Parkinson's Disease

Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly and, as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor symptoms are also known as "parkinsonism" or a "parkinsonian syndrome".
The cause of PD is unknown, with both inherited and environmental factors being believed to play a role. Those with a family member affected by PD are at an increased risk of getting the disease, with certain genes known to be inheritable risk factors. Other risk factors are those who have been exposed to certain pesticides and who have prior head injuries. Tobacco smokers and coffee and tea drinkers are at a reduced risk.
Diagnosis of typical cases is mainly based on symptoms, with motor symptoms being the chief complaint. Tests such as neuroimaging (MRI or imaging to look at dopamine neuronal dysfunction known as DaT scan) can be used to help rule out other diseases. Parkinson's disease typically occurs in people over the age of 60, of whom about one percent are affected. Males are more often affected than females at a ratio of around 3:2. When it is seen in people before the age of 50, it is called early-onset PD. In 2015, PD affected 6.2 million people and resulted in about 117,400 deaths globally. The average life expectancy following diagnosis is between 7 and 15 years.
There is no cure for PD; treatment aims to improve the symptoms. Initial treatment is typically with the medications levodopa (L-DOPA), MAO-B inhibitors, or dopamine agonists. As the disease progresses, these medications become less effective, while at the same time producing a side effect marked by involuntary muscle movements. At that time, medications may be used in combination and doses may be increased. Diet and certain forms of rehabilitation have shown some effectiveness at improving symptoms. Surgery to place microelectrodes for deep brain stimulation has been used to reduce motor symptoms in severe cases where drugs are ineffective. Evidence for treatments for the non-movement-related symptoms of PD, such as sleep disturbances and emotional problems, is less strong.
The disease is named after the English doctor James Parkinson, who published the first detailed description in An Essay on the Shaking Palsy, in 1817. Public awareness campaigns include World Parkinson's Day (on the birthday of James Parkinson, 11 April) and the use of a red tulip as the symbol of the disease. People with Parkinson's who have increased the public's awareness of the condition include the boxer Muhammad Ali, actor Michael J. Fox, Olympic cyclist Davis Phinney, and actor Alan Alda.
Classification
Parkinson's disease is the most common form of parkinsonism and is sometimes called "idiopathic parkinsonism", meaning parkinsonism with no identifiable cause. Scientists sometimes refer to Parkinson’s disease as a type of neurodegenerative disease called synucleinopathy due to an abnormal accumulation of the protein alpha-synuclein in the brain. The synucleinopathy classification distinguishes Parkinson's disease from other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, where the brain accumulates a different protein known as the tau protein.
Considerable clinical and pathological overlap exists between tauopathies and synucleinopathies, however there are also differences. In contrast to Parkinson's disease, people with Alzheimer's disease most commonly experience memory loss. The cardinal signs of Parkinson's disease (slowness, tremor, stiffness, and postural instability) are not normal features of Alzheimer's.
Attempts to classify Parkinson's disease into different subtypes have been made, with focus put on age of onset, progression of symptoms, and dominance of tremor. None have currently been widely adopted as a complete model.
Signs and symptoms

The most recognizable symptoms in Parkinson's disease are movement ("motor") related. Non-motor symptoms, which include autonomic dysfunction, neuropsychiatric problems (mood, cognition, behavior or thought alterations), and sensory (especially altered sense of smell) and sleep difficulties, are also common. Some of these non-motor symptoms may be present at the time of diagnosis.
Motor
Four motor symptoms are considered cardinal in PD: tremor, slowness of movement (bradykinesia), rigidity, and postural instability.
The most common presenting sign is a coarse slow tremor of the hand at rest which disappears during voluntary movement of the affected arm and in the deeper stages of sleep. It typically appears in only one hand, eventually affecting both hands as the disease progresses. Frequency of PD tremor is between 4 and 6 hertz (cycles per second). A feature of tremor is pill-rolling, the tendency of the index finger and thumb to touch and perform together a circular movement. The term derives from the similarity between the movement of people with PD and the early pharmaceutical technique of manually making pills.
