-
Rere-Related Disorders
GeneReviews
RERE -related disorders are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and are typically caused by a de novo pathogenic variant. ... Variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. ... Gene-targeted deletion/duplication testing will detect deletions ranging from a single exon to the whole gene; however, breakpoints of large deletions and/or deletion of adjacent genes (e.g., those with a larger 1p36 deletion) may not be detected by these methods. 6. ... This suggests that some changes in this domain may represent dominant negative alleles. The c.4313_4318dupTCCACC, p. ... See OMIM Phenotypic Series: Autosomal dominant ID, Autosomal recessive ID, Nonsyndromic X-linked ID, and Syndromic X-linked ID.
-
Minamata Disease
Wikipedia
A congenital form of the disease can also affect fetuses in the womb. Minamata disease was first discovered in the city of Minamata , Kumamoto Prefecture , Japan, in 1956. ... Chisso paid the cooperative ¥ 20 million (US$183,477) and set up a ¥15 million ($137,608) fund to promote the recovery of fishing. Protestors at the gates of the Chisso factory ( W. ... In most people's minds, the issue of Minamata disease had been resolved. 1959–1969 [ edit ] The years between the first set of "sympathy money" agreements in 1959 and the start of the first legal action to be taken against Chisso in 1969 are often called the "ten years of silence". ... Former Chisso President Kiichi Yoshioka admitted that the company promoted a theory of dumped World War II explosives, though it knew it to be unfounded. ... One photographer who arrived in 1960 was Shisei Kuwabara , straight from university and photo school, who had his photographs published in Weekly Asahi as early as May 1960. The first exhibition of his photographs of Minamata was held in the Fuji Photo Salon in Tokyo in 1962, and the first of his book-length anthologies, Minamata Disease , was published in Japan in 1965.
-
Cyclothymia (Cyclothymic Disorder)
Mayo Clinic
If you're reluctant to seek treatment, work up the courage to confide in someone who can help you take that first step. If a loved one has symptoms of cyclothymia, talk openly and honestly with that person about your concerns. ... Talk to your doctor if you have trouble quitting on your own. Check first before taking other medications. ... Do you have printed material that I can have? What websites do you recommend? Don't hesitate to ask any other questions. ... How have the people close to you described your symptoms? When did you or your loved ones first notice these symptoms? Have your symptoms been getting better or worse over time?
-
Agoraphobia
Mayo Clinic
The therapist may offer to see you first in your home or meet you in what you consider a safe place. ... Key personal information, especially any major stress or life changes that you had around the time your symptoms first started. Medical information, including other physical or mental health conditions that you have. ... Are there any printed materials that I can have? What websites do you suggest? Feel free to ask other questions during your appointment. What to expect from your doctor Your health care provider or mental health provider will likely ask you a number of questions, such as: What symptoms do you have that concern you? When did you first notice these symptoms? When are your symptoms most likely to occur?
-
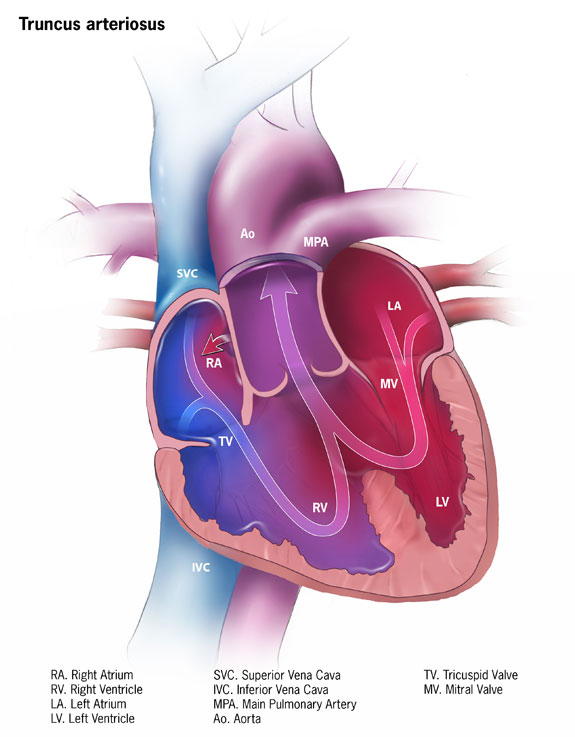
Truncus Arteriosus
Mayo Clinic
Symptoms Symptoms of truncus arteriosus usually occur in the first few days of life. They include: Blue or gray skin due to low oxygen levels. ... Surgery or other procedures Most infants with truncus arteriosus have surgery within the first few weeks after birth. The specific type of surgery depends on the baby's condition. ... If you've had truncus arteriosus repair surgery and want to become pregnant, talk to your health care provider first about the possible risks and complications. ... Are there any brochures or other printed material that I can have? What websites do you recommend? Don't hesitate to ask other questions.NKX2-6, PLXND1, SEMA3C, TBX1, GATA6, GJA8, PUF60, GP1BB, UFD1, MAPK1, GJA5, DLL4, HIRA, TMEM260, CRKL, NKX2-5, ARVCF, BCR, RREB1, COMT, NEK8, SEC24C, JMJD1C, FGFR3, APOE, GATA4, TP53, UGCG, NRP1, VEGFA, ZMYM2, TSC1, A1BG, RBX1, STUB1, TMEFF2, NOC2L, TGFA, KRT20, ZIC4, NRG4, PTCRA, C17orf97, MBOAT4, TNF, PTEN, TBX3, TBX2, PRDM1, CDKN2A, CRP, CTNNB1, CTSE, ERBB3, EREG, F11, FOXO1, GATA2, GDF1, GCLC, IL1B, ISL1, MEF2C, MET, COX2, NHS, NME1, NT5E, PAX3, PAX5, PAX6, PRKD1, PTH, PTGS2, RET, MTCO2P12
-
Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn (Anti-Rhc)
Wikipedia
Acute hemolytic transfusion reactions due to immune hemolysis may occur in patients who have no antibodies detectable by routine laboratory procedures." [12] Causes [ edit ] A Rhc negative mother can become sensitised by red blood cell (RBC) Rhc antigens by her first pregnancy with a Rhc positive fetus. ... The first is that of alloimmunization to the c, E, or, C antigens. ... However, if the patient presents in the first trimester with a 1:8 titer that remains stable at 1:8 throughout the second trimester, continued serial antibody titers are appropriate. ... "Iron status in infants with alloimmune haemolytic disease in the first three months of life". Vox Sanguinis . 105 (4): 328–33. doi : 10.1111/vox.12061 . ... PMID 21512623 . ^ Scheffer, PG; Van Der Schoot, CE; Page-Christiaens, Gcml; De Haas, M (2011).
-
Nasal Septum Perforation
Wikipedia
For perforations that bleed or are painful, initial management should include humidification and application of salves to the perforation edges to promote healing. Mucosalization of the perforation edges will help prevent pain and recurrent epistaxis and majority of septal perforations can be managed without surgery. ... Classically, a graft from the scalp utilizing temporalis fascia was used. Kridel, et al., first described the usage of acellular dermis so that no further incisions are required; they reported an excellent closure rate of over 90 percent.
-
Abortion In Liechtenstein
Wikipedia
Section 98 of the Penal Code additionally criminalizes performing or encouraging an abortion without a careful inquiry into its medical necessity as well as any type of promotion of abortion services. [3] Until the Criminal Code was amended in 2015, the exception for rape only applied if the woman was under 14 years old. [4] In the double referendum on abortion on 27 November 2005, 81% of voters rejected a "For Life" proposal to prohibit all abortion, while 80% passed the Landtag 's counter-proposal, which had been condemned by anti-abortion campaigners. [5] [6] [7] [8] A proposal to legalize abortion in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy or when the child would be disabled was defeated by 52.3% of voters in the 2011 referendum held on 18 September. [9] Prince Alois had previously threatened to veto the proposal if it passed. [10] [11] Women in Liechtenstein who choose to have an abortions must cross the border to either Switzerland or Austria to have the procedure carried out legally. [12] Women must also travel to those countries to obtain advice on their options, as they face the threat of prosecution at home. [13] It is estimated that approximately 50 women a year have abortions, either illegally in Liechtenstein or abroad in either Switzerland or Austria. [14] See also [ edit ] Healthcare in Liechtenstein References [ edit ] ^ "Schwangerschaftsabbruch: Status quo unverändert" [Abortion: Status quo unaltered].
-
Mn1 C-Terminal Truncation Syndrome
GeneReviews
Genetic counseling. MCTT syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder typically caused by a de novo MN1 pathogenic variant. ... Sequence analysis of MN1 is performed first to detect small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants. Note: Depending on the sequencing method used, single-exon, multiexon, or whole-gene deletions/duplications may not be detected. ... Variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. ... Feeding difficulties are more prominent early in infancy and may resolve after the first year of life. Hyperphagia has also been reported in three children [Miyake et al 2020].
-
Lmna-Related Dilated Cardiomyopathy
GeneReviews
LMNA -related DCM is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Some individuals diagnosed with LMNA -related DCM have an affected parent; the proportion of cases caused by a de novo pathogenic variant is unknown. ... Pathogenic variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. ... In general, joint contractures appear during the first two decades, followed by muscle weakness and wasting. ... In the report of Brodt et al, the progression from first observed conduction system disease to the onset of ventricular dysfunction in a subset of 64 individuals with LMNA variants was a median of seven years [Brodt et al 2013]. ... If molecular genetic testing is not possible, the first-degree relatives of a proband with LMNA -related DCM should be evaluated annually by medical history, physical examination, echocardiogram, and ECG to determine if any have detectable DCM and/or conduction system disease.
