Leprosy

Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae or Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damage may result in a lack of ability to feel pain, which can lead to the loss of parts of a person's extremities from repeated injuries or infection due to unnoticed wounds. An infected person may also experience muscle weakness and poor eyesight. Leprosy symptoms may begin within one year, but for some people symptoms may take 20 years or more to occur.
Leprosy is spread between people, although extensive contact is necessary. About 95% of people who contract M. leprae do not develop the disease. Spread is thought to occur through a cough or contact with fluid from the nose of a person infected by leprosy. Genetic factors and immune function play a role in how easily a person catches the disease. Leprosy does not spread during pregnancy to the unborn child, or through sexual contact. Leprosy occurs more commonly among people living in poverty. There are two main types of the disease – paucibacillary and multibacillary, which differ in the number of bacteria present. A person with paucibacillary disease has five or fewer poorly pigmented numb skin patches while a person with multibacillary disease has more than five skin patches. The diagnosis is confirmed by finding acid-fast bacilli in a biopsy of the skin.
Leprosy is curable with multidrug therapy. Treatment of paucibacillary leprosy is with the medications dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine for six months. Treatment for multibacillary leprosy uses the same medications for 12 months. A number of other antibiotics may also be used. These treatments are provided free of charge by the World Health Organization. People with leprosy can live with their families and go to school and work. In 2018, there were 209,000 leprosy cases globally, down from 5.2 million in the 1980s. The number of new cases in 2016 was 216,000. Most new cases occur in 14 countries, with India accounting for more than half. In the 20 years from 1994 to 2014, 16 million people worldwide were cured of leprosy. About 200 cases per year are reported in the United States.
Leprosy has affected humanity for thousands of years. The disease takes its name from the Greek word λέπρᾱ (léprā), from λεπῐ́ς (lepís; "scale"), while the term "Hansen's disease" is named after the Norwegian physician Gerhard Armauer Hansen. Leprosy has historically been associated with social stigma, which continues to be a barrier to self-reporting and early treatment. Separating people affected by leprosy by placing them in leper colonies still occurs in some areas of India, China, Africa, and Thailand. Most colonies have closed, as leprosy is not very contagious. Some consider the word "leper" offensive, preferring the phrase "person affected with leprosy". Leprosy is classified as a neglected tropical disease. World Leprosy Day was started in 1954 to draw awareness to those affected by leprosy.
Signs and symptoms
Common symptoms present in the different types of leprosy include a runny nose; dry scalp; eye problems; skin lesions; muscle weakness; reddish skin; smooth, shiny, diffuse thickening of facial skin, ear, and hand; loss of sensation in fingers and toes; thickening of peripheral nerves; a flat nose due to destruction of nasal cartilage; and changes in phonation and other aspects of speech production. In addition, atrophy of the testes and impotence may occur.
Leprosy can affect people in different ways. The average incubation period is 5 years. People may begin to notice symptoms within the first year or up to 20 years after infection. The first noticeable sign of leprosy is often the development of pale or pink coloured patches of skin that may be insensitive to temperature or pain. Patches of discolored skin are sometimes accompanied or preceded by nerve problems including numbness or tenderness in the hands or feet. Secondary infections (additional bacterial or viral infections) can result in tissue loss, causing fingers and toes to become shortened and deformed, as cartilage is absorbed into the body. A person's immune response differs depending on the form of leprosy.
Approximately 30% of people affected with leprosy experience nerve damage. The nerve damage sustained is reversible when treated early, but becomes permanent when appropriate treatment is delayed by several months. Damage to nerves may cause loss of muscle function, leading to paralysis. It may also lead to sensation abnormalities or numbness, which may lead to additional infections, ulcerations, and joint deformities.