Bradykinesia (slowness of movement) is found in every case of PD, and is due to disturbances in motor planning of movement initiation, and associated with difficulties along the whole course of the movement process, from planning to initiation to execution of a movement. Performance of sequential and simultaneous movement is impaired. Bradykinesia is the most handicapping symptom of Parkinson’s disease leading to difficulties with everyday tasks such as dressing, feeding, and bathing. It leads to particular difficulty in carrying out two independent motor activities at the same time and can be made worse by emotional stress or concurrent illnesses. Paradoxically people with Parkinson's disease can often ride a bicycle or climb stairs more easily than walk on a level. While most physicians may readily notice bradykinesia, formal assessment requires a person to do repetitive movements with their fingers and feet.
Rigidity is stiffness and resistance to limb movement caused by increased muscle tone, an excessive and continuous contraction of muscles. In parkinsonism, the rigidity can be uniform, known as "lead-pipe rigidity," or ratchety, known as "cogwheel rigidity." The combination of tremor and increased tone is considered to be at the origin of cogwheel rigidity. Rigidity may be associated with joint pain; such pain being a frequent initial manifestation of the disease. In early stages of Parkinson's disease, rigidity is often asymmetrical and it tends to affect the neck and shoulder muscles prior to the muscles of the face and extremities. With the progression of the disease, rigidity typically affects the whole body and reduces the ability to move.
Postural instability is typical in the later stages of the disease, leading to impaired balance and frequent falls, and secondarily to bone fractures, loss of confidence, and reduced mobility. Instability is often absent in the initial stages, especially in younger people, especially prior to the development of bilateral symptoms. Up to 40% of people diagnosed with PD may experience falls and around 10% may have falls weekly, with the number of falls being related to the severity of PD.
Other recognized motor signs and symptoms include gait and posture disturbances such as festination (rapid shuffling steps and a forward-flexed posture when walking with no flexed arm swing). Freezing of gait (brief arrests when the feet seem to get stuck to the floor, especially on turning or changing direction), a slurred monotonous quiet voice, mask-like facial expression, and handwriting that gets smaller and smaller are other common signs.
Neuropsychiatric
Parkinson's disease can cause neuropsychiatric disturbances, which can range from mild to severe. This includes disorders of cognition, mood, behavior, and thought.
Cognitive disturbances can occur in the early stages of the disease and sometimes prior to diagnosis, and increase in prevalence with duration of the disease. The most common cognitive deficit in PD is executive dysfunction, which can include problems with planning, cognitive flexibility, abstract thinking, rule acquisition, inhibiting inappropriate actions, initiating appropriate actions, working memory, and control of attention. Other cognitive difficulties include slowed cognitive processing speed, impaired recall and impaired perception and estimation of time. Nevertheless, improvement appears when recall is aided by cues. Visuospatial difficulties are also part of the disease, seen for example when the individual is asked to perform tests of facial recognition and perception of the orientation of drawn lines.
A person with PD has two to six times the risk of dementia compared to the general population. Up to 78% of people with PD have Parkinson's disease dementia. The prevalence of dementia increases with age and, to a lesser degree, duration of the disease. Dementia is associated with a reduced quality of life in people with PD and their caregivers, increased mortality, and a higher probability of needing nursing home care.
Impulse control disorders including pathological gambling, compulsive sexual behavior, binge eating, compulsive shopping and reckless generosity can be caused by medication, particularly orally active dopamine agonists. The dopamine dysregulation syndrome – with wanting of medication leading to overusage – is a rare complication of levodopa use.
Punding in which complicated repetitive aimless stereotyped behaviors occur for many hours is another disturbance caused by anti-Parkinson medication.
Psychosis
Psychosis can be considered a symptom with a prevalence at its widest range from 26 to 83%. Hallucinations or delusions occur in approximately 50% of people with PD over the course of the illness, and may herald the emergence of dementia. These range from minor hallucinations – "sense of passage" (something quickly passing beside the person) or "sense of presence" (the perception of something/someone standing just to the side or behind the person) – to full blown vivid, formed visual hallucinations and paranoid ideation. Auditory hallucinations are uncommon in PD, and are rarely described as voices. It is now believed that psychosis is an integral part of the disease. A psychosis with delusions and associated delirium is a recognized complication of anti-Parkinson drug treatment and may also be caused by urinary tract infections (as frequently occurs in the fragile elderly), but drugs and infection are not the only factors, and underlying brain pathology or changes in neurotransmitters or their receptors (e.g., acetylcholine, serotonin) are also thought to play a role in psychosis in PD.