-
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Wikipedia
While narcissists are preoccupied with attempting to belittle others, megalomaniacs believe they have already dominated others, and need to maintain the domination. ... Archived from the original on 11 January 2017 – via Google Books. ^ O'Donohue, William (2007). ... Archived from the original on 8 September 2017 – via Google Books. ^ Karterud, Sigmund; Øien, Maria; Pedersen, Geir (September–October 2011). ... ISBN 978-1608827602 . LCCN 2013014290 . ( first edition available on the Internet Archive ) Brown, Nina W. (2008). ... ISBN 978-1572245617 . LCCN 2008002242 . ( first edition available on the Internet Archive ) Hotchkiss, Sandy (2003).
-
Tk2-Related Mitochondrial Dna Maintenance Defect, Myopathic Form
GeneReviews
Sequence analysis of TK2 detects small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. Perform sequence analysis first. If only one or no pathogenic variant is found perform gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis to detect intragenic deletions or duplications. ... Pathogenic variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. ... Some affected individuals have elevated serum concentrations of aminotransferases and CK in the first year of life. Note: The observed elevation in serum transaminases may reflect skeletal muscle involvement [Zhang et al 2010]. ... Pompe disease is characterized by progressive proximal muscle weakness early in the first few months of life accompanied with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
-
Spermatogenic Failure 31
OMIM
Molecular Genetics In 2 infertile brothers with oligozoospermia and acephalic spermatozoa from a consanguineous Chinese family, Zhu et al. (2018) performed whole-exome sequencing and identified homozygosity for a nonsense mutation in the PMFBP1 gene (Q488X; 618085.0001). ... The mutations, which were found by whole-exome sequencing and confirmed by Sanger sequencing, were not present in the 1000 Genomes Project database and were present at low frequencies in the ExAC database.
-
Isolated Epispadias
Orphanet
In females, epispadias can be severe (with a cleft involving the whole urethra and the bladder neck, together with bladder mucosal prolapse), intermediate, or mild (with a gaping meatus). ... Differential diagnosis The typical clinical picture does not generally implicate any further differential diagnosis; however, epispadias is also a feature of the whole EEC spectrum (see this term). Antenatal diagnosis Prenatal diagnosis by ultrasound examination is very rare in patients with isolated epispadias due to the minor ultrasound features.
-
Retinitis Pigmentosa 81
OMIM
The mutation was not found in 150 ethnicity-matched controls or in 800 other controls, and screening whole-exome or whole-genome data from 1,771 and 120 patients, respectively, from pedigrees with inherited retinal diseases did not identify any additional mutations in the IFT43 gene.
-
Usher Syndrome, Type Iv
OMIM
Mapping By homozygosity mapping followed by whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing in 3 Yemenite Jewish families segregating an atypical form of Usher syndrome, Khateb et al. (2018) identified a single shared homozygous 66- to 69.4-Mb region on chromosome 17.
