Splenomegaly

Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension.
Definition
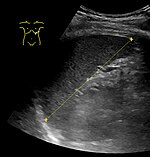
The standard system for classifying splenomegaly on radiography is:
- Normal (not splenomegaly): the largest dimension is less than 11 cm
- Moderate splenomegaly: the largest dimension is between 11–20 cm
- Severe splenomegaly: the largest dimension is greater than 20 cm
Also, a cutoff of a craniocaudal height of 13 cm is also used to define splenomegaly. In addition, individual intervals have been established:
| Height | Spleen length | |
|---|---|---|
| Women | Men | |
| 155 – 159 cm | 6.4 – 12 cm | |
| 160 – 164 cm | 7.4 - 12.2 cm | 8.9 - 11.3 cm |
| 165 – 169 cm | 7.5 – 11.9 cm | 8.5 – 12.5 cm |
| 170 – 174 cm | 8.3 – 13.0 cm | 8.6 – 13.1 cm |
| 175 – 179 cm | 8.1 – 12.3 cm | 8.6 – 13.4 cm |
| 180 – 184 cm | 9.3 – 13.4 cm | |
| 185 – 189 cm | 9.3 – 13.6 cm | |
| 190 – 194 cm | 9.7 – 14.3 cm | |
| 195 – 199 cm | 10.2 – 14.4 cm | |
| Age | Cutoff |
|---|---|
| 3 months | 6.0 cm |
| 6 months | 6.5 cm |
| 12 months | 7.0 cm |
| 2 years | 8.0 cm |
| 4 years | 9.0 |
| 6 years | 9.5 cm |
| 8 years | 10.0 cm |
| 10 years | 11.0 cm |
| 12 years | 11.5 cm |
| 15 years |
|
For children, the cutoffs for splenomegaly are given in this table, when measuring the greatest length of the spleen between its dome and its tip, in the coronal plane through its hilum while breathing quietly.
At autopsy, splenomegaly can be defined as a spleen weight above the upper limit of the standard reference range of 230 g (8.1 oz).
Splenomegaly refers strictly to spleen enlargement, and is distinct from hypersplenism, which connotes overactive function by a spleen of any size. Splenomegaly and hypersplenism should not be confused. Each may be found separately, or they may coexist. Clinically, if a spleen is palpable (felt via external examination), it means it is enlarged as it has to undergo at least twofold enlargement to become palpable. However, the tip of the spleen may be palpable in a newborn baby up to three months of age.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include abdominal pain, chest pain, chest pain similar to pleuritic pain when stomach, bladder or bowels are full, back pain, early satiety due to splenic encroachment, or the symptoms of anemia due to accompanying cytopenia.
Signs of splenomegaly may include a palpable left upper quadrant abdominal mass or splenic rub. It can be detected on physical examination by using Castell's sign, Traube's space percussion or Nixon's sign, but an ultrasound can be used to confirm diagnosis. In patients where the likelihood of splenomegaly is high, the physical exam is not sufficiently sensitive to detect it; abdominal imaging is indicated in such patients.
In cases of infectious mononucleosis splenomegaly is a common symptom and health care providers may consider using abdominal ultrasonography to get insight into a person's condition. However, because spleen size varies greatly, ultrasonography is not a valid technique for assessing spleen enlargement and should not be used in typical circumstances or to make routine decisions about fitness for playing sports.
Causes
The most common causes of splenomegaly in developed countries are infectious mononucleosis, splenic infiltration with cancer cells from a hematological malignancy and portal hypertension (most commonly secondary to liver disease, and sarcoidosis). Splenomegaly may also come from bacterial infections, such as syphilis or an infection of the heart's inner lining (endocarditis). Splenomegaly also occurs in mammals parasitized by Cuterebra fontinella.
The possible causes of moderate splenomegaly (spleen <1000 g) are many, and include:
| Increased function | Abnormal blood flow | Infiltration |
|---|---|---|
Removal of defective RBCs
Immune hyperplasia Response to infection (viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic)
Disordered immunoregulation
Extramedullary hematopoiesis
|
Organ Failure
Vascular
Infections
|
Metabolic diseases
Benign and malignant “infiltrations”
|

The causes of massive splenomegaly (spleen >1000 g) are
- chronic myelogenous leukemia
- myelofibrosis
- malaria
- splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Pathophysiology
Splenomegaly can be classified based on its pathophysiologic mechanism:
- Congestive, by pooled blood (e.g., portal hypertension)
- Infiltrative, by invasion by cells foreign to the splenic environment (e.g., metastases, myeloid neoplasms, lipid storage diseases)
- Immune, by an increase in immunologic activity and subsequent hyperplasia (e.g., endocarditis, sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Neoplastic, when resident immune cells originate a neoplasm (e.g., lymphoma).
Diagnosis
Abdominal CT is the most accurate.
Treatment
If the splenomegaly underlies hypersplenism, a splenectomy is indicated and will correct the hypersplenism. However, the underlying cause of the hypersplenism will most likely remain; consequently, a thorough diagnostic workup is still indicated, as, leukemia, lymphoma and other serious disorders can cause hypersplenism and splenomegaly. After splenectomy, however, patients have an increased risk for infectious diseases.
Patients undergoing splenectomy should be vaccinated against Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Meningococcus. They should also receive annual influenza vaccinations. Long-term prophylactic antibiotics may be given in certain cases.
As an adaptation
An enlarged spleen may be an inherited, adaptive trait selected in populations that need extra oxygen carry capacity such as deep sea divers.
See also
- Asplenia
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Portal hypertension
- Sign (medicine)
- Splenic infarction
- Tropical splenomegaly syndrome