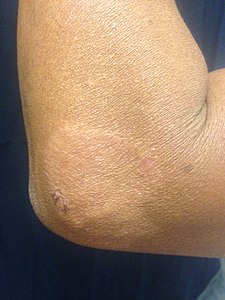
Paucibacillary leprosy (PB): Pale skin patch with loss of sensation

Skin lesions on the thigh of a person with leprosy
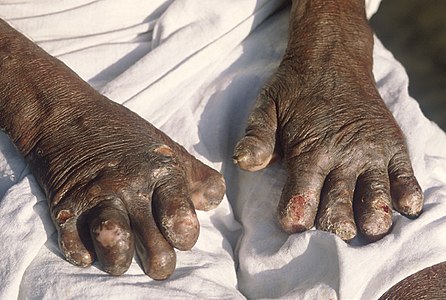
Hands deformed by leprosy
Cause
M. leprae and M. lepromatosis

M. leprae and M. lepromatosis are the mycobacteria that cause leprosy. M. lepromatosis is a relatively newly identified mycobacterium isolated from a fatal case of diffuse lepromatous leprosy in 2008. M. lepromatosis is indistinguishable clinically from M. leprae.
M. leprae is an intracellular, acid-fast bacterium that is aerobic and rod-shaped. M. leprae is surrounded by the waxy cell envelope coating characteristic of the genus Mycobacterium.
Genetically, M. leprae and M. lepromatosis lack the genes that are necessary for independent growth. M. leprae and M. lepromatosis are obligate intracellular pathogens, and can not be grown (cultured) in the laboratory. The inability to culture M. leprae and M. lepromatosis has resulted in a difficulty definitively identifying the bacterial organism under a strict interpretation of Koch's postulates.
While the causative organisms have to date been impossible to culture in vitro, it has been possible to grow them in animals such as mice and armadillos.
Naturally occurring infection has been reported in nonhuman primates (including the African chimpanzee, the sooty mangabey, and the cynomolgus macaque), armadillos, and red squirrels. Multilocus sequence typing of the armadillo M. leprae strains suggests that they were of human origin for at most a few hundred years. Thus, it is suspected that armadillos first acquired the organism incidentally from early American explorers. This incidental transmission was sustained in the armadillo population, and it may be transmitted back to humans, making leprosy a zoonotic disease (spread between humans and animals).
Red squirrels (Sciurus vulgaris), a threatened species in Great Britain, were found to carry leprosy in November 2016. It has been suggested that the trade in red squirrel fur, highly prized in the medieval period and intensively traded, may have been responsible for the leprosy epidemic in medieval Europe. A pre-Norman-era skull excavated in Hoxne, Suffolk, in 2017 was found to carry DNA from a strain of Mycobacterium leprae, which closely matched the strain carried by modern red squirrels on Brownsea Island, UK.
Risk factors
The greatest risk factor for developing leprosy is contact with another person infected by leprosy. People who are exposed to a person who has leprosy are 5–8 times more likely to develop leprosy than members of the general population. Leprosy also occurs more commonly among those living in poverty. Not all people who are infected with M. leprae develop symptoms.
Conditions that reduce immune function, such as malnutrition, other illnesses, or genetic mutations, may increase the risk of developing leprosy. Infection with HIV does not appear to increase the risk of developing leprosy. Certain genetic factors in the person exposed have been associated with developing lepromatous or tuberculoid leprosy.
Transmission
Transmission of leprosy occurs during close contact with those who are infected. Transmission of leprosy is not well understood, but the upper respiratory tract is thought to be the most likely entry route. Older research suggested the skin as the main route of transmission, but recent research has increasingly favored the respiratory route.
Leprosy is not sexually transmitted and is not spread through pregnancy to the unborn child. The majority (95%) of people who are exposed to M. Leprae do not develop leprosy; casual contact such as shaking hands and sitting next to someone with leprosy does not lead to transmission. People are considered non-infectious 72 hours after starting appropriate multi-drug therapy.
Two exit routes of M. leprae from the human body often described are the skin and the nasal mucosa, although their relative importance is not clear. Lepromatous cases show large numbers of organisms deep in the dermis, but whether they reach the skin surface in sufficient numbers is doubtful.
Leprosy may also be transmitted to humans by armadillos, although the mechanism is not fully understood.