-
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Mayo Clinic
Questions may include: When did you first notice this skin growth or lesion? Has it changed since you first noticed it? Is the growth or lesion painful? ... Treatment selection can also depend on whether this is a first-time or a recurring basal cell carcinoma. ... Your doctor may ask: When did you first notice this skin growth or lesion? Has it grown significantly since you first found it? Is the growth or lesion painful?PTCH1, SMO, XPA, ERCC2, DDB2, RASA1, XPC, ERCC5, ERCC4, ERCC3, STAT5B, TP53, MC1R, TYR, UBAC2, COLEC10, RGS22, ATP11A, KANK1, RALY, ZNF365, SMC2, EXO1, FOXP1, HERC2, SPATA48, ZFHX4-AS1, FOXP1-IT1, LINC00513, TRPS1, PTPN22, EFEMP2, CCDC88B, ZBTB7B, PPARGC1B, FLACC1, JDP2, PADI6, SLC6A17, CASC15, CDKN2B-AS1, CLPTM1L, STN1, TNS3, BACH2, SCAF1, RCC2, TGM3, HAUS6, CPVL, SLC45A2, FRMD4A, FGF10-AS1, IRF4, CTSH, HLA-B, LPP, GPR183, CYP1B1, RAC1, HAL, CTSS, CASP8, BRCA2, KRT5, GPX4, GLI1, VEGFA, CDKN2A, PTGS2, CXCL8, ING1, IL6, IGF1R, STAT3, GLI2, EGFR, EDN1, ITGAV, ATF2, RUNX3, BMP4, TYMP, KRT15, FOXP3, BMP2, TGFB1, TGFBR2, SOX9, TNF, CXCL12, CCL5, S100A6, WNT1, LGR5, TP63, CFLAR, PRKCA, PLAGL1, NDUFA1, MYCN, MUC1, MSH3, MCL1, LGALS7, KRT19, GREM1, ASIP
-
3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria, Type Iii
OMIM
A number sign (#) is used with this entry because 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type III, also known as autosomal recessive optic atrophy-3 or optic atrophy plus syndrome, is caused by mutation in the OPA3 gene (606580). See also autosomal dominant optic atrophy-3 (165300), an allelic disorder with a less severe phenotype. ... Clinical Features Costeff et al. (1989) described 19 patients with a familial syndrome consisting of infantile optic atrophy and an early-onset extrapyramidal movement disorder dominated by chorea. About half the patients developed spastic paraparesis during the second decade of life. ... Parental consanguinity was identified in 4 of the 10 sibships; 2 instances of first-cousin parents and 2 instances of first cousins once removed were observed. ... INHERITANCE - Autosomal recessive HEAD & NECK Eyes - Optic atrophy - Decreased visual acuity NEUROLOGIC Central Nervous System - Ataxia - Spasticity - Hyperreflexia - Extensor plantar responses - Extrapyramidal signs - Choreiform movements - Cognitive defects (variable from mild to severe) - Dysarthria LABORATORY ABNORMALITIES - Increased urinary 3-methylglutaconic acid MISCELLANEOUS - Onset of optic atrophy in infancy or early childhood - Neurologic features occur later in childhood - Increased prevalence in individuals of Jewish-Iraqi origin - Allelic disorder to autosomal dominant optic atrophy and cataract ( 165300 ) MOLECULAR BASIS - Caused by mutation in the OPA3 gene (OPA3, 606580.0001 ) ▲ Close
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Head And Neck
OMIM