Behavior and mood
Behavior and mood alterations are more common in PD without cognitive impairment than in the general population, and are usually present in PD with dementia. The most frequent mood difficulties are depression, apathy, and anxiety.
Depression has been estimated to appear in anywhere from 20 to 35% of people with PD, and can appear at any stage of the disease. In Parkinson's, depression can manifest with symptoms that are common to the disease process (fatigue, insomnia, and difficulty with concentration) which makes diagnosis difficult. The imbalance and change in dopamine, serotonin, and noradrenergic hormones are known to be a primary cause of depression in PD affected people. Another cause is the functional impairment that is caused by the disease. Symptoms of depression can include loss of interest, sadness, guilt, feelings of helplessness/hopelessness/guilt, and suicidal ideation. Suicidal ideation in PD affected people is higher than in the general population, but suicidal attempts themselves are lower than in people with depression without PD. Risk factors for depression in PD can include disease onset under age 50, being a woman, previous history of depression, severe motor symptoms, and others.
Anxiety has been estimated to have a prevalence in PD affected people around 30%-40% (however up to 60% has been found). Anxiety can often be found during "off" periods (periods of time where medication is not working as well as it did before) with PD affected people suffering from panic attacks more frequently compared to the general population. Both anxiety and depression have been found to be associated with decreased quality of life. Symptoms can range from mild and episodic to chronic with potential causes being abnormal gamma-aminobutyric acid levels as well as embarrassment or fear about their symptoms/disease. Risk factors for anxiety in PD are disease onset under age 50, women, and "off" periods.
Apathy and anhedonia can be defined as a loss of motivation and an impaired ability to experience pleasure, respectively. They are symptoms classically associated with depression however differ in PD affected people in treatment, mechanism, and doesn't always occur with depression. Apathy presents in around 16.5-40%. Symptoms of apathy include reduced initiative/interests in new activities or the world around them, emotional indifference, and loss of affection or concern for others. Apathy is associated with deficits in cognitive functions including executive and verbal memory.
Other
Sleep disorders are a feature of the disease and can be worsened by medications. Symptoms can manifest as daytime drowsiness (including sudden sleep attacks resembling narcolepsy), disturbances in REM sleep, or insomnia. REM behavior disorder (RBD), in which people act out dreams, sometimes injuring themselves or their bed partner, may begin many years before the development of motor or cognitive features of PD or DLB.
Alterations in the autonomic nervous system can lead to orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure upon standing), oily skin and excessive sweating, urinary incontinence, and altered sexual function. Constipation and impaired stomach emptying (gastric dysmotility) can be severe enough to cause discomfort and even endanger health. Changes in perception may include an impaired sense of smell, disturbed vision, pain, and paresthesia (tingling and numbness). All of these symptoms can occur years before diagnosis of the disease.
Causes
Many risk factors have been proposed, sometimes in relation to theories concerning possible mechanisms of the disease; however, none have been conclusively proven. The most frequently replicated relationships are an increased risk in those exposed to pesticides, and a reduced risk in smokers. There is a possible link between PD and H. pylori infection that can prevent the absorption of some drugs including levodopa.
Environmental factors and exposures
Exposure to pesticides and a history of head injury have each been linked with Parkinson disease (PD), but the risks are modest. Never having smoked cigarettes, and never drinking caffeinated beverages, are also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of urate in the blood serum is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-Induced Parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been indicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include but not are not limited to:
- Phenothiazines (chlorpromazine, promazine, etc.)
- Butyrophenones (haloperidol, benperidol, etc.)
- Metoclopramide
- Tetrabenazine
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is a drug known for causing irreversible parkinsonism that is commonly used in animal model research.