Genetics
| Name | Locus | OMIM | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPRS1 | 10p13 | 609888 | |
| LPRS2 | 6q25 | 607572 | PARK2, PACRG |
| LPRS3 | 4q32 | 246300 | TLR2 |
| LPRS4 | 6p21.3 | 610988 | LTA |
| LPRS5 | 4p14 | 613223 | TLR1 |
| LPRS6 | 13q14.11 | 613407 |
Not all people who are infected or exposed to M. leprae develop leprosy, and genetic factors are suspected to play a role in susceptibility to an infection. Cases of leprosy often cluster in families and several genetic variants have been identified. In many people who are exposed, the immune system is able to eliminate the leprosy bacteria during the early infection stage before severe symptoms develop. A genetic defect in cell-mediated immunity may cause a person to be susceptible to develop leprosy symptoms after exposure to the bacteria. The region of DNA responsible for this variability is also involved in Parkinson's disease, giving rise to current speculation that the two disorders may be linked at the biochemical level.
Mechanism
Most leprosy complications are the result of nerve damage. The nerve damage occurs due to direct invasion by the M. leprae bacteria and a person's immune response resulting in inflammation. The molecular mechanism underlying how M. leprae produces the symptoms of leprosy is not clear, but M. leprae has been shown to bind to Schwann cells, which may lead to nerve injury including demyelination and a loss of nerve function (specifically a loss of axonal conductance). Numerous molecular mechanisms have been associated with this nerve damage including the presence of a laminin-binding protein and the glycoconjugate (PGL-1) on the surface of M. leprae that can bind to laminin on peripheral nerves.
As part of the human immune response, white blood cell-derived macrophages may engulf M. leprae by phagocytosis.
In the initial stages, small sensory and autonomic nerve fibers in the skin of a person with leprosy are damaged. This damage usually results in hair loss to the area, a loss of the ability to sweat, and numbness (decreased ability to detect sensations such as temperature and touch). Further peripheral nerve damage may result in skin dryness, more numbness, and muscle weaknesses or paralysis in the area affected. The skin can crack and if the skin injuries are not carefully cared for, there is a risk for a secondary infection that can lead to more severe damage.
Diagnosis

In countries where people are frequently infected, a person is considered to have leprosy if they have one of the following two signs:
- Skin lesion consistent with leprosy and with definite sensory loss.
- Positive skin smears.
Skin lesions can be single or many, and usually hypopigmented, although occasionally reddish or copper-colored. The lesions may be flat (macules), raised (papules), or solid elevated areas (nodular). Experiencing sensory loss at the skin lesion is a feature that can help determine if the lesion is caused by leprosy or if the lesion is caused by another disorder such as tinea versicolor. Thickened nerves are associated with leprosy and can be accompanied by loss of sensation or muscle weakness, but without the characteristic skin lesion and sensory loss, muscle weakness is not considered a reliable sign of leprosy.
In some cases, acid-fast leprosy bacilli in skin smears are considered diagnostic; however, the diagnosis is typically made without laboratory tests, based on symptoms. If a person has a new leprosy diagnosis and already has a visible disability due to leprosy, the diagnosis is considered late.
In countries or areas where leprosy is uncommon, such as the United States, diagnosis of leprosy is often delayed because healthcare providers are unaware of leprosy and its symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment prevent nerve involvement, the hallmark of leprosy, and the disability it causes.
There is no recommended test to diagnose latent leprosy in people without symptoms. Few people with latent leprosy test positive for anti PGL-1. The presence of M. leprae bacterial DNA can be identified using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based technique. This molecular test alone is not sufficient to diagnose a person, but this approach may be used to identify someone who is at high risk of developing or transmitting leprosy such as those with few lesions or an atypical clinical presentation.
Classification
Several different approaches for classifying leprosy exist. There are similarities between the classification approaches.
- The World Health Organization system distinguishes "paucibacillary" and "multibacillary" based upon the proliferation of bacteria. ("pauci-" refers to a low quantity.)
- The Ridley-Jopling scale provides five gradations.
- The ICD-10, though developed by the WHO, uses Ridley-Jopling and not the WHO system. It also adds an indeterminate ("I") entry.