Mutation in Genes Involved in Squamous Differentiation To explore the genetic origins of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, Agrawal et al. (2011) used whole-exome sequencing and gene copy number analyses to study 32 primary tumors. ... Stransky et al. (2011) independently analyzed whole-exome sequencing data from 74 tumor-normal pairs. ... They showed that HPV-associated tumors are dominated by helical domain mutations of the oncogene PIK3CA, novel alterations involving loss of TRAF3 (601896), and amplification of the cell cycle gene E2F1 (189971).PTEN, ING1, PIK3CA, TP53, EGFR, CDKN2A, NFE2L2, CCND1, PTGS2, STAT3, MET, AKT1, NOTCH1, CDK4, MGMT, YAP1, IGF1, IL1A, CASP8, WEE1, CDK2, SOD2, CCNA1, ABCC1, TNFRSF10B, ABCB1, ATP7B, CDK6, ABCG2, HOXD10, ABCC2, KISS1, IL1RAP, ING3, MERTK, TSC2, CCNE1, IRS1, CCNB1, CCNA2, NDRG1, CCNE2, TBCK, MAPK9, IFNL3, TNNI3K, HOXA5, HOXD11, NSDHL, NAMPT, VAMP7, MIR222, MAPK1, SMAD4, CTNNB1, ERBB2, HRAS, FGFR3, BRAF, FBXW7, CREBBP, MAP2K1, EP300, RAC1, MTOR, HGF, UVRAG, HIF1A, XRCC1, PDCD1, H3C11, GSTT1, CD44, GSTP1, ANO1, GSTM1, CKAP4, VIM, VEGFA, CTLA4, IDH2, MMP2, TGFA, MIR21, TGFB1, PIK3CB, CYP1A1, TNF, MLH1, KRAS, ERCC1, U2AF1, EGF, MMP9, IL6, CTTN, COX2, TP63, ERBB3, GNAS, B2M, BMI1, MTCO2P12, MAP2K2, HPGDS, ALDH1A1, BCL2, PPP2R1A, RHOA, SMUG1, ATM, PIK3CD, H3P10, CD274, RPE65, PIK3CG, SOX2, MAPK14, MCL1, MIR375, XRCC3, TGFBR1, CXCL14, FHIT, POLDIP2, RAD51, AIMP2, CXCL8, RNF19A, EIF4E, MDM2, AHSA1, LINC01194, CRK, IL2, ADH1B, ERCC2, IGF1R, EZH2, GRAP2, FOXP3, ELAVL2, MYC, TIMP3, DCTN6, CCR7, MMP1, EPHB2, GAL, TMED7, ZNRD2, PSMD9, TICAM2, FN1, CXCR4, STAT1, H3P23, GALR1, AREG, JAK2, CXCL12, IFI27, EPCAM, MTDH, TSPAN31, TMED7-TICAM2, OGG1, S100A4, HAVCR2, NANS, SLPI, CYP1B1, PDCD1LG2, IL1B, CASP3, TERT, NBN, FGF2, MMP14, SERPINA5, BSG, MAPK3, POU5F1P3, POU5F1P4, NFKB1, ERBB4, MTHFR, SLCO6A1, GSTK1, ALDH2, POU5F1, ZFP36, SET, FOXM1, MIR146A, PTPRJ, RASSF1, TP73, HLA-A, ARHGAP24, EFNB2, POSTN, FGFR1, E2F1, RAD21, PTK2B, OBP2A, EGR1, ZBTB32, EPHA2, ERCC4, IFNG, SLC2A1, EPHB4, IGFBP3, DAPK1, KIF22, MMP3, CSF2, SEMA4D, MIR205, MIR206, CA9, NT5E, CDH1, SERPINE1, NR1I2, MAP2K7, MIR34A, GALR2, MIR31, NLRP2, HSPB3, MSH2, BRCA1, SOCS3, MIR99A, MTR, AXL, MYO1B, AVP, PMAIP1, XPA, AURKA, SERPINB3, AZIN2, HOTAIR, ADH1C, HDAC9, PARP1, S100A8, VEGFC, CD47, HSPB1, PPFIA1, FAT1, HSPB2, ERCC5, GADL1, BDNF, NME1, STC2, CD34, NGFR, IFNA1, CIP2A, IFNA13, HP, FGFR4, FSD1L, PIWIL1, FSD1, LGALS1, PDK1, DNMT3B, SNAI2, CD163, MIR137, SRC, CYP2E1, MTRNR2L12, MIR203A, ITGB1, LINC00460, PECAM1, FAS, GLI1, TYMS, CCL2, HMGA2, PIWIL4, XPC, IL13, IL10, MIR204, SOAT1, MDM4, PTK2, AKR1A1, PITX2, SAI1, FBLIM1, SST, GRPR, BRD4, STK11, DKK3, DNER, UBE2Q2, PCNA, NLRP3, HELLS, SERPINB4, LDHA, TAC1, COL18A1, IL18, SLC22A3, SNCA, WWOX, TWIST1, FRTS1, JUN, LRP1, SIRT1, KDR, KIR2DS1, TGFBR2, LOXL2, KNG1, KRT17, KRT19, RAD17, LOXL4, CSMD1, MIF, NTRK1, PTPA, SH3GL2, HSP90AA1, TNC, IFI16, TLR4, MAPK8, NEDD9, SLC1A5, GOPC, MRC1, IGFBP7, OGFR, RB1, ACKR3, SLC3A2, MIR93, MALAT1, MIR125A, CAV1, CASP9, KLF4, EDNRB, BRCA2, PDE5A, ESR1, PDPN, ETS1, FCGR3A, FASLG, MTRNR2L13, XIAP, HPSE, APEX1, MIR134, CD68, ANXA1, CYP2D6, SPHK1, CRABP2, CCN2, COL1A2, E2F7, CXADR, XRCC6P5, CYP26A1, MIR150, CDKN2B, TRIM24, CDK9, FADD, CDC25A, DHCR24, NQO1, ANXA5, MIRLET7D, ZEB2, ACTB, FOS, SLC7A5, ALB, GABPA, SPATA2, RARB, NM, SLC16A3, NOS2, SLC16A4, NGF, NXT1, BBC3, MAU2, CDKN1B, CCNL1, SETD2, DIABLO, ADORA2A, RAB25, CD40, STAT5A, STAT5B, MIR499A, RRM2, SCAF11, ENTPD1, SHMT1, SIRT3, S100A2, SYT1, MIR363, DNM1L, KIR2DL5B, NTSR1, NEDD8, TMPRSS11E