Toxin-Induced Parkinsonism
Some toxins can cause parkinsonism. These toxins include but are not limited to manganese and carbon disulfide
Genetics
Research indicates that PD is the product of a complex interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Around 15% of individuals with PD have a first-degree relative who has the disease, and 5–10% of people with PD are known to have forms of the disease that occur because of a mutation in one of several specific genes. Harboring one of these gene mutations may not lead to the disease; susceptibility factors put the individual at an increased risk, often in combination with other risk factors, which also affect age of onset, severity and progression. At least 11 autosomal dominant and 9 autosomal recessive gene mutations have been implicated in the development of PD. The autosomal dominant genes include SNCA, PARK3, UCHL1, LRRK2, GIGYF2, HTRA2, EIF4G1, TMEM230, CHCHD2, RIC3, VPS35. Autosomal recessive genes include PRKN, PINK1, PARK7, ATP13A2, PLA2G6, FBXO7, DNAJC6, SYNJ1, and VPS13C. Some genes are x-linked or have unknown inheritance pattern: those include PARK10, PARK12, and PARK16. 22q11 deletion is also known to be associated with PD. An autosomal dominant form has been associated with mutations in the LRP10 gene.
About 5% of people with PD have mutations in the GBA1 gene. These mutations are present in less than 1% of the unaffected population. The risk of developing PD is increased 20–30 fold if these mutations are present. PD associated with these mutations has the same clinical features, but an earlier age of onset and a more rapid cognitive and motor decline. This gene encodes glucocerebrosidase. Low levels of this enzyme cause Gaucher's disease.
SNCA gene mutations are important in PD because the protein which this gene encodes, alpha-synuclein, is the main component of the Lewy bodies that accumulate in the brains of people with PD. Alpha-synuclein activates ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated), a major DNA damage repair signaling kinase. In addition, alpha-synuclein activates the non-homologous end joining DNA repair pathway. The aggregation of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies appears to be a link between reduced DNA repair and brain cell death in PD.
Mutations in some genes, including SNCA, LRRK2 and GBA, have been found to be risk factors for "sporadic" (non-familial) PD. Mutations in the gene LRRK2 are the most common known cause of familial and sporadic PD, accounting for approximately 5% of individuals with a family history of the disease and 3% of sporadic cases. A mutation in GBA presents the greatest genetic risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
Several Parkinson-related genes are involved in the function of lysosomes, organelles that digest cellular waste products. It has been suggested that some cases of PD may be caused by lysosomal disorders that reduce the ability of cells to break down alpha-synuclein.
Vascular Parkinsonism
Vascular parkinsonism is the phenomena of the presence of Parkinson's disease symptoms combined with findings of vascular events (such as a cerebral stroke). The damaging of the dopaminergic pathways are similar causes of both vascular parkinsonism and idiopathic Parkinson's Disease, so they can present with many of the same symptoms. Differentiation can be made with careful bedside examination, history taking, and imaging.
Other identifiable causes of parkinsonism include infections and metabolic derangement. Several neurodegenerative disorders also may present with parkinsonism and are sometimes referred to as "atypical parkinsonism" or "Parkinson plus" syndromes (illnesses with parkinsonism plus some other features distinguishing them from PD). They include multiple system atrophy, progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). Dementia with Lewy bodies is another synucleinopathy and it has close pathological similarities with PD, especially with the subset of PD cases with dementia known as Parkinson's disease dementia. The relationship between PD and DLB is complex and incompletely understood. They may represent parts of a continuum with variable distinguishing clinical and pathological features or they may prove to be separate diseases.
Pathophysiology
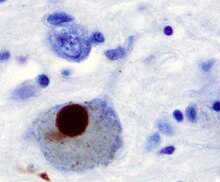
The main pathological characteristics of PD are cell death in the brain's basal ganglia (affecting up to 70% of the dopamine secreting neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta by the end of life). In Parkinson's disease, alpha-synuclein becomes misfolded and clump together with other alpha-synuclein. Cells are unable to remove these clumps and the alpha synuclein becomes cytotoxic, damaging the cells. These clumps can be seen in neurons under a microscope and are called Lewy bodies. Loss of neurons is accompanied by the death of astrocytes (star-shaped glial cells) and a significant increase in the number of microglia (another type of glial cell) in the substantia nigra. Braak staging is a way to explain the progression of the parts of the brain affected by Parkinson's disease. According to this staging, PD starts in the medulla and the olfactory bulb before moving to the substantia nigra pars compacta and the rest of the midbrain/basal foerbrain. Movement symptom onset is associated when the disease begins to affect the substantia nigra pars compacta.