- In MeSH, three groupings are used.
| WHO | Ridley-Jopling | ICD-10 | MeSH | Description | Lepromin test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paucibacillary | tuberculoid ("TT"), borderline tuberculoid ("BT") |
A30.1, A30.2 | Tuberculoid | It is characterized by one or more hypopigmented skin macules and patches where skin sensations are lost because of damaged peripheral nerves that have been attacked by the human host's immune cells. TT is characterized by the formation of epithelioid cell granulomas with a large number of epithelioid cells. In this form of leprosy Mycobacterium leprae are either absent from the lesion or occur in very small numbers. This type of leprosy is most benign. | Positive |
| Multibacillary | midborderline or borderline ("BB") |
A30.3 | Borderline | Borderline leprosy is of intermediate severity and is the most common form. Skin lesions resemble tuberculoid leprosy, but are more numerous and irregular; large patches may affect a whole limb, and peripheral nerve involvement with weakness and loss of sensation is common. This type is unstable and may become more like lepromatous leprosy or may undergo a reversal reaction, becoming more like the tuberculoid form. | |
| Multibacillary | borderline lepromatous ("BL"), and lepromatous ("LL") |
A30.4, A30.5 | Lepromatous | It is associated with symmetric skin lesions, nodules, plaques, thickened dermis, and frequent involvement of the nasal mucosa resulting in nasal congestion and nose bleeds, but, typically, detectable nerve damage is late. Loss of eyebrows and lashes can be seen in advanced disease. LL is characterized by the absence of epithelioid cells in the lesions. In this form of leprosy Mycobacterium leprae are found in lesion in large numbers. This is the most unfavorable clinical variant of leprosy, which occurs with a generalized lesion of the skin, mucous membranes, eyes, peripheral nerves, lymph nodes, and internal organs. | Negative |
Leprosy may also occur with only neural involvement, without skin lesions.
Prevention
Early detection of the disease is important, since physical and neurological damage may be irreversible even if cured. Medications can decrease the risk of those living with people who have leprosy from acquiring the disease and likely those with whom people with leprosy come into contact outside the home. The WHO recommends that preventive medicine be given to people who are in close contact with someone who has leprosy. The suggested preventive treatment is a single dose of rifampicin (SDR) in adults and children over 2 years old who do not already have leprosy or tuberculosis. Preventive treatment is associated with a 57% reduction in infections within 2 years and a 30% reduction in infections within 6 years.
The Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine offers a variable amount of protection against leprosy in addition to its target of tuberculosis. It appears to be 26% to 41% effective (based on controlled trials) and about 60% effective based on observational studies with two doses possibly working better than one. The WHO concluded in 2018 that the BCG vaccine at birth reduces leprosy risk and is recommended in countries with high incidence of TB and leprosy. Development of a more effective vaccine is ongoing.
Treatment
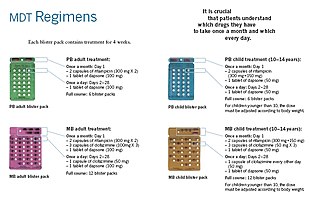
Anti-leprosy medication
A number of leprostatic agents are available for treatment. A 3-drug regimen of rifampicin, dapsone and clofazimine is recommended for all people with leprosy, for 6 months for paucibacillary leprosy and 12 months for multibacillary leprosy.
Multidrug therapy (MDT) remains highly effective, and people are no longer infectious after the first monthly dose. It is safe and easy to use under field conditions due to its presentation in calendar blister packs. Post-treatment relapse rates remain low. Resistance has been reported in several countries, although the number of cases is small. People with rifampicin-resistant leprosy may be treated with second line drugs such as fluoroquinolones, minocycline, or clarithromycin, but the treatment duration is 24 months due to their lower bactericidal activity. Evidence on the potential benefits and harms of alternative regimens for drug-resistant leprosy is not yet available.
Skin changes
For people with nerve damage, protective footwear may help prevent ulcers and secondary infection. Canvas shoes may be better than PVC-boots. There may be no difference between double rocker shoes and below-knee plaster.
Topical ketanserin seems to have a better effect on ulcer healing than clioquinol cream or zinc paste, but the evidence for this is weak. Phenytoin applied to the skin improves skin changes to a greater degree when compared to saline dressings.