, NCAM1, BCL10, CCR4, RABGEF1, H3P9, CD200, TBC1D9, KLF6, MIR30A, MSH3, PDCD4, SQSTM1, CRMP1, CRP, MIR29A, ACACB, CCL18, MSMB, CD247, MTRR, CEBPA, NAB2, TBX3, KIR2DL5A, TCF21, MUC1, MIR98, MST1, MIR96, SGSM3, INTS2, AGR2, COX1, MTUS1, CEP55, SERPINB2, LAT, KLRC4-KLRK1, PTGS1, LRPPRC, PTCH1, GDF15, EBI3, ATF4, ATP2A2, ALDH3A1, ATP2A3, ATR, BCL2A1, BCL2L1, TERF2IP, CEACAM1, PTHLH, RELA, ING4, TLR8, RAP1A, RAF1, ANGPTL4, ANXA2, PLAAT4, MICA, APC, SLC6A8, AMCN, PTX3, RPL17-C18orf32, BIRC2, TMX2-CTNND1, SMARCA2, PRKAB1, PRKAA2, PRKAA1, RUNX2, ATG16L1, SERPINE2, MAPKAPK2, PFKFB3, PER1, COMMD3-BMI1, PDLIM7, BHMT, PDGFRA, AURKB, CCK, DCLK1, CLOCK, PRKN, RPL17, PIN1, CALR, CALCR, MRPL28, MIR608, AHR, DDX58, SLC9A3R2, BST2, DAPK2, NOX4, KRT8P3, AKT2, POLD1, KL, CDKN2B-AS1, TFAP2A, GNG7, NRG1, SESN2, FLT4, IL13RA2, HLA-C, ECE1, SUB1, ABCC3, TMPRSS13, MIR100, BRIP1, KHDRBS1, DYRK1A, MIR107, ISG20, TXNRD1, ITGAM, KIR3DL1, MIR10B, ITK, IVL, DSPP, MIR141, JUNB, FGF3, JUND, FOSB, MLRL, RIPK1, MIR149, CBLL2, FUT1, IL6ST, EIF4EBP1, IL4R, ROBO3, FGFR2, GEMIN2, VDR, NMU, DENR, VTN, HCG22, KDM5B, STING1, FOXO3, IDUA, ESR2, UTRN, HOXA10, HOXA9, LMLN, HOPX, ERCC3, EPO, EPHX1, IGF2, IGFBP5, EPHA3, NR1H2, HMOX1, ELF3, TIGIT, IL2RA, FLT1, KIR2DS4, AJUBA, CHEK2, GPX1, TIMP2, TMC8, LOX, TIMM8A, PROM1, MIR200A, LTA, CYP1A2, GEM, WNK1, TACSTD2, MIR200B, GRP, SMAD2, SMAD3, IRX1, MIR200C, IL24, MAGEA3, CTNND1, ZNF35, MAL, MIR211, GORASP1, CD46, CSNK2A2, CSF3, DEK, GLS, CSF1R, MVP, CYP2C19, KLRK1, GSTM2, MIR184, TP53BP1, GTF2H1, DNAJB7, KRT8, IL18R1, MIR182, GATA3, TNFRSF10A, XRCC6, FXR1, DAP, DCC, MUL1, TNFSF10, SEC62, PPARGC1A, TMC6, DNAJC2, ARPC5, PTENP1, TSPAN1, HUWE1, AFF4, ESM1, WWTR1, CHD5, SNORD44, FBXO4, LYVE1, SLC17A5, PWP1, SCO2, RALBP1, RNU6-6P, BCL2L11, RAB40B, DCTN3, RBX1, ABCC5, CHP1, KLK8, LHX6, SLCO2B1, SMR3A, PTPRT, BTG3, SMG1, ACOT7, SDCCAG8, CLUH, VASH1, GPNMB, NTNG1, MLXIP, HEY1, NXF1, ZHX2, CRTAP, SIRT4, DICER1, MMRN1, MYBBP1A, NCBP2, SATB2, ATG7, RCHY1, DKK1, TXNIP, PRDX4, RHOBTB2, SULF1, JMJD6, P2RX2, GPD1L, TRIM32, OLFM4, STAMBP, TPX2, NINL, KDM6B, SUZ12, SRRM2, PUF60, RACK1, SEPTIN9, RAD50, NIPBL, TNFAIP8, GRAP, ALG3, FJX1, CTDSPL, DLEU1, MICU1, CERS1, SEMA3A, PHB2, IL17RA, SH3BP4, POLD3, GNA13, SLC7A11, LDOC1, NUP62, CTCF, PSD4, CXCR6, BPNT1, TUBB4B, SEC14L2, DLC1, TUSC2, ITGA11, SNX5, DERL1, AGO2, MIR106B, RASSF3, C3orf35, ACTBL2, ADGRD2, SOX2-OT, TEX45, LINC01116, RNF144A-AS1, GTF2H5, MIRLET7B, MIRLET7C, MIRLET7E, MIRLET7I, MIR122, BMP6P1, MIR143, MIR145, MIR155, MIR15A, MIR15B, MIR186, MIR191, MIR195, MIR196A2, MIR19A, MIR20A, MIR212, MIR22, OR10A4, CERS6, MIR26B, PWAR1, RHPN1, UHRF2, LRG1, THEM4, TWIST2, GSTO2, REG3G, UPRT, NEK7, CTCFL, OR2AG1, LINC00355, PRIMA1, LINC00052, RICTOR, ZNF569, COMMD1, LINC00964, MAGEB6, XIRP1, COMMD6, ARID2, APOBEC3A, MPEG1, MARCHF8, ALKBH3, HOXA11-AS, CTAG1A, MIR223, MIR27A, IL17B, MIR548H4, MIR618, MIR675, MIR300, MIR876, MIR877, MIR934, MIR885, MIR874, KTN1-AS1, PLA2G4B, MIR1275, MIR1301, MIR1251, HOTTIP, MIR605, MIR642B, LINC00958, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, MIR499B, PCAT1, CASC9, IL12A-AS1, LINC01615, TP53COR1, MYOSLID, LRP1-AS, LOC107987479, LOC110806263, MIR612, MIR590, MIR29C, MIR422A, MIR302A, MIR30E, MIR34B, MIR9-1, MIR9-3, DEFB103A, POTEKP, MIR135B, MIR328, MIR340, MIR376C, MIR372, MIR196B, MIR425, MIR574, CKMT1A, MIR31HG, MIR494, MIR193B, MIR506, MIR486-1, POTEM, MIR205HG, SKOR2, XAGE1B, XAGE1A, LGALS7B, SNORD116@, CYGB, HELQ, CYTOR, ATG2B, SLC38A2, EPB41L4A-DT, PCDH18, DDIT4, EGLN1, FEV, LY6K, NSUN2, NSD3, CMTM6, CT55, HCFC1R1, TMEM45A, FANCL, TLR9, DPPA4, SLC47A1, ZNF654, SPTLC3, LAPTM4B, MEG3, ZNF331, SAGE1, SUPT20H, CCDC88A, ZNF395, DEFB103B, CMAS, DCUN1D1, DUOX1, EGLN3, FAM135B, RBMS3, SLCO1B3, MYLIP, RACGAP1, SERTAD1, SH3KBP1, STOML2, RRM2B, DELEC1, ASAP1, F11R, ASCC1, GMNN, NDUFA13, SPA17, HSD17B12, DCTN4, PLCE1, CDKN2A-DT, TNFRSF12A, FZR1, RHCG, ISYNA1, DTL, SIRT7, SIRT6, MED15, TRIM33, PNO1, C1GALT1, SMYD2, TCHP, ZNF703, CPEB4, ULBP1, CD276, WNT5B, CLPTM1L, MAGED4B, ACTL8, BCL2L12, TLCD3B, ATG10, CCDC8, MYCBPAP, DOT1L, PRDM9, SNORD35B, MAK16, CCDC54, RITA1, ZNRF1, SNORD14B, SNORD14C, SNORD14D, SNORD14E, WNT3A, LINC00473, IL33, SLFN11, TRPM3, NAA25, DOCK5, WLS, SLC12A9, SMURF1, PBXIP1, SCYL1, TENM2, GATAD2B, SEMA6A, ZNF471, ARHGAP21, ANKRD36B, TP53INP2, POPDC3, ARHGEF28, NSD1, BCL11B, MRPL41, TMEM237, MARCKSL1, GGCT, FTO, CHAC1, GCC1, SLC52A2, NEIL1, NLRX1, LIN28A, ELMO3, FGF19, NAT1, DLEC1, GNB3, FOLR1, FOLR2, FTH1, FTL, GAST, FUT4, GAGE1, GAB1, GDF1, GDNF, GJA1, GJB2, GLB1, GCLC, GNRHR, E2F2, SFN, GPI, GPR4, LPAR4, GPR42, GSK3B, GSM1, GSN, GTF2H2, GTF2H3, GTF2H4, GZMB, GZMM, H2AX, FOLH1, FLOT2, FLNB, MLANA, E2F5, TYMP, ECT2, EDNRA, ELAVL1, ELK3, MARK2, ENG, EPHA1, EPHA8, EPHB1, EPHB3, EREG, ERCC6, EXT1, F2, F2R, F3, FANCA, FANCC, FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FCGR2A, FCGR3B, FES, FGF7, FHL1, FKBP4, HDAC1, HDGF, HIC1, ITGA5, ITGB4, JAK1, JAK3, CD82, KCNH1, KCNH2, KIR2DL2, KIR3DL2, KIT, KIF11, KRT5, KRT13, KRT16, KRT18, LAG3, LAMA3, LAMB3, LAMP1, LAMC2, STMN1, LASP1, LCN2, LGALS3, LGALS7, LGALS9, LIG4, LPP, LTB, LTF, ITGA9, ITGA3, HK2, ITGA2, HLA-B, HLA-G, HMGB1, HMGB2, HNF4A, HNRNPC, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HOXB9, HOXC6, HOXD@, HRG, HSF2, HSPA1A, HSPA4, HSPA5, HYAL1, ID2, IFN1@, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IKBKB, IL4, IL15, TNFRSF9, IDO1, ING2, INHBA, IRF6, E2F3, DUSP5, NUAK1, CAPN6, ATP5MC2, ATP5PF, KIF1A, AZGP1, BAG1, BAX, BMP4, BMP7, DST, BRS3, BUB1, PTTG1IP, DDR1, CANX, CASP6, DUSP4, CASP7, CASR, CAT, RUNX1, CBL, SERPINH1, CBR1, CBS, CCT, CD1A, CD9, CD28, CD33, CD40LG, ATP5MC1, ATP5F1A, ZFHX3, ARNTL, ACACA, ACHE, ACTA1, ACTG1, ACTG2, ACTL6A, ACVRL1, ADA, ADH7, ADORA2B, ADRA1A, ADRA2B, GRK2, AP1G1, AGER, JAG1, ALCAM, ALK, ALOX5, ANXA6, APAF1, BIRC3, APP, ARF1, ARF6, ARG1, ARG2, RHOC, ARHGAP1, CD69, CD70, CD151, CST2, CST5, CST6, CSTA, CTAG1B, CTNNA2, CTSH, CUX1, CYP2A6, CYP2A13, CYP2C9, CYP2J2, DDB1, DDB2, DDC, AKR1C1, GADD45A, DDX3X, DDX5, DECR1, DIAPH1, DLAT, DYNC1H1, DNMT1, ATN1, DSC1, DSG3, HBEGF, DTX1, DUSP1, CST3, CSPG4, CDK1, CSH2, CDC42, CDH2, CDH11, CDH13, CDK5, CDK7, CDKN1A, CDKN1C, CDKN3, CDX1, CEBPB, CENPF, CHEK1, CHRNA4, CISH, CKMT1B, CLU, COL5A1, COL11A1, COL11A2, COMT, MAP3K8, COX5B, CRABP1, ATF2, CRYAB, CRYZ, CSE1L, CSH1, LYN, SMAD1, MAGEA1, TRAF3, PRDX2, TEAD4, TERC, TFAM, TFDP2, TFE3, TFRC, TGFB2, TGFB3, NKX2-1, TMSB4X, TNNC2, TNFAIP2, TRAF2, TRAF6, MAGEA11, TRPC6, TTK, TNFRSF4, TXN, USP4, UQCRFS1, NSD2, WNT1, WNT11, WRN, WT1, XPO1