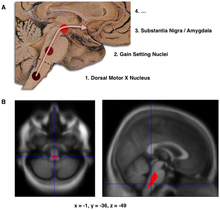
- Schematic initial progression of Lewy body deposits in the first stages of Parkinson's disease, as proposed by Braak and colleagues
- Localization of the area of significant brain volume reduction in initial PD compared with a group of participants without the disease in a neuroimaging study, which concluded that brainstem damage may be the first identifiable stage of PD neuropathology
There are five major pathways in the brain connecting other brain areas with the basal ganglia. These are known as the motor, oculo-motor, associative, limbic and orbitofrontal circuits, with names indicating the main projection area of each circuit. All of them are affected in PD, and their disruption explains many of the symptoms of the disease, since these circuits are involved in a wide variety of functions, including movement, attention and learning. Scientifically, the motor circuit has been examined the most intensively.
A particular conceptual model of the motor circuit and its alteration with PD has been of great influence since 1980, although some limitations have been pointed out which have led to modifications. In this model, the basal ganglia normally exert a constant inhibitory influence on a wide range of motor systems, preventing them from becoming active at inappropriate times. When a decision is made to perform a particular action, inhibition is reduced for the required motor system, thereby releasing it for activation. Dopamine acts to facilitate this release of inhibition, so high levels of dopamine function tend to promote motor activity, while low levels of dopamine function, such as occur in PD, demand greater exertions of effort for any given movement. Thus, the net effect of dopamine depletion is to produce hypokinesia, an overall reduction in motor output. Drugs that are used to treat PD, conversely, may produce excessive dopamine activity, allowing motor systems to be activated at inappropriate times and thereby producing dyskinesias.
Brain cell death
There is speculation of several mechanisms by which the brain cells could be lost. One mechanism consists of an abnormal accumulation of the protein alpha-synuclein bound to ubiquitin in the damaged cells. This insoluble protein accumulates inside neurons forming inclusions called Lewy bodies. According to the Braak staging, a classification of the disease based on pathological findings proposed by Heiko Braak, Lewy bodies first appear in the olfactory bulb, medulla oblongata and pontine tegmentum; individuals at this stage may be asymptomatic or may have early non-motor symptoms (such as loss of sense of smell, or some sleep or automatic dysfunction). As the disease progresses, Lewy bodies develop in the substantia nigra, areas of the midbrain and basal forebrain and, finally, the neocortex. These brain sites are the main places of neuronal degeneration in PD; however, Lewy bodies may not cause cell death and they may be protective (with the abnormal protein sequestered or walled off). Other forms of alpha-synuclein (e.g., oligomers) that are not aggregated in Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites may actually be the toxic forms of the protein. In people with dementia, a generalized presence of Lewy bodies is common in cortical areas. Neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques, characteristic of Alzheimer's disease, are not common unless the person is demented.
Other cell-death mechanisms include proteasomal and lysosomal system dysfunction and reduced mitochondrial activity. Iron accumulation in the substantia nigra is typically observed in conjunction with the protein inclusions. It may be related to oxidative stress, protein aggregation and neuronal death, but the mechanisms are not fully understood.
Diagnosis
A physician will initially assess for Parkinson's disease with a careful medical history and neurological examination. People may be given levodopa, with any resulting improvement in motor impairment helping to confirm the PD diagnosis. The finding of Lewy bodies in the midbrain on autopsy is usually considered final proof that the person had PD. The clinical course of the illness over time may reveal it is not Parkinson's disease, requiring that the clinical presentation be periodically reviewed to confirm accuracy of the diagnosis.