Epidemiology
 6/67/Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png/400px-Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png" decoding="async" width="400" height="231" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/67/Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png/600px-Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/67/Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png/800px-Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png 2x" data-file-width="3168" data-file-height="1832">
6/67/Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png/400px-Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png" decoding="async" width="400" height="231" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/67/Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png/600px-Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/67/Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png/800px-Leprosy_new_case_detection_2016_rates%2C_2016_%28cropped%29.png 2x" data-file-width="3168" data-file-height="1832"> 
In 2018, there were 208,619 new cases of leprosy recorded, a slight decrease from 2017. In 2015, 94% of the new leprosy cases were confined to 14 countries. India reported the greatest number of new cases (60% of reported cases), followed by Brazil (13%) and Indonesia (8%). Although the number of cases worldwide continues to fall, there are parts of the world where leprosy is more common, including Brazil, South Asia (India, Nepal, Bhutan), some parts of Africa (Tanzania, Madagascar, Mozambique), and the western Pacific. About 150 to 250 cases are diagnosed in the United States each year.
In the 1960s, there were tens of millions of leprosy cases recorded when the bacteria started to develop resistance to dapsone, the most common treatment option at the time. International (e.g., the WHO's "Global Strategy for Reducing Disease Burden Due to Leprosy") and national (e.g., the International Federation of Anti-Leprosy Associations) initiatives have reduced the total number and the number of new cases of the disease.
Disease burden
The number of new leprosy cases is difficult to measure and monitor due to leprosy's long incubation period, delays in diagnosis after onset of the disease, and lack of medical care in affected areas. The registered prevalence of the disease is used to determine disease burden. Registered prevalence is a useful proxy indicator of the disease burden, as it reflects the number of active leprosy cases diagnosed with the disease and receiving treatment with MDT at a given point in time. The prevalence rate is defined as the number of cases registered for MDT treatment among the population in which the cases have occurred, again at a given point in time.
History

Using comparative genomics, in 2005, geneticists traced the origins and worldwide distribution of leprosy from East Africa or the Near East along human migration routes. They found four strains of M. leprae with specific regional locations. Strain 1 occurs predominantly in Asia, the Pacific region, and East Africa; strain 4, in West Africa and the Caribbean; strain 3 in Europe, North Africa, and the Americas; and strain 2 only in Ethiopia, Malawi, Nepal, north India, and New Caledonia.
On the basis of this, they offer a map of the dissemination of leprosy in the world. This confirms the spread of the disease along the migration, colonisation, and slave trade routes taken from East Africa to India, West Africa to the New World, and from Africa into Europe and vice versa.
The oldest skeletal evidence for the disease dates from 2000 BC, as found in human remains from the archaeological sites of Balathal in India and Harappa in Pakistan.
Although retrospectively identifying descriptions of leprosy-like symptoms is difficult, what appears to be leprosy was discussed by Hippocrates in 460 BC. In 1846, Francis Adams produced The Seven Books of Paulus Aegineta which included a commentary on all medical and surgical knowledge and descriptions and remedies to do with leprosy from the Romans, Greeks, and Arabs.
Interpretations of the presence of leprosy have been made on the basis of descriptions in ancient Indian (Atharvaveda and Kausika Sutra), Greek, and Middle Eastern (Tzaraath) documentary sources that describe skin afflictions.
Leprosy probably did not exist in Greece or the Middle East before Common Era. It did not exist in the Americas before colonization by modern Europeans. It did not exist in Polynesia until the middle of the 19th century.
Skeletal remains from the second millennium BCE, discovered in 2009, represent the oldest documented evidence for leprosy. Located at Balathal, in Rajasthan, northwest India, the discoverers suggest that if the disease did migrate from Africa to India, during the third millennium BCE "at a time when there was substantial interaction among the Indus Civilization, Mesopotamia, and Egypt, there needs to be additional skeletal and molecular evidence of leprosy in India and Africa so as to confirm the African origin of the disease." A proven human case was verified by DNA taken from the shrouded remains of a man discovered in a tomb next to the Old City of Jerusalem dated by radiocarbon methods to 1–50 AD.

However, a study published in 2018 found the oldest strains of leprosy in remains from Europe, the oldest strain being from Great Chesterford in southeast England and dating back to 415 to 545 AD. These findings suggest a different path for the spread of leprosy, meaning it may have originated in Western Eurasia. This study also indicates that there were more strains in Europe at the time than previously determined.