, XRCC2, XRCC5, TRBV20OR9-2, ZEB1, TBP, SERPINA7, SLC16A1, SLC19A1, SLCO2A1, SLCO1A2, SLN, SMARCD1, SMO, SMPD1, SIGLEC1, FSCN1, SOX4, SOX11, SPARC, SPOCK1, SPP1, SPRR2A, SRI, SRPK2, SSTR1, SSTR4, SULT1E1, STIM1, SULT1A1, ADAM17, TACR1, TALDO1, TAP1, TAT, TAZ, YY1, YWHAZ, ZNF195, CLDN1, LATS1, P2RX6, ATG12, NEURL1, PCSK7, LPAR2, MAP3K13, IL32, STK17A, TRIP13, TRIP12, ZFYVE9, NCR1, QKI, GSTO1, AIM2, FHL5, ATG5, PMPCB, PTGES, TP53I3, BCAR1, APOBEC3B, CYTIP, NCOR2, TRAF4, MAML1, MELK, FARP2, DNAJA3, GPRC5A, SCLC1, RPL14, SLC25A16, ADAM12, FOSL1, TAM, TKTL1, ARID1A, TAGLN2, ULK1, CUL4B, CUL3, SUPT3H, BHLHE40, LY6D, TNFSF11, USO1, NCOA1, SOCS1, EIF3A, BECN1, JMJD7-PLA2G4B, NOL4, CTNNAL1, GPAA1, NRP1, FCGBP, PER3, ARHGEF7, SELENBP1, LIMD1, SLC9A1, SLC6A2, SERPINA3, NTRK2, NTS, NR4A2, OAT, ODC1, OXA1L, P2RX1, P2RX3, P2RX4, P2RX5, P2RX7, P2RY1, P2RY2, P4HA1, PRDX1, PDGFA, PDHA1, PFN2, PHF2, SERPINB13, PKD1, PKM, PLAGL1, PLAU, PLEC, PLG, PLK1, PLXNB1, PRRX1, SEPTIN4, DDR2, PNP, PRKCA, NOVA1, MAGEB2, MCM7, MDK, ME1, MEFV, MFAP2, KITLG, MICE, MME, MMP8, MMP10, MMP17, MSN, MST1R, COX3, CYTB, MTHFD1, MUTYH, MVD, MXI1, MYH2, CEACAM6, NDN, NEFL, NEK2, NEU1, NEUROD1, NFYA, NOS3, POLB, PKN2, SLC2A4, RFC1, RNASE3, SNORD15A, RPA3, RPS6KA3, RPS19, RPS27, RPS29, RXRA, RYR2, S100A7, S100A9, SAA1, SAT1, SBF1, SCD, CCL15, CCL21, CCL22, CCL23, CXCL5, SDC1, SDCBP, SELL, SFRP1, SFRP4, SRSF3, SHMT2, SKP2, SLC2A3, RFPL1, REV3L, PRKD1, RET, PRKDC, MAPK10, EIF2AK2, PRLR, PRNP, PSMD10, PTBP1, PTGER3, PTH, PTK7, PTPN13, PTPRC, PTPRK, PVR, PVT1, PXN, PYGM, RAD51C, RAD51B, MOK, RAP1GAP, RARA, RARG, RBL2, RBP2, RBP3, RECQL, REL, REN, H3P40
-
Pneumothorax, Primary Spontaneous
OMIM
Stephenson (1976) discussed an association between spontaneous pneumothorax and apical bullae, apical scars, and sharpness of the inner border of the first or second ribs. Leman and Dines (1973) described a family in which 4 members, a man and 3 daughters, including identical twins, had recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax. ... Gunji et al. (2007) reported 5 unrelated patients with multiple lung cysts and recurrent spontaneous pneumothorax. The mean age at onset of first pneumothorax was 30.4 years; none of the patients had skin or renal features. ... In 33, a family history of pneumothorax was obtained. Autosomal dominant inheritance with reduced penetrance in females was suggested by many of the pedigrees in the literature and in this study. ... The affected family reported by Morrison et al. (1998) showed autosomal dominant inheritance. Mapping By a genomewide scan in a large Finnish family with a dominantly inherited tendency to primary spontaneous pneumothorax, Painter et al. (2005) found linkage of PSP to chromosome 17p11. Molecular Genetics In affected members of a large Finnish family with autosomal dominant spontaneous pneumothorax, Painter et al. (2005) identified a heterozygous 4-bp deletion in the FLCN gene (607273.0009).FLCN, MPRIP, STXBP3, REG1A, PSPH, PSPN, BPIFA2, RIDA, MSMB, TPO, MMP9, MAPT, NFE2L2, GABPA, CERS1, TIMP3, GNLY, FBLN5, HIF3A, FLAD1, LRRK2, CCL4L2, CCL4L1, LINC00977, NF1P1, TIMP4, CASP8, RAPSN, TIMP2, CCL4, DCTN1, FMR1, GDF1, HIF1A, HMOX1, LAG3, LAMC2, SMAD2, SMAD3, SMAD4, MMP2, MMP7, MUSK, NEFL, CSF2, LINC00824