEC23A, POMT1, TRIM32, B4GALT7, MRAS, CILK1, RAB3GAP1, SGPL1, RAB18, PHF8, TXNRD2, KDM6B, ANKLE2, FGF17, SLC35D1, HESX1, PEX11B, POLR3A, AP1S2, BCL10, B4GAT1, IFT27, KCNQ1OT1, MAPRE2, HERC2, CLP1, PNPLA6, MBTPS2, SDCCAG8, GJB6, KDM5B, DLL3, BRSK2, CTCF, CPLX1, ABL1, DYNC2LI1, OTUD6B, TMEM67, ATPAF2, ALKBH8, BBIP1, G6PC3, CHST14, TOE1, TTC8, TBC1D20, DIS3L2, BBS5, DNAJC19, EVC2, DNAJC21, RIPPLY2, MPLKIP, NKX2-6, WDR34, LHX4, POMGNT2, PLVAP, FUZ, KLHL15, B9D2, CDT1, VANGL1, SPRY4, LAS1L, CDCA7, HES7, BRIP1, ARL6, POMK, PHF6, UQCC2, TMEM107, SLX4, GATA5, A2ML1, B3GLCT, FREM2, NALCN, H19, KANSL1, CCDC141, DOK7, SNORD115-1, RSPO2, KIF7, EBF3, FEZF1, MYMK, GTF2H5, CRPPA, PWRN1, SNORD116-1, RNU4ATAC, BRWD3, STAC3, GSC, VPS13B, MESP2, CCBE1, B3GALNT2, CKAP2L, CEP120, ESCO2, C8orf37, BBS12, PHACTR1, ARX, ARID2, UBR1, STT3B, TUBB, HYLS1, JMJD1C, CEP290, FRAS1, DHDDS, PACS1, CEP55, SETD5, ATAD3A, BBS7, FANCI, POMGNT1, PEX26, VAC14, FANCL, POLR3B, WDR11, MBD5, MCTP2, HDAC8, ASH1L, KMT2E, RFWD3, WDR60, DAZ3, MAGEL2, SUFU, RAB23, WWOX, MAP3K20, FGFRL1, RIN2, TMCO1, LZTFL1, PHIP, IL17RD, SAMD9, BCOR, NSUN2, MKS1, TMEM70, LZTR1, MRAP, DAZ2, TCTN2, THOC6, MTMR14, PORCN, COLEC11, ALG8, FTO, ALG12, FKRP, TMEM231, LMBR1, FAT4, DYNC2H1, TBL1XR1, PALB2, BBS10, EHMT1, CSPP1, NXN, NSD1, HYMAI, ZSWIM6, RPGRIP1, DAZ4, SELENON, ARID1B, WDR35, CC2D2A, IFT80, FANCM, STRA6, DMRT3, HPSE2, ALX4, PROK2, PIEZO2, PRDM16, SMOC1, RBM10, SMC1A, MKKS, GLI1, GATA6, GDF1, GJA5, GJB2, GPC3, GLE1, GLI2, GABRD, GLI3, GNRH1, GP1BB, GRIA3, GTF2E2, GTF2I, GATA1, FZD2, FANCC, GPC4, FANCE, FANCB, FANCF, FANCG, FBN1, FKTN, FGD1, MTOR, FGF14, FGFR3, FGFR2, FLI1, FLNB, FMR1, HBA1, HBA2, HNRNPK, KMT2A, LIMK1, SMAD4, MC2R, MEFV, MAP3K1, MID1, MTM1, HRAS, MUSK, MYF6, MYH3, MYH11, MYL2, MYLK, LIG4, LHX1, LFNG, LETM1, KRAS, KIT, KISS1, KCNQ1, STT3A, ITGA7, IRF6, IPW, INSR, INPPL1, IGF2, HSPG2, HSD17B3, FANCD2, FANCA, NDN, CDH11, BRCA2, BUB1B, MYRF, TMEM258, CDC6, CDC42, CDKN1C, BRCA1, CHD4, AKR1C4, CHRNG, ERCC8, CLCN4, COL3A1, BRAF, BMP4, EZH2, ARVCF, ACTA2, ACTG2, AEBP1, JAG1, BIN1, ANK1, RERE, BLM, ATR, AXL, BBS1, BBS2, BBS4, BDNF, COL4A1, COL6A1, COMT, EP300, DVL1, DVL3, EFNB1, MEGF8, EIF2S3, ELN, ERCC2, CREBBP, ERCC3, ERCC4, ERCC5, ERCC6, EVC, EXT2, DUSP6, SLC26A2, ATN1, DNMT3A, DNM2, DMPK, DLX4, DKC1, DHODH, DHCR7, AKR1C2, DDB2, DCC, DAG1, CYB5A, CTBP1, NKX2-5, MYOD1, H19-ICR, NDP, SMARCB1, XRCC2, ROBO1, RPL10, XPC, RRAS, RREB1, XPA, WNT7A, RYR1, WNT5A, SALL1, SKI, NF1, WNT3, SMARCA2, RIT1, RFC2, DPF2, RAD51C, PEX5, PYCR1, RAC1, RAD21, RAD51, ZBTB16, MKRN3, RASA2, YY1, RAP1A, RAP1B, XRCC4, RAPSN, RARB, SMARCA4, SMARCC2, PEX19, SMARCE1, HNF1B, TCOF1, TFAP2A, NSD2, TPM2, TPM3, WHCR, TSPY1, TSPYL1, HIRA, TWIST1, UBA1, UBE2A, CLIP2, KDM6A, TBX3, TCF4, TBCE, SOX9, SMS, SNRPN, SOS2, SOX2, SOX3, SOX4, NELFA, TBX1, SOX10, SOX11, SRD5A2, STK11, VAMP7, TAF6, PEX2, UFD1, PEX1, NRAS, PMM2, RNF113A, PIK3CA, PIK3C2A, PEX14, PEX13, NUP88, SIX6, ORC1, ORC4, OTX2, PEX12, PAX6, PEX10, PEX6, PTCH1, PBX1, PDE4D, KAT6A, ROR2, PLAGL1, TUBA1A, MAP2K2, MAP2K1, PRKAR1A, POLD1, PPP1CB, SHOC2, NPHP1, NOTCH3, POR, POLE, NOTCH2, KMT2D, SSTR4, LPAR2, ACKR3, GPR42, EDNRA, CXCR6, BRS3, ADRA1A, ADRA2B, HOXA10, TGCT1, MMP11, POU5F1P3, EGR4, POU5F1P4, GPRC6A, SLC22A3, BRD2, SOD1, AZF1, GGCT, HOXA11, POU5F1, ZNF214, ZNF215, AHR, FZD4, MKX, KIR2DS2, CD44, FCGR1CP, MRGPRX1, USP1, IL27, UTF1, CFTR, ATP2B1, ATP2A1, CAT, CALCA, IL31, AXIN1, GPR166P, VN1R17P, NANOS2, OXER1, NR1I2, STRA8, MIR34C, RBMY2DP, ALPG, MIR210, RBMY1D, BAX, SPAG5, PIWIL4, PDE4A, STRBP, IGFBP3, PGK2, LPAR3, MARCHF1, HMGA2, KIR2DS1, KIR3DL2, LCN2, PDE4B, LHCGR, DUOX1, IL17D, HLA-DRB1, LIFR, REG3A, MMP1, MMP2, NUMA1, MYH2, DKKL1, MYH7, IL22, SYCP3, NOX4, DUOX2, HSPA4, HLA-DQB1, UCHL1, SLC52A2, CIRBP, GPR151, TPT1, GTSF1, MRGPRX4, MRGPRX3, TGFBR3, ST13, E2F1, F2R, PAICS, PLK4, FCGR1A, MYDGF, FCGR1B, RPL29, HHIP, GART, LGR6, IL21, PTBP2, MIER1, GHSR, PTGDS, NPBWR2, PRDM9, PARPBP
-
Apathy
Wikipedia
.; Lockwood, P.; Apps, M.A.; Muhammed, K.; Husain, M. (2017). "Distinct Subtypes of Apathy Revealed by the Apathy Motivation Index" .GRN, TBK1, MAPT, ACAT1, DNAJC6, TARDBP, ATP13A2, DNAJC13, PARK7, SQSTM1, CHMP2B, VCP, UCHL1, SPAST, SNCA, PSEN1, ATXN10, GIGYF2, PRKAR1B, COQ2, HTRA2, TREM2, TMEM106B, VPS13C, VPS35, JPH3, PINK1, EHMT1, LRRK2, HGSNAT, C9orf72, TMEM240, CHCHD10, PRNP, SMARCB1, PODXL, CACNA1A, FUS, DNMT1, GBA, PDGFB, DCTN1, GM2A, HEXA, CSF1R, HLA-DQB1, HMGCL, EIF4G1, PRKN, APOE, MCIDAS, ACHE, CSF2, SLC6A4, LAMC2, TLE5, SLC6A3, COMT, DRD1, USH1G, AR, BDNF, PRX, DRD3, CRP, PRND, DRD4, CFLAR, SGCA, MSN, SOD1, MC4R, LIPA, TRPV1, IGFALS, ENPEP, ADAMTS2, RAPGEF4, MAPK8IP3, HCRT, SMUG1, TPSG1, NPS
-
Mullerian Anomalies
Wikipedia
PMID 22049383 . ^ Chan YY, Jayaprakasan K, Zamora J, Thornton JG, Raine-Fenning N, Coomarasamy A (2011). ... PMID 18539641 . ^ a b c d e f Cheroki C, Krepischi-Santos AC, Szuhai K, Brenner V, Kim CA, Otto PA, Rosenberg C (April 2008). ... PMID 24050215 . ^ a b Heinonen PK, Kuismanen K, Ashorn R (April 2000). "Assisted reproduction in women with uterine anomalies". ... PMID 11699126 . ^ Chan YY, Jayaprakasan K, Tan A, Thornton JG, Coomarasamy A, Raine-Fenning NJ (October 2011).
- Subcutaneous Emphysema Wikipedia
-
Externalizing Disorders
Wikipedia
PMID 16351376 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u "Disruptive, Impulse-Control, and Conduct Disorders".
-
Echinococcosis
Wikipedia
PMID 12643838 . ^ a b c d e John, David T.; William Petri, William A.; Markell, Edward K.; Voge, Marietta (January 2006). "7: The Cestodes: Echinococcus granulosus , E. multiloularis and E. vogeli (Hyatid Disease)" . ... Lancet Infect Dis . 7 (6): 385–94. doi : 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70134-2 . PMID 17521591 . ^ Dang Z, Yagi K, Oku Y, et al. (December 2009). "Evaluation of Echinococcus multilocularis tetraspanins as vaccine candidates against primary alveolar echinococcosis". ... PMC 2768250 . PMID 19881979 . ^ Jani K (July 2014). "Spillage-free laparoscopic management of hepatic hydatid disease using the hydatid trocar canula" . ... Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. ^ Lassen, B.; Janson, M.; Viltrop, A.; Neare, K.; Hütt, P.; Golovljova, I.; Tummeleht, L.; Jokelainen, P. (2016). ... PMID 27723790 . ^ Marcinkutė, A.; Moks, E.; Saarma, U.; Jokelainen, P.; Bagrade, G.; Laivacuma, S.; Strupas, K.; Sokolovas, V.; Deplazes, P. (2015).