The causative agent of leprosy, M. leprae, was discovered by G. H. Armauer Hansen in Norway in 1873, making it the first bacterium to be identified as causing disease in humans.
The first effective treatment (promin) became available in the 1940s. In the 1950s, dapsone was introduced. The search for further effective antileprosy drugs led to the use of clofazimine and rifampicin in the 1960s and 1970s. Later, Indian scientist Shantaram Yawalkar and his colleagues formulated a combined therapy using rifampicin and dapsone, intended to mitigate bacterial resistance. Multi-drug therapy (MDT) combining all three drugs was first recommended by the WHO in 1981. These three antileprosy drugs are still used in the standard MDT regimens.
Leprosy was once believed to be highly contagious and was treated with mercury, as was syphilis, which was first described in 1530. Many early cases thought to be leprosy could actually have been syphilis.
Resistance has developed to initial treatment. Until the introduction of MDT in the early 1980s, leprosy could not be diagnosed and treated successfully within the community.
Japan still has sanatoriums (although Japan's sanatoriums no longer have active leprosy cases, nor are survivors held in them by law).
The importance of the nasal mucosa in the transmission of M leprae was recognized as early as 1898 by Schäffer, in particular, that of the ulcerated mucosa. The mechanism of plantar ulceration in leprosy and its treatment was first described by Dr Ernest W Price.
Society and culture
 6/65/Leprosorium.jpg/290px-Leprosorium.jpg" decoding="async" width="290" height="144" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Leprosorium.jpg/435px-Leprosorium.jpg 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Leprosorium.jpg/580px-Leprosorium.jpg 2x" data-file-width="1000" data-file-height="497">
6/65/Leprosorium.jpg/290px-Leprosorium.jpg" decoding="async" width="290" height="144" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Leprosorium.jpg/435px-Leprosorium.jpg 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Leprosorium.jpg/580px-Leprosorium.jpg 2x" data-file-width="1000" data-file-height="497"> The word "leprosy" comes from the Greek word "λέπος (lépos) – skin" and "λεπερός (leperós) – scaly man.
India
British India enacted the Leprosy Act of 1898 which institutionalized those affected and segregated them by sex to prevent reproduction. The act was difficult to enforce but was repealed in 1983 only after multidrug therapy had become widely available. In 1983, the National Leprosy Elimination Programme, previously the National Leprosy Control Programme, changed its methods from surveillance to the treatment of people with leprosy. India still accounts for over half of the global disease burden. According to WHO, new cases in India during 2019 diminished to 114,451 patients (57% of the world's total new cases). Until 2019, one could justify a petition for divorce with the spouse's diagnosis of leprosy.
Treatment cost
Between 1995 and 1999, the WHO, with the aid of the Nippon Foundation, supplied all endemic countries with free multidrug therapy in blister packs, channeled through ministries of health. This free provision was extended in 2000 and again in 2005, 2010 and 2015 with donations by the multidrug therapy manufacturer Novartis through the WHO. In the latest agreement signed between the company and the WHO in October 2015, the provision of free multidrug therapy by the WHO to all endemic countries will run until the end of 2020. At the national level, nongovernment organizations affiliated with the national program will continue to be provided with an appropriate free supply of multidrug therapy by the WHO.
Historical texts
Written accounts of leprosy date back thousands of years. Various skin diseases translated as leprosy appear in the ancient Indian text, the Atharava Veda, by 600 BC. Another Indian text, the Manusmriti (200 BC), prohibited contact with those infected with the disease and made marriage to a person infected with leprosy punishable.
The Hebraic root tsara or tsaraath (צָרַע,—tsaw-rah'—to be struck with leprosy, to be leprous) and the Greek (λεπρός—lepros), are of broader classification than the more narrow use of the term related to Hansen's Disease. Any progressive skin disease (a whitening or splotchy bleaching of skin, raised manifestations of scales, scabs, infections, rashes, etc....) as well as generalized molds and surface discoloration of any clothing, leather, or discoloration on walls or surfaces throughout homes all came under the "law of leprosy" (Leviticus 14:54–57). Ancient sources also such as the Talmud (Sifra 63) make clear that tzaraath refers to various types of lesions or stains associated with ritual impurity and occurring on cloth, leather, or houses, as well as skin. The New Testament describes instances of Jesus healing people with leprosy in Luke 17:11, although the relationship between this disease, tzaraath, and Hansen's disease is not established.
