Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome 2
A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS2) is caused by heterozygous mutation in the NKX2-5 gene (600584) on chromosome 5q35.1.
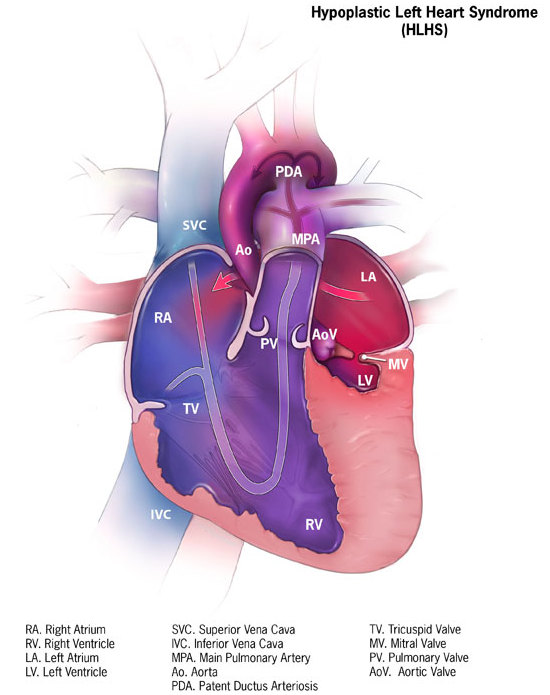
DescriptionHypoplastic left heart syndrome results from defective development of the aorta proximal to the entrance of the ductus arteriosus and hypoplasia of the left ventricle and mitral valve. As a result of the abnormal circulation, the ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale are patent and the right atrium, right ventricle, and pulmonary artery are enlarged (Brekke, 1953).
For a discussion of genetic heterogeneity of hypoplastic left heart syndrome, see HLHS1 (241550).
Molecular GeneticsIn 1 (1%) of 80 patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome, McElhinney et al. (2003) identified heterozygosity for a missense mutation in the NKX2-5 gene (R25C; 600584.0004).
In 1 of 9 patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome, Stallmeyer et al. (2010) identified heterozygosity for the R25C mutation in the NKX2-5 gene. The complete cardiac phenotype of the male infant included atresia of the aortic and mitral valves and a small VSD that required corrective surgery.