Other causes that can secondarily produce parkinsonism are stroke and drugs. Parkinson plus syndromes such as progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy must be ruled out. Anti-Parkinson's medications are typically less effective at controlling symptoms in Parkinson plus syndromes. Faster progression rates, early cognitive dysfunction or postural instability, minimal tremor or symmetry at onset may indicate a Parkinson plus disease rather than PD itself. Genetic forms with an autosomal dominant or recessive pattern of inheritance are sometimes referred to as familial Parkinson's disease or familial parkinsonism.
Medical organizations have created diagnostic criteria to ease and standardize the diagnostic process, especially in the early stages of the disease. The most widely known criteria come from the UK Queen Square Brain Bank for Neurological Disorders and the U.S. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. The Queen Square Brain Bank criteria require slowness of movement (bradykinesia) plus either rigidity, resting tremor, or postural instability. Other possible causes of these symptoms need to be ruled out. Finally, three or more of the following supportive features are required during onset or evolution: unilateral onset, tremor at rest, progression in time, asymmetry of motor symptoms, response to levodopa for at least five years, clinical course of at least ten years and appearance of dyskinesias induced by the intake of excessive levodopa.
When PD diagnoses are checked by autopsy, movement disorders experts are found on average to be 79.6% accurate at initial assessment and 83.9% accurate after they have refined their diagnosis at a follow-up examination. When clinical diagnoses performed mainly by nonexperts are checked by autopsy, average accuracy is 73.8%. Overall, 80.6% of PD diagnoses are accurate, and 82.7% of diagnoses using the Brain Bank criteria are accurate.
A task force of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society (MDS) has proposed diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease as well as research criteria for the diagnosis of prodromal disease, but these will require validation against the more established criteria.
Imaging
Computed tomography (CT) scans of people with PD usually appear normal. MRI has become more accurate in diagnosis of the disease over time, specifically through iron-sensitive T2* and SWI sequences at a magnetic field strength of at least 3T, both of which can demonstrate absence of the characteristic 'swallow tail' imaging pattern in the dorsolateral substantia nigra. In a meta-analysis, absence of this pattern was highly sensitive and specific for the disease. A 2020 meta-analysis found that neuromelanin-MRI had a favorable diagnostic performance in discriminating individuals with Parkinson's from healthy subjects. Diffusion MRI has shown potential in distinguishing between PD and Parkinson plus syndromes, though its diagnostic value is still under investigation. CT and MRI are also used to rule out other diseases that can be secondary causes of parkinsonism, most commonly encephalitis and chronic ischemic insults, as well as less frequent entities such as basal ganglia tumors and hydrocephalus.
The metabolic activity of dopamine transporters in the basal ganglia can be directly measured with PET and SPECT scans, with the DaTSCAN being a common proprietary version of this study. It has shown high agreement with clinical diagnoses of Parkinson's. Reduced dopamine-related activity in the basal ganglia can help exclude drug-induced Parkinsonism. This finding is not entirely specific, however, and can be seen with both PD and Parkinson-plus disorders. In the United States, DaTSCANs are only FDA approved to distinguish Parkinson’s disease or Parkinsonian syndromes from essential tremor.
Differential diagnosis
Other conditions that can have similar presentations to PD include:
- Arthritis
- Corticobasal syndrome
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Depression
- Drug induced parkinsonism
- Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome
- Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17
- Huntington’s disease
- Idiopathic basal ganglia calcification
- Multiple system atrophy
- Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation
- Normal-pressure hydrocephalus
- Obsessional slowness
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Psychogenic parkinsonism
- Toxins
- Wilson’s disease
- Vascular parkinsonism
Prevention
Exercise in middle age may reduce the risk of Parkinson's disease later in life. Caffeine also appears protective with a greater decrease in risk occurring with a larger intake of caffeinated beverages such as coffee. People who smoke cigarettes or use smokeless tobacco are less likely than non-smokers to develop PD, and the more they have used tobacco, the less likely they are to develop PD. It is not known what underlies this effect. Tobacco use may actually protect against PD, or it may be that an unknown factor both increases the risk of PD and causes an aversion to tobacco or makes it easier to stop using tobacco.
Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, have been proposed to protect against the disease, but results of studies have been contradictory and no positive effect has been proven. The results regarding fat and fatty acids have been contradictory, with various studies reporting protective effects, risk-increasing effects or no effects. There have been preliminary indications that the use of anti-inflammatory drugs and calcium channel blockers may be protective. A 2010 meta-analysis found that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (apart from aspirin), have been associated with at least a 15 percent (higher in long-term and regular users) reduction in the incidence of the development of Parkinson's disease.
Management
 1/10/Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png/220px-Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png" decoding="async" width="220" height="220" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/10/Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png/330px-Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/10/Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png/440px-Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png 2x" data-file-width="8500" data-file-height="8500">
1/10/Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png/220px-Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png" decoding="async" width="220" height="220" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/10/Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png/330px-Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/10/Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png/440px-Pharmacological_treatment_of_Parkinson%27s_disease.png 2x" data-file-width="8500" data-file-height="8500"> There is no cure for Parkinson's disease. Medications, surgery, and physical treatment may provide relief, improve the quality of a persons life, and are much more effective than treatments available for other neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, motor neuron disease, and Parkinson plus syndromes. The main families of drugs useful for treating motor symptoms are levodopa (always combined with a dopa decarboxylase inhibitor and sometimes also with a COMT inhibitor, dopamine agonists and MAO-B inhibitors. The stage of the disease and the age at disease onset determine which group is most useful.
Braak staging of Parkinson's disease gives six stages, that can be used to identify early stages, later stages, and late stages. The initial stage in which some disability has already developed and requires pharmacological treatment is followed by later stages associated with the development of complications related to levodopa usage, and a third stage when symptoms unrelated to dopamine deficiency or levodopa treatment may predominate.
Treatment in the first stage aims for an optimal trade-off between symptom control and treatment side-effects. The start of levodopa treatment may be postponed by initially using other medications such as MAO-B inhibitors and dopamine agonists instead, in the hope of delaying the onset of complications due to levodopa use. However, levodopa is still the most effective treatment for the motor symptoms of PD and should not be delayed in people when their quality of life is impaired. Levodopa-related dyskinesias correlate more strongly with duration and severity of the disease than duration of levodopa treatment, so delaying this therapy may not provide much longer dyskinesia-free time than early use.
In later stages the aim is to reduce PD symptoms while controlling fluctuations in the effect of the medication. Sudden withdrawals from medication or its overuse have to be managed. When oral medications are not enough to control symptoms, surgery, deep brain stimulation, subcutaneous waking day apomorphine infusion and enteral dopa pumps may be useful. Late stage PD presents many challenges requiring a variety of treatments including those for psychiatric symptoms particularly depression, orthostatic hypotension, bladder dysfunction and erectile dysfunction. In the final stages of the disease, palliative care is provided to improve a person's quality of life.
Medications
Levodopa
The motor symptoms of PD are the result of reduced dopamine production in the brain's basal ganglia. Dopamine does not cross the blood-brain barrier, so it cannot be taken as a medicine to boost the brain's depleted levels of dopamine. However a precursor of dopamine, levodopa, can pass through to the brain where it is readily converted to dopamine, and administration of levodopa temporarily diminishes the motor symptoms of PD. Levodopa has been the most widely used PD treatment for over 40 years.
Only 5–10% of levodopa crosses the blood–brain barrier. Much of the remainder is metabolized to dopamine elsewhere in the body, causing a variety of side effects including nausea, vomiting and orthostatic hypotension. Carbidopa and benserazide are dopa decarboxylase inhibitors which do not cross the blood-brain barrier and inhibit the conversion of levodopa to dopamine outside the brain, reducing side effects and improving the availability of levodopa for passage into the brain. One of these drugs is usually taken along with levodopa, often combined with levodopa in the same pill.
Levodopa-use leads in the long term to the development of complications: involuntary movements called dyskinesias, and fluctuations in the effectiveness of the medication. When fluctuations occur, a person can cycle through phases with good response to medication and reduced PD symptoms ("on" state), and phases with poor response to medication and significant PD symptoms ("off" state). Using lower doses of levodopa may reduce the risk and severity of these levodopa-induced complications. A former strategy to reduce levodopa-related dyskinesia and fluctuations was to withdraw levodopa medication for some time. This is now discouraged since it can bring on dangerous side effects such as neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Most people with PD will eventually need levodopa and will later develop levodopa-induced fluctuations and dyskinesias.