The biblical perception that people with leprosy were unclean can be found in a passage from Leviticus 13: 44–46. While this text defines the leper as impure, it did not explicitly make a moral judgement on those with leprosy. Some Early Christians believed that those affected by leprosy were being punished by God for sinful behavior. Moral associations have persisted throughout history. Pope Gregory the Great (540–604) and Isidor of Seville (560–636) considered people with the disease to be heretics.
Middle Ages

It is believed that a rise in leprosy in Western Europe occurred in the Middle Ages based on the increased number of hospitals created to treat people with leprosy in the 12th and 13th centuries. France alone had nearly 2,000 leprosariums during this period.
The social perception of leprosy in medieval communities was generally one of fear, and people infected with the disease were thought to be unclean, untrustworthy, and morally corrupt. Segregation from mainstream society was common, and people with leprosy were often required to wear clothing that identified them as such or carry a bell announcing their presence. The third Lateran Council of 1179 and a 1346 edict by King Edward expelled lepers from city limits. Because of the moral stigma of the disease, methods of treatment were both physical and spiritual, and leprosariums were established under the purview of the Roman Catholic Church.
19th century

Norway
Norway was the location of a progressive stance on leprosy tracking and treatment and played an influential role in European understanding of the disease. In 1832, Dr. JJ Hjort conducted the first leprosy survey, thus establishing a basis for epidemiological surveys. Subsequent surveys resulted in the establishment of a national leprosy registry to study the causes of leprosy and for tracking of the rate of infection.
Early leprosy research throughout Europe was conducted by Norwegian scientists Daniel Cornelius Danielssen and Carl Wilhelm Boeck. Their work resulted in the establishment of the National Leprosy Research and Treatment Center. Danielssen and Boeck believed the cause of leprosy transmission was hereditary. This stance was influential in advocating for the isolation of those infected by sex to prevent reproduction.
Colonialism and imperialism

Though leprosy in Europe was again on the decline by the 1860s, Western countries embraced isolation treatment out of fear of the spread of disease from developing countries, minimal understanding of bacteriology, lack of diagnostic ability or knowledge of how contagious the disease was, and missionary activity. Growing imperialism and pressures of the industrial revolution resulted in a Western presence in countries where leprosy was endemic, namely the British presence in India. Isolation treatment methods were observed by Surgeon-Mayor Henry Vandyke Carter of the British Colony in India while visiting Norway, and these methods were applied in India with the financial and logistical assistance of religious missionaries. Colonial and religious influence and associated stigma continued to be a major factor in the treatment and public perception of leprosy in endemic developing countries until the mid-twentieth century.
Stigma
Despite effective treatment and education efforts, leprosy stigma continues to be problematic in developing countries where the disease is common. Leprosy is most common amongst impoverished or marginalized populations where social stigma is likely to be compounded by other social inequities. Fears of ostracism, loss of employment, or expulsion from family and society may contribute to a delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Folk beliefs, lack of education, and religious connotations of the disease continue to influence social perceptions of those afflicted in many parts of the world. In Brazil, for example, folklore holds that leprosy is transmitted by dogs, it is a disease associated with sexual promiscuity, and is sometimes thought to be a punishment for sins or moral transgressions (distinct from other diseases and misfortunes in general being accorded to the will of God). Socioeconomic factors also have a direct impact. Lower-class domestic workers who are often employed by those in a higher socioeconomic class may find their employment in jeopardy as physical manifestations of the disease become apparent. Skin discoloration and darker pigmentation resulting from the disease also have social repercussions.
In extreme cases in northern India, leprosy is equated with an "untouchable" status that "often persists long after individuals with leprosy have been cured of the disease, creating lifelong prospects of divorce, eviction, loss of employment, and ostracism from family and social networks."

Leprosy in Tahiti, circa 1895