There are controlled-release versions of levodopa. Older controlled-release levodopa preparations have poor and unreliable absorption and bioavailability and have not demonstrated improved control of PD motor symptoms or a reduction in levodopa-related complications when compared to immediate release preparations. A newer extended-release levodopa preparation does seem to be more effective in reducing fluctuation,s but in many people problems persist. Intestinal infusions of levodopa (Duodopa) can result in striking improvements in fluctuations compared to oral levodopa when the fluctuations are due to insufficient uptake caused by gastroparesis. Other oral, longer acting formulations are under study and other modes of delivery (inhaled, transdermal) are being developed.
COMT inhibitors

During the course of Parkinson's disease, affected people can experience what's known as a "wearing off phenomena" where they have a recurrence of symptoms after a dose of levodopa but right before their next dose. Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), is a protein that degrades levodopa before it can cross the blood-brain barrier and these inhibitors allow for more levodopa to cross. They are normally not used in the management of early symptoms however can be used in conjunction with levodopa/carbidopa when a person is experiencing the "wearing off phenomena" with their motor symptoms.
There are three COMT inhibitors available to treat adults with Parkinson’s Disease and end-of-dose motor fluctuations: opicapone, entacapone and tolcapone. Tolcapone has been available for several years however its usefulness is limited by possible liver damage complications and therefore requires liver function monitoring. Entacapone and opicapone have not been shown to cause significant alterations to liver function. Licensed preparations of entacapone contain entacapone alone or in combination with carbidopa and levodopa. Opicapone is a once-daily COMT inhibitor.
Dopamine agonists
Several dopamine agonists that bind to dopamine receptors in the brain have similar effects to levodopa. These were initially used as a complementary therapy to levodopa for individuals experiencing levodopa complications (on-off fluctuations and dyskinesias); they are now mainly used on their own as first therapy for the motor symptoms of PD with the aim of delaying the initiation of levodopa therapy and so delaying the onset of levodopa's complications. Dopamine agonists include bromocriptine, pergolide, pramipexole, ropinirole, piribedil, cabergoline, apomorphine and lisuride.
Though dopamine agonists are less effective than levodopa at controlling PD motor symptoms, they are usually effective enough to manage these symptoms in the first years of treatment. Dyskinesias due to dopamine agonists are rare in younger people who have PD but, along with other complications, become more common with older age at onset. Thus dopamine agonists are the preferred initial treatment for younger onset PD, and levodopa is preferred for older onset PD.
Dopamine agonists produce significant, although usually mild, side effects including drowsiness, hallucinations, insomnia, nausea, and constipation. Sometimes side effects appear even at a minimal clinically effective dose, leading the physician to search for a different drug. Agonists have been related to impulse control disorders (such as compulsive sexual activity, eating, gambling and shopping) even more strongly than levodopa. They tend to be more expensive than levodopa.
Apomorphine, a non-orally administered dopamine agonist, may be used to reduce off periods and dyskinesia in late PD. It is administered by intermittent injections or continuous subcutaneous infusions. Since secondary effects such as confusion and hallucinations are common, individuals receiving apomorphine treatment should be closely monitored. Two dopamine agonists that are administered through skin patches (lisuride and rotigotine) and are useful for people in the initial stages and possibly to control off states in those in the advanced state.
MAO-B inhibitors
MAO-B inhibitors (safinamide, selegiline and rasagiline) increase the amount of dopamine in the basal ganglia by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B), an enzyme which breaks down dopamine. Like dopamine agonists, their use may delay the commencement of levodopa therapy in early disease, but MAO-B inhibitors produce more adverse effects and are less effective than levodopa at controlling PD motor symptoms. There are few studies of their effectiveness in the advanced stage, although results suggest that they are useful to reduce fluctuations between on and off periods. An initial study indicated that selegiline in combination with levodopa increased the risk